Understanding Sounds, Missing the Questions: The Challenge of Object Hallucination in Large Audio-Language Models
The official Github page of the paper "Understanding Sounds, Missing the Questions: The Challenge of Object Hallucination in Large Audio-Language Models".
- Authors: Chun-Yi Kuan, Wei-Ping Huang, Hung-yi Lee | National Taiwan University.
- Accepted to Interspeech2024.
- ArXiv Link: https://arxiv.org/abs/2406.08402
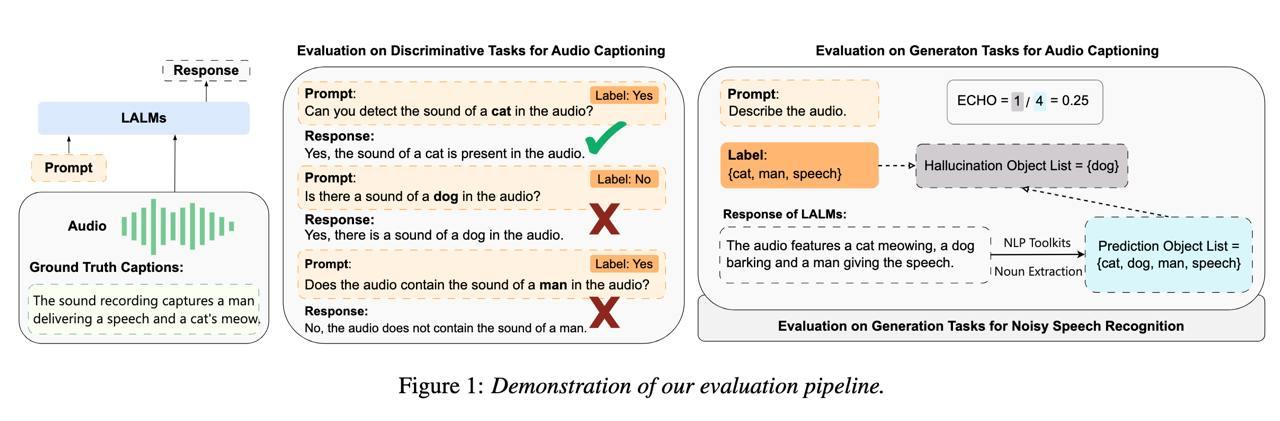
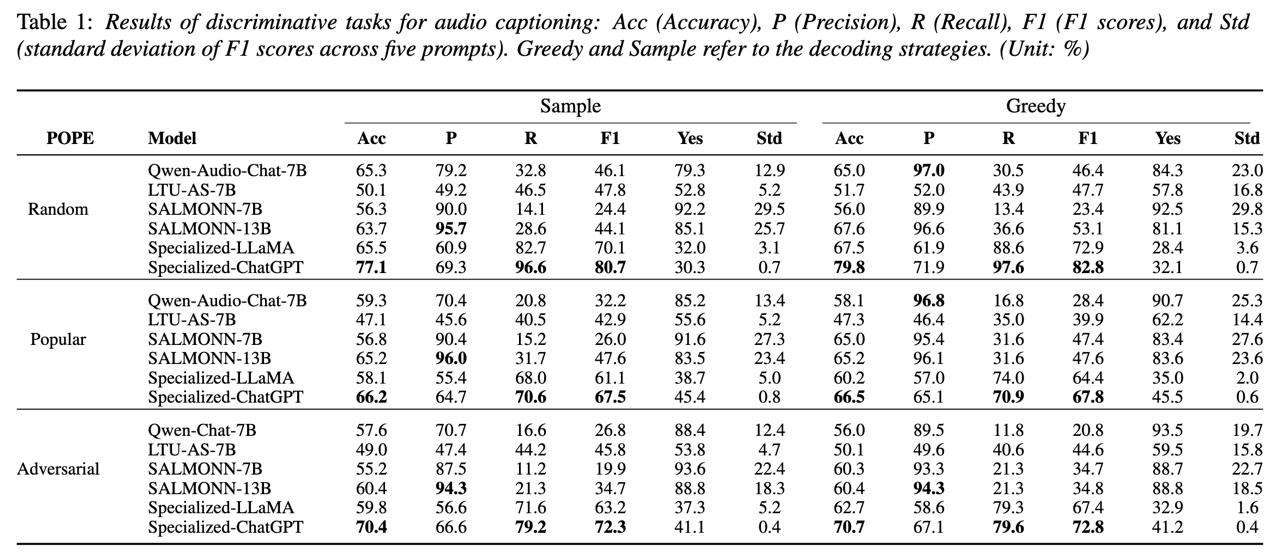
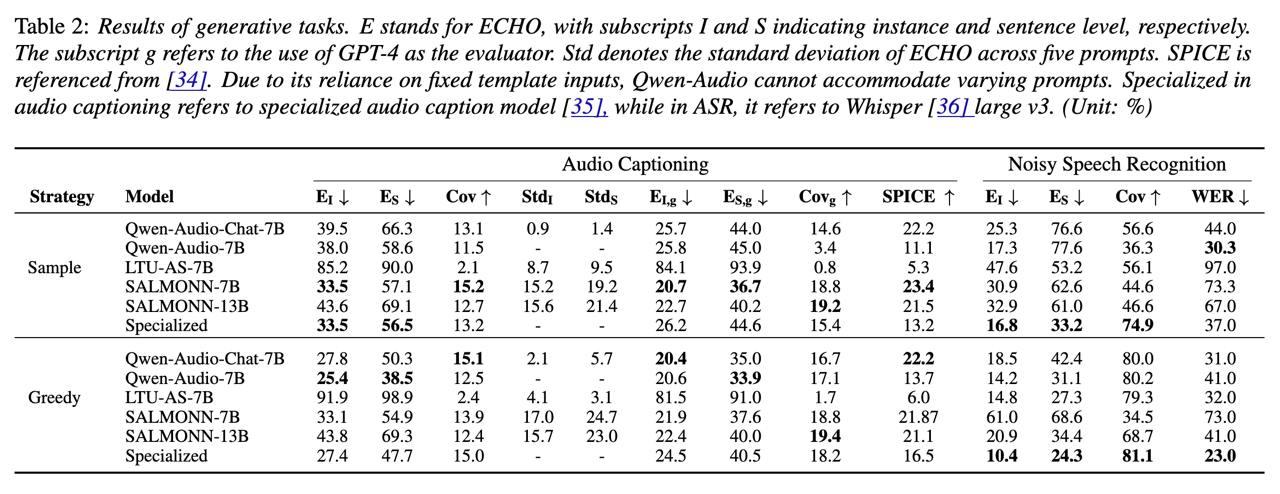
Large audio-language models (LALMs) enhance traditional large language models by integrating audio perception capabilities, allowing them to tackle audio-related tasks. Previous research has primarily focused on assessing the performance of LALMs across various tasks, yet overlooking their reliability, particularly concerning issues like object hallucination. In our study, we introduce methods to assess the extent of object hallucination of publicly available LALMs. Our findings reveal that LALMs are comparable to specialized audio captioning models in their understanding of audio content, but struggle to answer discriminative questions, specifically those requiring the identification of the presence of particular object sounds within an audio clip. This limitation highlights a critical weakness in current LALMs: their inadequate understanding of discriminative queries. Moreover, we explore the potential of prompt engineering to enhance LALMs’ performance on discriminative questions.
-
Hugging Face Link:
- Discriminative Tasks
- Random Sampling: https://huggingface.co/datasets/kuanhuggingface/AudioHallucination_AudioCaps-Random
- Popular Sampling: https://huggingface.co/datasets/kuanhuggingface/AudioHallucination_AudioCaps-Popular
- Adversarial Sampling: https://huggingface.co/datasets/kuanhuggingface/AudioHallucination_AudioCaps-Adversarial
- Discriminative Tasks
-
Hugging Face Dataset:
- Discriminative Tasks
- Random Sampling:
kuanhuggingface/AudioHallucination_AudioCaps-Random - Popular Sampling:
kuanhuggingface/AudioHallucination_AudioCaps-Popular - Adversarial Sampling:
kuanhuggingface/AudioHallucination_AudioCaps-Adversarial
- Random Sampling:
- Discriminative Tasks
Description of fields in the dataset:
audio_index- The ID in AudioCaps, e.g., Y7fmOlUlwoNg corresponds to Y7fmOlUlwoNg.wav
prompt_text- The input text prompt.
object- The object that large audio-language models need to recognize in the audio.
attribute- Indicates whether the object truly exists in the audio; positive means it exists, negative means it does not.
label- The correct answer corresponding to the prompt_text.
sampling- How the negative sample object is selected; random means it is chosen randomly from the AudioCaps test split, excluding the ground truth for that audio.
-
Qwen-Audio-Chat
- Qwen-audio: Advancing universal audio understanding via unified large-scale audio-language models [ArXiv]
-
SALMONN
- SALMONN: Towards Generic Hearing Abilities for Large Language Models [ArXiv]
-
LTU-AS
- Joint Audio and Speech Understanding [ArXiv]
-
Cascade (Whisper + LLaMA-2 7b, Whisper + gpt-3.5-turbo)