- Review how to send a PATCH request using HTML forms and JavaScript
- Review how to send a DELETE request using HTML buttons and JavaScript
- Explain the difference between optimistic and pessimistic rendering
- Demo: Delete
- In renderBookCard, within the callback passed to the eventListener on the delete button, create a DELETE request.
- Update the DOM pessimistically
- Demo Update:
- In renderBookCard create an input.
- Set its value to the books inventory.
- Assigned its type to number.
- Append the input to the li
- Add an eventListener to the input.
- Pass the event listener a callback that performs a PATCH request.
- Review the differences between a PUT and PATCH
- Refactor
- Put the DELETE request into a separate function
- Put the PATCH request into a separate function
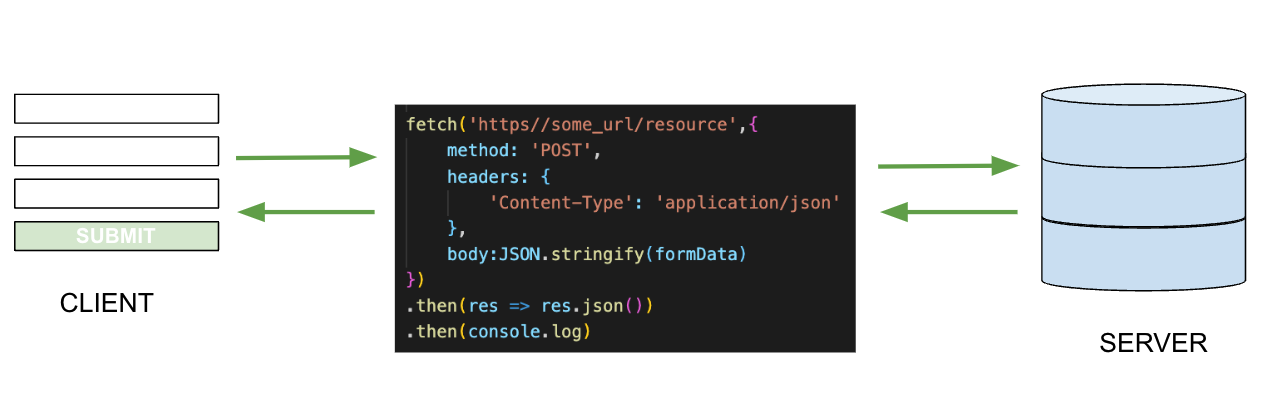
Posts send data to the server. The information is usually sent from a FORM, creating a resource in the database. A POST is typically for creating new data instead of updating data, like PUT or PATCH.
A POST requires an additional argument, a request/config object.
// Method: The HTTP method used in this request. Fetch requests are GET by default. Though they can take a request object, it's not necessary. Other requests, such as POST, require the method to identify what type of request it is.
// Headers: An object that contains additional information for the request. The Content-Type indicates the original media type of the data.
// Body: The data from the request. Before the request can be sent the data must be converted to JSON.
fetch(url, {
method: 'POST',
headers: {
'Content-Type': 'application/json'
},
body:JSON.stringify(formData)
})
Patch updates/modifies a resource.
// The url in a patch requires an id to identify the resource being updated.
// The HTTP method is 'PATCH'
// The body can take the full resource or one property of the resource.
fetch(url/:id, {
method: 'PATCH',
headers: {
'Content-Type': 'application/json'
},
body:JSON.stringify({prop:value})
})
Delete removes a resource from the server. Unlike Post and Patch it doesn't require headers or a body, though some backend frameworks may require a header.
// Delete does require the method and the id of the resource being deleted.
fetch(url/:id, {
method: 'DELETE',
})