给你一个有 n 个节点的 无向 图,节点编号为 1 到 n 。再给你整数 n 和一个二维整数数组 edges ,其中 edges[i] = [ai, bi] 表示节点 ai 和 bi 之间有一条边。图不一定连通。
你可以给图中添加 至多 两条额外的边(也可以一条边都不添加),使得图中没有重边也没有自环。
如果添加额外的边后,可以使得图中所有点的度数都是偶数,返回 true ,否则返回 false 。
点的度数是连接一个点的边的数目。
示例 1:
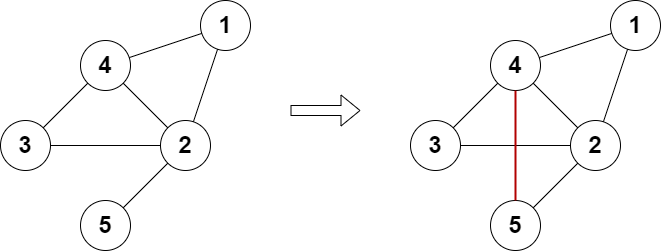
输入:n = 5, edges = [[1,2],[2,3],[3,4],[4,2],[1,4],[2,5]] 输出:true 解释:上图展示了添加一条边的合法方案。 最终图中每个节点都连接偶数条边。
示例 2:
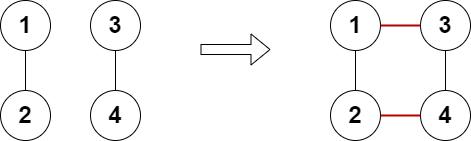
输入:n = 4, edges = [[1,2],[3,4]] 输出:true 解释:上图展示了添加两条边的合法方案。
示例 3:
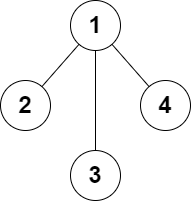
输入:n = 4, edges = [[1,2],[1,3],[1,4]] 输出:false 解释:无法添加至多 2 条边得到一个符合要求的图。
提示:
3 <= n <= 1052 <= edges.length <= 105edges[i].length == 21 <= ai, bi <= nai != bi- 图中不会有重边
我们先通过 edges 构建图
如果 true 即可。
如果 true;否则,如果我们能找到第三个点 true;否则,返回 false。
如果 true;否则,返回 false。
其它情况,返回 false。
时间复杂度
class Solution:
def isPossible(self, n: int, edges: List[List[int]]) -> bool:
g = defaultdict(set)
for a, b in edges:
g[a].add(b)
g[b].add(a)
vs = [i for i, v in g.items() if len(v) & 1]
if len(vs) == 0:
return True
if len(vs) == 2:
a, b = vs
if a not in g[b]:
return True
return any(a not in g[c] and c not in g[b] for c in range(1, n + 1))
if len(vs) == 4:
a, b, c, d = vs
if a not in g[b] and c not in g[d]:
return True
if a not in g[c] and b not in g[d]:
return True
if a not in g[d] and b not in g[c]:
return True
return False
return Falseclass Solution {
public boolean isPossible(int n, List<List<Integer>> edges) {
Set<Integer>[] g = new Set[n + 1];
Arrays.setAll(g, k -> new HashSet<>());
for (var e : edges) {
int a = e.get(0), b = e.get(1);
g[a].add(b);
g[b].add(a);
}
List<Integer> vs = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
if (g[i].size() % 2 == 1) {
vs.add(i);
}
}
if (vs.size() == 0) {
return true;
}
if (vs.size() == 2) {
int a = vs.get(0), b = vs.get(1);
if (!g[a].contains(b)) {
return true;
}
for (int c = 1; c <= n; ++c) {
if (a != c && b != c && !g[a].contains(c) && !g[c].contains(b)) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
if (vs.size() == 4) {
int a = vs.get(0), b = vs.get(1), c = vs.get(2), d = vs.get(3);
if (!g[a].contains(b) && !g[c].contains(d)) {
return true;
}
if (!g[a].contains(c) && !g[b].contains(d)) {
return true;
}
if (!g[a].contains(d) && !g[b].contains(c)) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
return false;
}
}class Solution {
public:
bool isPossible(int n, vector<vector<int>>& edges) {
vector<unordered_set<int>> g(n + 1);
for (auto& e : edges) {
int a = e[0], b = e[1];
g[a].insert(b);
g[b].insert(a);
}
vector<int> vs;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
if (g[i].size() % 2) {
vs.emplace_back(i);
}
}
if (vs.size() == 0) {
return true;
}
if (vs.size() == 2) {
int a = vs[0], b = vs[1];
if (!g[a].count(b)) return true;
for (int c = 1; c <= n; ++c) {
if (a != b && b != c && !g[a].count(c) && !g[c].count(b)) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
if (vs.size() == 4) {
int a = vs[0], b = vs[1], c = vs[2], d = vs[3];
if (!g[a].count(b) && !g[c].count(d)) return true;
if (!g[a].count(c) && !g[b].count(d)) return true;
if (!g[a].count(d) && !g[b].count(c)) return true;
return false;
}
return false;
}
};func isPossible(n int, edges [][]int) bool {
g := make([]map[int]bool, n+1)
for _, e := range edges {
a, b := e[0], e[1]
if g[a] == nil {
g[a] = map[int]bool{}
}
if g[b] == nil {
g[b] = map[int]bool{}
}
g[a][b], g[b][a] = true, true
}
vs := []int{}
for i := 1; i <= n; i++ {
if len(g[i])%2 == 1 {
vs = append(vs, i)
}
}
if len(vs) == 0 {
return true
}
if len(vs) == 2 {
a, b := vs[0], vs[1]
if !g[a][b] {
return true
}
for c := 1; c <= n; c++ {
if a != c && b != c && !g[a][c] && !g[c][b] {
return true
}
}
return false
}
if len(vs) == 4 {
a, b, c, d := vs[0], vs[1], vs[2], vs[3]
if !g[a][b] && !g[c][d] {
return true
}
if !g[a][c] && !g[b][d] {
return true
}
if !g[a][d] && !g[b][c] {
return true
}
return false
}
return false
}