SoomRV is a simple superscalar out-of-order RISC-V core able to execute up to 4 instructions per cycle and capable of booting Linux. Check the latest CI logs to see a Linux boot log!
For running SoomRV on FPGA, have a look at the SoomRV-Arty Repo.

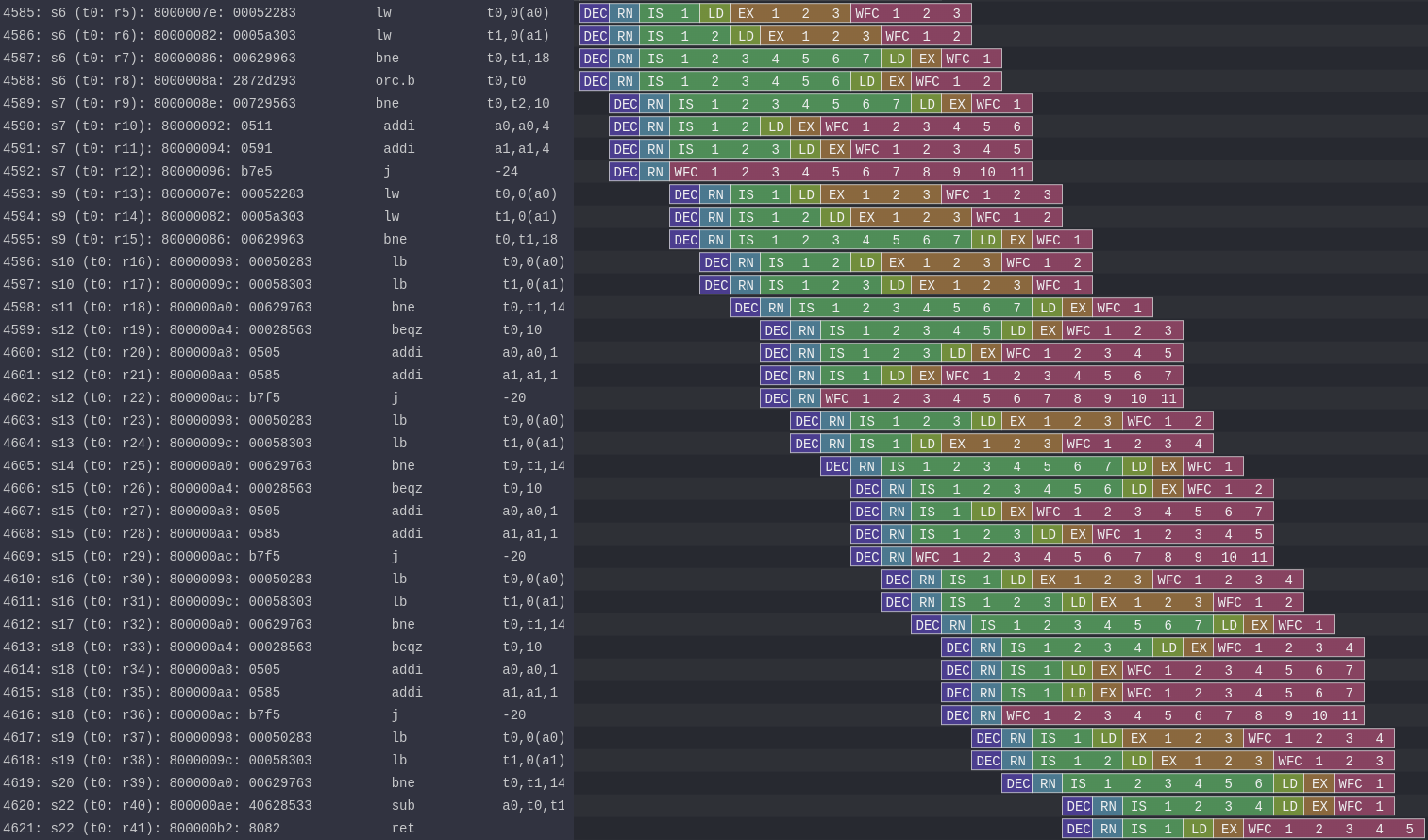
Sample strcmp Execution (visualized using Konata)
- RV32IMAC+ Instruction Set
- 4-wide superscalar OoO Execution (tag-indexed register file, load after issue)
- Implements RISC-V Privileged Spec (M/S/U mode, virtual memory, boots Linux)
- IFetch: 16 byte fetch, TAGE direction predictor, recovering return stack
- Memory: 2 loads per cycle, VIPT cache, late store data gathering, through-memory dependency tracking
- Default configuration scores 5.42 CoreMark/MHz and 4.0 to 11.8 DMIPS/MHz depending on compiler flags (see CI).
- Install the RV32 Linux Toolchain as well as Verilator (at least version 5.0).
- Run
make setupto build submodules. - Run
maketo build a binary with Verilator (alternatively,make tracewill also generate VCD traces). - To run bare-metal code, use
./obj_dir/VTop <assembly file>or<baremetal elf file>. For example, run./obj_dir/VTop test_programs/dhry_1.sto run Dhrystone. Optionally add--perfcto print out perf counters, or-x <start_time>to specify when to enable tracing (-x0for tracing from start). - To run Linux, use
./obj_dir/VTop --perfc --device-tree=test_programs/linux/device_tree.dtb test_programs/linux/linux_image.elf(ormake linuxfor a full build). Log in asroot, no password. Building Linux and booting it in simulation takes at least a few hours!
The console input is line-buffered for easier input at low simulation speed. Within Linux, you will thus see all input lines twice.
While running, the simulator will save its state about once a minute if
--backup-file=<NAME>.backup is specified. Simulation can then be restarted
at the backup by running ./obj_dir/VTop <NAME>.backup. The file name must
end with .backup. If cosim is enabled, a matching .backup_cosim file will
be written/read as well.
This is on by default for make linux. To restart a crashed or closed Linux boot
at the last checkpoint, use e.g. ./obj_dir/VTop soomrv.backup --backup-file=soomrv2.backup.
(There seem to be some spurious segfaults in the Verilator-generated code.)
For a general overview of the implementation, see Overview.
SoomRV is released under the MIT License. Use of this source code is governed by a MIT-style license that can be found in the LICENSE file.
riscv-isa-sim(akaSpike): released under the 3-Clause BSD License, used in conjunction with the simulator.hardfloat: released under the 3-Clause BSD License.