forked from twistedfall/opencv-rust
-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 0
/
photo.rs
1733 lines (1594 loc) · 79.6 KB
/
photo.rs
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
197
198
199
200
201
202
203
204
205
206
207
208
209
210
211
212
213
214
215
216
217
218
219
220
221
222
223
224
225
226
227
228
229
230
231
232
233
234
235
236
237
238
239
240
241
242
243
244
245
246
247
248
249
250
251
252
253
254
255
256
257
258
259
260
261
262
263
264
265
266
267
268
269
270
271
272
273
274
275
276
277
278
279
280
281
282
283
284
285
286
287
288
289
290
291
292
293
294
295
296
297
298
299
300
301
302
303
304
305
306
307
308
309
310
311
312
313
314
315
316
317
318
319
320
321
322
323
324
325
326
327
328
329
330
331
332
333
334
335
336
337
338
339
340
341
342
343
344
345
346
347
348
349
350
351
352
353
354
355
356
357
358
359
360
361
362
363
364
365
366
367
368
369
370
371
372
373
374
375
376
377
378
379
380
381
382
383
384
385
386
387
388
389
390
391
392
393
394
395
396
397
398
399
400
401
402
403
404
405
406
407
408
409
410
411
412
413
414
415
416
417
418
419
420
421
422
423
424
425
426
427
428
429
430
431
432
433
434
435
436
437
438
439
440
441
442
443
444
445
446
447
448
449
450
451
452
453
454
455
456
457
458
459
460
461
462
463
464
465
466
467
468
469
470
471
472
473
474
475
476
477
478
479
480
481
482
483
484
485
486
487
488
489
490
491
492
493
494
495
496
497
498
499
500
501
502
503
504
505
506
507
508
509
510
511
512
513
514
515
516
517
518
519
520
521
522
523
524
525
526
527
528
529
530
531
532
533
534
535
536
537
538
539
540
541
542
543
544
545
546
547
548
549
550
551
552
553
554
555
556
557
558
559
560
561
562
563
564
565
566
567
568
569
570
571
572
573
574
575
576
577
578
579
580
581
582
583
584
585
586
587
588
589
590
591
592
593
594
595
596
597
598
599
600
601
602
603
604
605
606
607
608
609
610
611
612
613
614
615
616
617
618
619
620
621
622
623
624
625
626
627
628
629
630
631
632
633
634
635
636
637
638
639
640
641
642
643
644
645
646
647
648
649
650
651
652
653
654
655
656
657
658
659
660
661
662
663
664
665
666
667
668
669
670
671
672
673
674
675
676
677
678
679
680
681
682
683
684
685
686
687
688
689
690
691
692
693
694
695
696
697
698
699
700
701
702
703
704
705
706
707
708
709
710
711
712
713
714
715
716
717
718
719
720
721
722
723
724
725
726
727
728
729
730
731
732
733
734
735
736
737
738
739
740
741
742
743
744
745
746
747
748
749
750
751
752
753
754
755
756
757
758
759
760
761
762
763
764
765
766
767
768
769
770
771
772
773
774
775
776
777
778
779
780
781
782
783
784
785
786
787
788
789
790
791
792
793
794
795
796
797
798
799
800
801
802
803
804
805
806
807
808
809
810
811
812
813
814
815
816
817
818
819
820
821
822
823
824
825
826
827
828
829
830
831
832
833
834
835
836
837
838
839
840
841
842
843
844
845
846
847
848
849
850
851
852
853
854
855
856
857
858
859
860
861
862
863
864
865
866
867
868
869
870
871
872
873
874
875
876
877
878
879
880
881
882
883
884
885
886
887
888
889
890
891
892
893
894
895
896
897
898
899
900
901
902
903
904
905
906
907
908
909
910
911
912
913
914
915
916
917
918
919
920
921
922
923
924
925
926
927
928
929
930
931
932
933
934
935
936
937
938
939
940
941
942
943
944
945
946
947
948
949
950
951
952
953
954
955
956
957
958
959
960
961
962
963
964
965
966
967
968
969
970
971
972
973
974
975
976
977
978
979
980
981
982
983
984
985
986
987
988
989
990
991
992
993
994
995
996
997
998
999
1000
pub mod photo {
//! # Computational Photography
//!
//! This module includes photo processing algorithms
//! # Inpainting
//! # Denoising
//! # HDR imaging
//!
//! This section describes high dynamic range imaging algorithms namely tonemapping, exposure alignment,
//! camera calibration with multiple exposures and exposure fusion.
//!
//! # Contrast Preserving Decolorization
//!
//! Useful links:
//!
//! <http://www.cse.cuhk.edu.hk/leojia/projects/color2gray/index.html>
//!
//! # Seamless Cloning
//!
//! Useful links:
//!
//! <https://www.learnopencv.com/seamless-cloning-using-opencv-python-cpp>
//!
//! # Non-Photorealistic Rendering
//!
//! Useful links:
//!
//! <http://www.inf.ufrgs.br/~eslgastal/DomainTransform>
//!
//! <https://www.learnopencv.com/non-photorealistic-rendering-using-opencv-python-c/>
//!
//! # C API
use crate::{mod_prelude::*, core, sys, types};
pub mod prelude {
pub use { super::TonemapConst, super::Tonemap, super::TonemapDragoConst, super::TonemapDrago, super::TonemapReinhardConst, super::TonemapReinhard, super::TonemapMantiukConst, super::TonemapMantiuk, super::AlignExposuresConst, super::AlignExposures, super::AlignMTBConst, super::AlignMTB, super::CalibrateCRFConst, super::CalibrateCRF, super::CalibrateDebevecConst, super::CalibrateDebevec, super::CalibrateRobertsonConst, super::CalibrateRobertson, super::MergeExposuresConst, super::MergeExposures, super::MergeDebevecConst, super::MergeDebevec, super::MergeMertensConst, super::MergeMertens, super::MergeRobertsonConst, super::MergeRobertson };
}
/// Use Navier-Stokes based method
pub const INPAINT_NS: i32 = 0;
/// Use the algorithm proposed by Alexandru Telea [Telea04](https://docs.opencv.org/4.7.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_Telea04)
pub const INPAINT_TELEA: i32 = 1;
pub const LDR_SIZE: i32 = 256;
/// The classic method, color-based selection and alpha masking might be time consuming and often leaves an undesirable
/// halo. Seamless cloning, even averaged with the original image, is not effective. Mixed seamless cloning based on a loose selection proves effective.
pub const MIXED_CLONE: i32 = 2;
/// Monochrome transfer allows the user to easily replace certain features of one object by alternative features.
pub const MONOCHROME_TRANSFER: i32 = 3;
/// The power of the method is fully expressed when inserting objects with complex outlines into a new background
pub const NORMAL_CLONE: i32 = 1;
/// Normalized Convolution Filtering
pub const NORMCONV_FILTER: i32 = 2;
/// Recursive Filtering
pub const RECURS_FILTER: i32 = 1;
/// Given an original color image, two differently colored versions of this image can be mixed
/// seamlessly.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * src: Input 8-bit 3-channel image.
/// * mask: Input 8-bit 1 or 3-channel image.
/// * dst: Output image with the same size and type as src .
/// * red_mul: R-channel multiply factor.
/// * green_mul: G-channel multiply factor.
/// * blue_mul: B-channel multiply factor.
///
/// Multiplication factor is between .5 to 2.5.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * red_mul: 1.0f
/// * green_mul: 1.0f
/// * blue_mul: 1.0f
#[inline]
pub fn color_change(src: &dyn core::ToInputArray, mask: &dyn core::ToInputArray, dst: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, red_mul: f32, green_mul: f32, blue_mul: f32) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(src);
extern_container_arg!(mask);
extern_container_arg!(dst);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_colorChange_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_float_float_float(src.as_raw__InputArray(), mask.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), red_mul, green_mul, blue_mul, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Creates AlignMTB object
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * max_bits: logarithm to the base 2 of maximal shift in each dimension. Values of 5 and 6 are
/// usually good enough (31 and 63 pixels shift respectively).
/// * exclude_range: range for exclusion bitmap that is constructed to suppress noise around the
/// median value.
/// * cut: if true cuts images, otherwise fills the new regions with zeros.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * max_bits: 6
/// * exclude_range: 4
/// * cut: true
#[inline]
pub fn create_align_mtb(max_bits: i32, exclude_range: i32, cut: bool) -> Result<core::Ptr<dyn crate::photo::AlignMTB>> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_createAlignMTB_int_int_bool(max_bits, exclude_range, cut, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Ptr::<dyn crate::photo::AlignMTB>::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Creates CalibrateDebevec object
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * samples: number of pixel locations to use
/// * lambda: smoothness term weight. Greater values produce smoother results, but can alter the
/// response.
/// * random: if true sample pixel locations are chosen at random, otherwise they form a
/// rectangular grid.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * samples: 70
/// * lambda: 10.0f
/// * random: false
#[inline]
pub fn create_calibrate_debevec(samples: i32, lambda: f32, random: bool) -> Result<core::Ptr<dyn crate::photo::CalibrateDebevec>> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_createCalibrateDebevec_int_float_bool(samples, lambda, random, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Ptr::<dyn crate::photo::CalibrateDebevec>::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Creates CalibrateRobertson object
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * max_iter: maximal number of Gauss-Seidel solver iterations.
/// * threshold: target difference between results of two successive steps of the minimization.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * max_iter: 30
/// * threshold: 0.01f
#[inline]
pub fn create_calibrate_robertson(max_iter: i32, threshold: f32) -> Result<core::Ptr<dyn crate::photo::CalibrateRobertson>> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_createCalibrateRobertson_int_float(max_iter, threshold, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Ptr::<dyn crate::photo::CalibrateRobertson>::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Creates MergeDebevec object
#[inline]
pub fn create_merge_debevec() -> Result<core::Ptr<dyn crate::photo::MergeDebevec>> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_createMergeDebevec(ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Ptr::<dyn crate::photo::MergeDebevec>::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Creates MergeMertens object
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * contrast_weight: contrast measure weight. See MergeMertens.
/// * saturation_weight: saturation measure weight
/// * exposure_weight: well-exposedness measure weight
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * contrast_weight: 1.0f
/// * saturation_weight: 1.0f
/// * exposure_weight: 0.0f
#[inline]
pub fn create_merge_mertens(contrast_weight: f32, saturation_weight: f32, exposure_weight: f32) -> Result<core::Ptr<dyn crate::photo::MergeMertens>> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_createMergeMertens_float_float_float(contrast_weight, saturation_weight, exposure_weight, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Ptr::<dyn crate::photo::MergeMertens>::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Creates MergeRobertson object
#[inline]
pub fn create_merge_robertson() -> Result<core::Ptr<dyn crate::photo::MergeRobertson>> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_createMergeRobertson(ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Ptr::<dyn crate::photo::MergeRobertson>::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Creates TonemapDrago object
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * gamma: gamma value for gamma correction. See createTonemap
/// * saturation: positive saturation enhancement value. 1.0 preserves saturation, values greater
/// than 1 increase saturation and values less than 1 decrease it.
/// * bias: value for bias function in [0, 1] range. Values from 0.7 to 0.9 usually give best
/// results, default value is 0.85.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * gamma: 1.0f
/// * saturation: 1.0f
/// * bias: 0.85f
#[inline]
pub fn create_tonemap_drago(gamma: f32, saturation: f32, bias: f32) -> Result<core::Ptr<dyn crate::photo::TonemapDrago>> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_createTonemapDrago_float_float_float(gamma, saturation, bias, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Ptr::<dyn crate::photo::TonemapDrago>::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Creates TonemapMantiuk object
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * gamma: gamma value for gamma correction. See createTonemap
/// * scale: contrast scale factor. HVS response is multiplied by this parameter, thus compressing
/// dynamic range. Values from 0.6 to 0.9 produce best results.
/// * saturation: saturation enhancement value. See createTonemapDrago
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * gamma: 1.0f
/// * scale: 0.7f
/// * saturation: 1.0f
#[inline]
pub fn create_tonemap_mantiuk(gamma: f32, scale: f32, saturation: f32) -> Result<core::Ptr<dyn crate::photo::TonemapMantiuk>> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_createTonemapMantiuk_float_float_float(gamma, scale, saturation, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Ptr::<dyn crate::photo::TonemapMantiuk>::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Creates TonemapReinhard object
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * gamma: gamma value for gamma correction. See createTonemap
/// * intensity: result intensity in [-8, 8] range. Greater intensity produces brighter results.
/// * light_adapt: light adaptation in [0, 1] range. If 1 adaptation is based only on pixel
/// value, if 0 it's global, otherwise it's a weighted mean of this two cases.
/// * color_adapt: chromatic adaptation in [0, 1] range. If 1 channels are treated independently,
/// if 0 adaptation level is the same for each channel.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * gamma: 1.0f
/// * intensity: 0.0f
/// * light_adapt: 1.0f
/// * color_adapt: 0.0f
#[inline]
pub fn create_tonemap_reinhard(gamma: f32, intensity: f32, light_adapt: f32, color_adapt: f32) -> Result<core::Ptr<dyn crate::photo::TonemapReinhard>> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_createTonemapReinhard_float_float_float_float(gamma, intensity, light_adapt, color_adapt, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Ptr::<dyn crate::photo::TonemapReinhard>::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// Creates simple linear mapper with gamma correction
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * gamma: positive value for gamma correction. Gamma value of 1.0 implies no correction, gamma
/// equal to 2.2f is suitable for most displays.
/// Generally gamma \> 1 brightens the image and gamma \< 1 darkens it.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * gamma: 1.0f
#[inline]
pub fn create_tonemap(gamma: f32) -> Result<core::Ptr<dyn crate::photo::Tonemap>> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_createTonemap_float(gamma, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
let ret = unsafe { core::Ptr::<dyn crate::photo::Tonemap>::opencv_from_extern(ret) };
Ok(ret)
}
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * search_window: 21
/// * block_size: 7
/// * stream: Stream::Null()
#[inline]
pub fn fast_nl_means_denoising_colored_1(src: &core::GpuMat, dst: &mut core::GpuMat, h_luminance: f32, photo_render: f32, search_window: i32, block_size: i32, stream: &mut core::Stream) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_fastNlMeansDenoisingColored_const_GpuMatR_GpuMatR_float_float_int_int_StreamR(src.as_raw_GpuMat(), dst.as_raw_mut_GpuMat(), h_luminance, photo_render, search_window, block_size, stream.as_raw_mut_Stream(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Modification of fastNlMeansDenoising function for colored images
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * src: Input 8-bit 3-channel image.
/// * dst: Output image with the same size and type as src .
/// * h_luminance: Parameter regulating filter strength. Big h value perfectly removes noise but
/// also removes image details, smaller h value preserves details but also preserves some noise
/// * photo_render: float The same as h but for color components. For most images value equals 10 will be
/// enough to remove colored noise and do not distort colors
/// * search_window: Size in pixels of the window that is used to compute weighted average for
/// given pixel. Should be odd. Affect performance linearly: greater search_window - greater
/// denoising time. Recommended value 21 pixels
/// * block_size: Size in pixels of the template patch that is used to compute weights. Should be
/// odd. Recommended value 7 pixels
/// * stream: Stream for the asynchronous invocations.
///
/// The function converts image to CIELAB colorspace and then separately denoise L and AB components
/// with given h parameters using FastNonLocalMeansDenoising::simpleMethod function.
/// ## See also
/// fastNlMeansDenoisingColored
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * search_window: 21
/// * block_size: 7
/// * stream: Stream::Null()
#[inline]
pub fn fast_nl_means_denoising_colored_cuda(src: &dyn core::ToInputArray, dst: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, h_luminance: f32, photo_render: f32, search_window: i32, block_size: i32, stream: &mut core::Stream) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(src);
extern_container_arg!(dst);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_fastNlMeansDenoisingColored_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_float_float_int_int_StreamR(src.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), h_luminance, photo_render, search_window, block_size, stream.as_raw_mut_Stream(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * search_window: 21
/// * block_size: 7
/// * stream: Stream::Null()
#[inline]
pub fn fast_nl_means_denoising_1(src: &core::GpuMat, dst: &mut core::GpuMat, h: f32, search_window: i32, block_size: i32, stream: &mut core::Stream) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_fastNlMeansDenoising_const_GpuMatR_GpuMatR_float_int_int_StreamR(src.as_raw_GpuMat(), dst.as_raw_mut_GpuMat(), h, search_window, block_size, stream.as_raw_mut_Stream(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Perform image denoising using Non-local Means Denoising algorithm
/// <http://www.ipol.im/pub/algo/bcm_non_local_means_denoising> with several computational
/// optimizations. Noise expected to be a gaussian white noise
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * src: Input 8-bit 1-channel, 2-channel or 3-channel image.
/// * dst: Output image with the same size and type as src .
/// * h: Parameter regulating filter strength. Big h value perfectly removes noise but also
/// removes image details, smaller h value preserves details but also preserves some noise
/// * search_window: Size in pixels of the window that is used to compute weighted average for
/// given pixel. Should be odd. Affect performance linearly: greater search_window - greater
/// denoising time. Recommended value 21 pixels
/// * block_size: Size in pixels of the template patch that is used to compute weights. Should be
/// odd. Recommended value 7 pixels
/// * stream: Stream for the asynchronous invocations.
///
/// This function expected to be applied to grayscale images. For colored images look at
/// FastNonLocalMeansDenoising::labMethod.
/// ## See also
/// fastNlMeansDenoising
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * search_window: 21
/// * block_size: 7
/// * stream: Stream::Null()
#[inline]
pub fn fast_nl_means_denoising_cuda(src: &dyn core::ToInputArray, dst: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, h: f32, search_window: i32, block_size: i32, stream: &mut core::Stream) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(src);
extern_container_arg!(dst);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_fastNlMeansDenoising_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_float_int_int_StreamR(src.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), h, search_window, block_size, stream.as_raw_mut_Stream(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * search_window: 21
/// * block_size: 7
/// * border_mode: BORDER_DEFAULT
/// * stream: Stream::Null()
#[inline]
pub fn non_local_means_1(src: &core::GpuMat, dst: &mut core::GpuMat, h: f32, search_window: i32, block_size: i32, border_mode: i32, stream: &mut core::Stream) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_nonLocalMeans_const_GpuMatR_GpuMatR_float_int_int_int_StreamR(src.as_raw_GpuMat(), dst.as_raw_mut_GpuMat(), h, search_window, block_size, border_mode, stream.as_raw_mut_Stream(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Performs pure non local means denoising without any simplification, and thus it is not fast.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * src: Source image. Supports only CV_8UC1, CV_8UC2 and CV_8UC3.
/// * dst: Destination image.
/// * h: Filter sigma regulating filter strength for color.
/// * search_window: Size of search window.
/// * block_size: Size of block used for computing weights.
/// * borderMode: Border type. See borderInterpolate for details. BORDER_REFLECT101 ,
/// BORDER_REPLICATE , BORDER_CONSTANT , BORDER_REFLECT and BORDER_WRAP are supported for now.
/// * stream: Stream for the asynchronous version.
/// ## See also
/// fastNlMeansDenoising
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * search_window: 21
/// * block_size: 7
/// * border_mode: BORDER_DEFAULT
/// * stream: Stream::Null()
#[inline]
pub fn non_local_means(src: &dyn core::ToInputArray, dst: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, h: f32, search_window: i32, block_size: i32, border_mode: i32, stream: &mut core::Stream) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(src);
extern_container_arg!(dst);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_cuda_nonLocalMeans_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_float_int_int_int_StreamR(src.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), h, search_window, block_size, border_mode, stream.as_raw_mut_Stream(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Transforms a color image to a grayscale image. It is a basic tool in digital printing, stylized
/// black-and-white photograph rendering, and in many single channel image processing applications
/// [CL12](https://docs.opencv.org/4.7.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_CL12) .
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * src: Input 8-bit 3-channel image.
/// * grayscale: Output 8-bit 1-channel image.
/// * color_boost: Output 8-bit 3-channel image.
///
/// This function is to be applied on color images.
#[inline]
pub fn decolor(src: &dyn core::ToInputArray, grayscale: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, color_boost: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(src);
extern_container_arg!(grayscale);
extern_container_arg!(color_boost);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_decolor_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR(src.as_raw__InputArray(), grayscale.as_raw__OutputArray(), color_boost.as_raw__OutputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Primal-dual algorithm is an algorithm for solving special types of variational problems (that is,
/// finding a function to minimize some functional). As the image denoising, in particular, may be seen
/// as the variational problem, primal-dual algorithm then can be used to perform denoising and this is
/// exactly what is implemented.
///
/// It should be noted, that this implementation was taken from the July 2013 blog entry
/// [MA13](https://docs.opencv.org/4.7.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_MA13) , which also contained (slightly more general) ready-to-use source code on Python.
/// Subsequently, that code was rewritten on C++ with the usage of openCV by Vadim Pisarevsky at the end
/// of July 2013 and finally it was slightly adapted by later authors.
///
/// Although the thorough discussion and justification of the algorithm involved may be found in
/// [ChambolleEtAl](https://docs.opencv.org/4.7.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_ChambolleEtAl), it might make sense to skim over it here, following [MA13](https://docs.opencv.org/4.7.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_MA13) . To begin
/// with, we consider the 1-byte gray-level images as the functions from the rectangular domain of
/// pixels (it may be seen as set
///  for some
/// ) into . We shall denote the noised images as  and with
/// this view, given some image 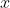 of the same size, we may measure how bad it is by the formula
///
/// 
///
///  here denotes -norm and as you see, the first addend states that we want our
/// image to be smooth (ideally, having zero gradient, thus being constant) and the second states that
/// we want our result to be close to the observations we've got. If we treat 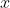 as a function, this is
/// exactly the functional what we seek to minimize and here the Primal-Dual algorithm comes into play.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * observations: This array should contain one or more noised versions of the image that is to
/// be restored.
/// * result: Here the denoised image will be stored. There is no need to do pre-allocation of
/// storage space, as it will be automatically allocated, if necessary.
/// * lambda: Corresponds to 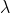 in the formulas above. As it is enlarged, the smooth
/// (blurred) images are treated more favorably than detailed (but maybe more noised) ones. Roughly
/// speaking, as it becomes smaller, the result will be more blur but more sever outliers will be
/// removed.
/// * niters: Number of iterations that the algorithm will run. Of course, as more iterations as
/// better, but it is hard to quantitatively refine this statement, so just use the default and
/// increase it if the results are poor.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * lambda: 1.0
/// * niters: 30
#[inline]
pub fn denoise_tvl1(observations: &core::Vector<core::Mat>, result: &mut core::Mat, lambda: f64, niters: i32) -> Result<()> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_denoise_TVL1_const_vectorLMatGR_MatR_double_int(observations.as_raw_VectorOfMat(), result.as_raw_mut_Mat(), lambda, niters, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// This filter enhances the details of a particular image.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * src: Input 8-bit 3-channel image.
/// * dst: Output image with the same size and type as src.
/// * sigma_s: %Range between 0 to 200.
/// * sigma_r: %Range between 0 to 1.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * sigma_s: 10
/// * sigma_r: 0.15f
#[inline]
pub fn detail_enhance(src: &dyn core::ToInputArray, dst: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, sigma_s: f32, sigma_r: f32) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(src);
extern_container_arg!(dst);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_detailEnhance_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_float_float(src.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), sigma_s, sigma_r, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Filtering is the fundamental operation in image and video processing. Edge-preserving smoothing
/// filters are used in many different applications [EM11](https://docs.opencv.org/4.7.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_EM11) .
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * src: Input 8-bit 3-channel image.
/// * dst: Output 8-bit 3-channel image.
/// * flags: Edge preserving filters: cv::RECURS_FILTER or cv::NORMCONV_FILTER
/// * sigma_s: %Range between 0 to 200.
/// * sigma_r: %Range between 0 to 1.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * flags: 1
/// * sigma_s: 60
/// * sigma_r: 0.4f
#[inline]
pub fn edge_preserving_filter(src: &dyn core::ToInputArray, dst: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, flags: i32, sigma_s: f32, sigma_r: f32) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(src);
extern_container_arg!(dst);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_edgePreservingFilter_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_int_float_float(src.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), flags, sigma_s, sigma_r, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Modification of fastNlMeansDenoisingMulti function for colored images sequences
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * srcImgs: Input 8-bit 3-channel images sequence. All images should have the same type and
/// size.
/// * imgToDenoiseIndex: Target image to denoise index in srcImgs sequence
/// * temporalWindowSize: Number of surrounding images to use for target image denoising. Should
/// be odd. Images from imgToDenoiseIndex - temporalWindowSize / 2 to
/// imgToDenoiseIndex - temporalWindowSize / 2 from srcImgs will be used to denoise
/// srcImgs[imgToDenoiseIndex] image.
/// * dst: Output image with the same size and type as srcImgs images.
/// * templateWindowSize: Size in pixels of the template patch that is used to compute weights.
/// Should be odd. Recommended value 7 pixels
/// * searchWindowSize: Size in pixels of the window that is used to compute weighted average for
/// given pixel. Should be odd. Affect performance linearly: greater searchWindowsSize - greater
/// denoising time. Recommended value 21 pixels
/// * h: Parameter regulating filter strength for luminance component. Bigger h value perfectly
/// removes noise but also removes image details, smaller h value preserves details but also preserves
/// some noise.
/// * hColor: The same as h but for color components.
///
/// The function converts images to CIELAB colorspace and then separately denoise L and AB components
/// with given h parameters using fastNlMeansDenoisingMulti function.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * h: 3
/// * h_color: 3
/// * template_window_size: 7
/// * search_window_size: 21
#[inline]
pub fn fast_nl_means_denoising_colored_multi(src_imgs: &dyn core::ToInputArray, dst: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, img_to_denoise_index: i32, temporal_window_size: i32, h: f32, h_color: f32, template_window_size: i32, search_window_size: i32) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(src_imgs);
extern_container_arg!(dst);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_fastNlMeansDenoisingColoredMulti_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_int_int_float_float_int_int(src_imgs.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), img_to_denoise_index, temporal_window_size, h, h_color, template_window_size, search_window_size, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Modification of fastNlMeansDenoising function for colored images
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * src: Input 8-bit 3-channel image.
/// * dst: Output image with the same size and type as src .
/// * templateWindowSize: Size in pixels of the template patch that is used to compute weights.
/// Should be odd. Recommended value 7 pixels
/// * searchWindowSize: Size in pixels of the window that is used to compute weighted average for
/// given pixel. Should be odd. Affect performance linearly: greater searchWindowsSize - greater
/// denoising time. Recommended value 21 pixels
/// * h: Parameter regulating filter strength for luminance component. Bigger h value perfectly
/// removes noise but also removes image details, smaller h value preserves details but also preserves
/// some noise
/// * hColor: The same as h but for color components. For most images value equals 10
/// will be enough to remove colored noise and do not distort colors
///
/// The function converts image to CIELAB colorspace and then separately denoise L and AB components
/// with given h parameters using fastNlMeansDenoising function.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * h: 3
/// * h_color: 3
/// * template_window_size: 7
/// * search_window_size: 21
#[inline]
pub fn fast_nl_means_denoising_colored(src: &dyn core::ToInputArray, dst: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, h: f32, h_color: f32, template_window_size: i32, search_window_size: i32) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(src);
extern_container_arg!(dst);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_fastNlMeansDenoisingColored_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_float_float_int_int(src.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), h, h_color, template_window_size, search_window_size, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Modification of fastNlMeansDenoising function for images sequence where consecutive images have been
/// captured in small period of time. For example video. This version of the function is for grayscale
/// images or for manual manipulation with colorspaces. For more details see
/// <http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/summary?doi=10.1.1.131.6394>
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * srcImgs: Input 8-bit or 16-bit (only with NORM_L1) 1-channel,
/// 2-channel, 3-channel or 4-channel images sequence. All images should
/// have the same type and size.
/// * imgToDenoiseIndex: Target image to denoise index in srcImgs sequence
/// * temporalWindowSize: Number of surrounding images to use for target image denoising. Should
/// be odd. Images from imgToDenoiseIndex - temporalWindowSize / 2 to
/// imgToDenoiseIndex - temporalWindowSize / 2 from srcImgs will be used to denoise
/// srcImgs[imgToDenoiseIndex] image.
/// * dst: Output image with the same size and type as srcImgs images.
/// * templateWindowSize: Size in pixels of the template patch that is used to compute weights.
/// Should be odd. Recommended value 7 pixels
/// * searchWindowSize: Size in pixels of the window that is used to compute weighted average for
/// given pixel. Should be odd. Affect performance linearly: greater searchWindowsSize - greater
/// denoising time. Recommended value 21 pixels
/// * h: Array of parameters regulating filter strength, either one
/// parameter applied to all channels or one per channel in dst. Big h value
/// perfectly removes noise but also removes image details, smaller h
/// value preserves details but also preserves some noise
/// * normType: Type of norm used for weight calculation. Can be either NORM_L2 or NORM_L1
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * template_window_size: 7
/// * search_window_size: 21
/// * norm_type: NORM_L2
#[inline]
pub fn fast_nl_means_denoising_multi_vec(src_imgs: &dyn core::ToInputArray, dst: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, img_to_denoise_index: i32, temporal_window_size: i32, h: &core::Vector<f32>, template_window_size: i32, search_window_size: i32, norm_type: i32) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(src_imgs);
extern_container_arg!(dst);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_fastNlMeansDenoisingMulti_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_int_int_const_vectorLfloatGR_int_int_int(src_imgs.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), img_to_denoise_index, temporal_window_size, h.as_raw_VectorOff32(), template_window_size, search_window_size, norm_type, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Modification of fastNlMeansDenoising function for images sequence where consecutive images have been
/// captured in small period of time. For example video. This version of the function is for grayscale
/// images or for manual manipulation with colorspaces. For more details see
/// <http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/summary?doi=10.1.1.131.6394>
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * srcImgs: Input 8-bit 1-channel, 2-channel, 3-channel or
/// 4-channel images sequence. All images should have the same type and
/// size.
/// * imgToDenoiseIndex: Target image to denoise index in srcImgs sequence
/// * temporalWindowSize: Number of surrounding images to use for target image denoising. Should
/// be odd. Images from imgToDenoiseIndex - temporalWindowSize / 2 to
/// imgToDenoiseIndex - temporalWindowSize / 2 from srcImgs will be used to denoise
/// srcImgs[imgToDenoiseIndex] image.
/// * dst: Output image with the same size and type as srcImgs images.
/// * templateWindowSize: Size in pixels of the template patch that is used to compute weights.
/// Should be odd. Recommended value 7 pixels
/// * searchWindowSize: Size in pixels of the window that is used to compute weighted average for
/// given pixel. Should be odd. Affect performance linearly: greater searchWindowsSize - greater
/// denoising time. Recommended value 21 pixels
/// * h: Parameter regulating filter strength. Bigger h value
/// perfectly removes noise but also removes image details, smaller h
/// value preserves details but also preserves some noise
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * h: 3
/// * template_window_size: 7
/// * search_window_size: 21
#[inline]
pub fn fast_nl_means_denoising_multi(src_imgs: &dyn core::ToInputArray, dst: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, img_to_denoise_index: i32, temporal_window_size: i32, h: f32, template_window_size: i32, search_window_size: i32) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(src_imgs);
extern_container_arg!(dst);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_fastNlMeansDenoisingMulti_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_int_int_float_int_int(src_imgs.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), img_to_denoise_index, temporal_window_size, h, template_window_size, search_window_size, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Perform image denoising using Non-local Means Denoising algorithm
/// <http://www.ipol.im/pub/algo/bcm_non_local_means_denoising/> with several computational
/// optimizations. Noise expected to be a gaussian white noise
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * src: Input 8-bit or 16-bit (only with NORM_L1) 1-channel,
/// 2-channel, 3-channel or 4-channel image.
/// * dst: Output image with the same size and type as src .
/// * templateWindowSize: Size in pixels of the template patch that is used to compute weights.
/// Should be odd. Recommended value 7 pixels
/// * searchWindowSize: Size in pixels of the window that is used to compute weighted average for
/// given pixel. Should be odd. Affect performance linearly: greater searchWindowsSize - greater
/// denoising time. Recommended value 21 pixels
/// * h: Array of parameters regulating filter strength, either one
/// parameter applied to all channels or one per channel in dst. Big h value
/// perfectly removes noise but also removes image details, smaller h
/// value preserves details but also preserves some noise
/// * normType: Type of norm used for weight calculation. Can be either NORM_L2 or NORM_L1
///
/// This function expected to be applied to grayscale images. For colored images look at
/// fastNlMeansDenoisingColored. Advanced usage of this functions can be manual denoising of colored
/// image in different colorspaces. Such approach is used in fastNlMeansDenoisingColored by converting
/// image to CIELAB colorspace and then separately denoise L and AB components with different h
/// parameter.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * template_window_size: 7
/// * search_window_size: 21
/// * norm_type: NORM_L2
#[inline]
pub fn fast_nl_means_denoising_vec(src: &dyn core::ToInputArray, dst: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, h: &core::Vector<f32>, template_window_size: i32, search_window_size: i32, norm_type: i32) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(src);
extern_container_arg!(dst);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_fastNlMeansDenoising_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const_vectorLfloatGR_int_int_int(src.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), h.as_raw_VectorOff32(), template_window_size, search_window_size, norm_type, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Perform image denoising using Non-local Means Denoising algorithm
/// <http://www.ipol.im/pub/algo/bcm_non_local_means_denoising/> with several computational
/// optimizations. Noise expected to be a gaussian white noise
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * src: Input 8-bit 1-channel, 2-channel, 3-channel or 4-channel image.
/// * dst: Output image with the same size and type as src .
/// * templateWindowSize: Size in pixels of the template patch that is used to compute weights.
/// Should be odd. Recommended value 7 pixels
/// * searchWindowSize: Size in pixels of the window that is used to compute weighted average for
/// given pixel. Should be odd. Affect performance linearly: greater searchWindowsSize - greater
/// denoising time. Recommended value 21 pixels
/// * h: Parameter regulating filter strength. Big h value perfectly removes noise but also
/// removes image details, smaller h value preserves details but also preserves some noise
///
/// This function expected to be applied to grayscale images. For colored images look at
/// fastNlMeansDenoisingColored. Advanced usage of this functions can be manual denoising of colored
/// image in different colorspaces. Such approach is used in fastNlMeansDenoisingColored by converting
/// image to CIELAB colorspace and then separately denoise L and AB components with different h
/// parameter.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * h: 3
/// * template_window_size: 7
/// * search_window_size: 21
#[inline]
pub fn fast_nl_means_denoising(src: &dyn core::ToInputArray, dst: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, h: f32, template_window_size: i32, search_window_size: i32) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(src);
extern_container_arg!(dst);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_fastNlMeansDenoising_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_float_int_int(src.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), h, template_window_size, search_window_size, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Applying an appropriate non-linear transformation to the gradient field inside the selection and
/// then integrating back with a Poisson solver, modifies locally the apparent illumination of an image.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * src: Input 8-bit 3-channel image.
/// * mask: Input 8-bit 1 or 3-channel image.
/// * dst: Output image with the same size and type as src.
/// * alpha: Value ranges between 0-2.
/// * beta: Value ranges between 0-2.
///
/// This is useful to highlight under-exposed foreground objects or to reduce specular reflections.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * alpha: 0.2f
/// * beta: 0.4f
#[inline]
pub fn illumination_change(src: &dyn core::ToInputArray, mask: &dyn core::ToInputArray, dst: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, alpha: f32, beta: f32) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(src);
extern_container_arg!(mask);
extern_container_arg!(dst);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_illuminationChange_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_float_float(src.as_raw__InputArray(), mask.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), alpha, beta, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Restores the selected region in an image using the region neighborhood.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * src: Input 8-bit, 16-bit unsigned or 32-bit float 1-channel or 8-bit 3-channel image.
/// * inpaintMask: Inpainting mask, 8-bit 1-channel image. Non-zero pixels indicate the area that
/// needs to be inpainted.
/// * dst: Output image with the same size and type as src .
/// * inpaintRadius: Radius of a circular neighborhood of each point inpainted that is considered
/// by the algorithm.
/// * flags: Inpainting method that could be cv::INPAINT_NS or cv::INPAINT_TELEA
///
/// The function reconstructs the selected image area from the pixel near the area boundary. The
/// function may be used to remove dust and scratches from a scanned photo, or to remove undesirable
/// objects from still images or video. See <http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Inpainting> for more details.
///
///
/// Note:
/// * An example using the inpainting technique can be found at
/// opencv_source_code/samples/cpp/inpaint.cpp
/// * (Python) An example using the inpainting technique can be found at
/// opencv_source_code/samples/python/inpaint.py
#[inline]
pub fn inpaint(src: &dyn core::ToInputArray, inpaint_mask: &dyn core::ToInputArray, dst: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, inpaint_radius: f64, flags: i32) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(src);
extern_container_arg!(inpaint_mask);
extern_container_arg!(dst);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_inpaint_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_double_int(src.as_raw__InputArray(), inpaint_mask.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), inpaint_radius, flags, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// @example samples/cpp/tutorial_code/photo/non_photorealistic_rendering/npr_demo.cpp
/// An example using non-photorealistic line drawing functions
///
/// Pencil-like non-photorealistic line drawing
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * src: Input 8-bit 3-channel image.
/// * dst1: Output 8-bit 1-channel image.
/// * dst2: Output image with the same size and type as src.
/// * sigma_s: %Range between 0 to 200.
/// * sigma_r: %Range between 0 to 1.
/// * shade_factor: %Range between 0 to 0.1.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * sigma_s: 60
/// * sigma_r: 0.07f
/// * shade_factor: 0.02f
#[inline]
pub fn pencil_sketch(src: &dyn core::ToInputArray, dst1: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, dst2: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, sigma_s: f32, sigma_r: f32, shade_factor: f32) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(src);
extern_container_arg!(dst1);
extern_container_arg!(dst2);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_pencilSketch_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_float_float_float(src.as_raw__InputArray(), dst1.as_raw__OutputArray(), dst2.as_raw__OutputArray(), sigma_s, sigma_r, shade_factor, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// @example samples/cpp/tutorial_code/photo/seamless_cloning/cloning_demo.cpp
/// An example using seamlessClone function
///
/// Image editing tasks concern either global changes (color/intensity corrections, filters,
/// deformations) or local changes concerned to a selection. Here we are interested in achieving local
/// changes, ones that are restricted to a region manually selected (ROI), in a seamless and effortless
/// manner. The extent of the changes ranges from slight distortions to complete replacement by novel
/// content [PM03](https://docs.opencv.org/4.7.0/d0/de3/citelist.html#CITEREF_PM03) .
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * src: Input 8-bit 3-channel image.
/// * dst: Input 8-bit 3-channel image.
/// * mask: Input 8-bit 1 or 3-channel image.
/// * p: Point in dst image where object is placed.
/// * blend: Output image with the same size and type as dst.
/// * flags: Cloning method that could be cv::NORMAL_CLONE, cv::MIXED_CLONE or cv::MONOCHROME_TRANSFER
#[inline]
pub fn seamless_clone(src: &dyn core::ToInputArray, dst: &dyn core::ToInputArray, mask: &dyn core::ToInputArray, p: core::Point, blend: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, flags: i32) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(src);
extern_container_arg!(dst);
extern_container_arg!(mask);
extern_container_arg!(blend);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_seamlessClone_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_Point_const__OutputArrayR_int(src.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__InputArray(), mask.as_raw__InputArray(), p.opencv_as_extern(), blend.as_raw__OutputArray(), flags, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Stylization aims to produce digital imagery with a wide variety of effects not focused on
/// photorealism. Edge-aware filters are ideal for stylization, as they can abstract regions of low
/// contrast while preserving, or enhancing, high-contrast features.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * src: Input 8-bit 3-channel image.
/// * dst: Output image with the same size and type as src.
/// * sigma_s: %Range between 0 to 200.
/// * sigma_r: %Range between 0 to 1.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * sigma_s: 60
/// * sigma_r: 0.45f
#[inline]
pub fn stylization(src: &dyn core::ToInputArray, dst: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, sigma_s: f32, sigma_r: f32) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(src);
extern_container_arg!(dst);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_stylization_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_float_float(src.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), sigma_s, sigma_r, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// By retaining only the gradients at edge locations, before integrating with the Poisson solver, one
/// washes out the texture of the selected region, giving its contents a flat aspect. Here Canny Edge %Detector is used.
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * src: Input 8-bit 3-channel image.
/// * mask: Input 8-bit 1 or 3-channel image.
/// * dst: Output image with the same size and type as src.
/// * low_threshold: %Range from 0 to 100.
/// * high_threshold: Value \> 100.
/// * kernel_size: The size of the Sobel kernel to be used.
///
///
/// Note:
/// The algorithm assumes that the color of the source image is close to that of the destination. This
/// assumption means that when the colors don't match, the source image color gets tinted toward the
/// color of the destination image.
///
/// ## C++ default parameters
/// * low_threshold: 30
/// * high_threshold: 45
/// * kernel_size: 3
#[inline]
pub fn texture_flattening(src: &dyn core::ToInputArray, mask: &dyn core::ToInputArray, dst: &mut dyn core::ToOutputArray, low_threshold: f32, high_threshold: f32, kernel_size: i32) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(src);
extern_container_arg!(mask);
extern_container_arg!(dst);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_textureFlattening_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR_const__OutputArrayR_float_float_int(src.as_raw__InputArray(), mask.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw__OutputArray(), low_threshold, high_threshold, kernel_size, ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
/// Constant methods for [crate::photo::AlignExposures]
pub trait AlignExposuresConst: core::AlgorithmTraitConst {
fn as_raw_AlignExposures(&self) -> *const c_void;
}
/// The base class for algorithms that align images of the same scene with different exposures
pub trait AlignExposures: core::AlgorithmTrait + crate::photo::AlignExposuresConst {
fn as_raw_mut_AlignExposures(&mut self) -> *mut c_void;
/// Aligns images
///
/// ## Parameters
/// * src: vector of input images
/// * dst: vector of aligned images
/// * times: vector of exposure time values for each image
/// * response: 256x1 matrix with inverse camera response function for each pixel value, it should
/// have the same number of channels as images.
#[inline]
fn process(&mut self, src: &dyn core::ToInputArray, dst: &mut core::Vector<core::Mat>, times: &dyn core::ToInputArray, response: &dyn core::ToInputArray) -> Result<()> {
extern_container_arg!(src);
extern_container_arg!(times);
extern_container_arg!(response);
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_AlignExposures_process_const__InputArrayR_vectorLMatGR_const__InputArrayR_const__InputArrayR(self.as_raw_mut_AlignExposures(), src.as_raw__InputArray(), dst.as_raw_mut_VectorOfMat(), times.as_raw__InputArray(), response.as_raw__InputArray(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
}
/// Constant methods for [crate::photo::AlignMTB]
pub trait AlignMTBConst: crate::photo::AlignExposuresConst {
fn as_raw_AlignMTB(&self) -> *const c_void;
#[inline]
fn get_max_bits(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_AlignMTB_getMaxBits_const(self.as_raw_AlignMTB(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}
#[inline]
fn get_exclude_range(&self) -> Result<i32> {
return_send!(via ocvrs_return);
unsafe { sys::cv_AlignMTB_getExcludeRange_const(self.as_raw_AlignMTB(), ocvrs_return.as_mut_ptr()) };
return_receive!(unsafe ocvrs_return => ret);
let ret = ret.into_result()?;
Ok(ret)
}