Vector Search Engine for the next generation of AI applications
Qdrant (read: quadrant) is a vector similarity search engine and vector database. It provides a production-ready service with a convenient API to store, search, and manage points—vectors with an additional payload Qdrant is tailored to extended filtering support. It makes it useful for all sorts of neural-network or semantic-based matching, faceted search, and other applications.
Qdrant is written in Rust 🦀, which makes it fast and reliable even under high load. See benchmarks.
With Qdrant, embeddings or neural network encoders can be turned into full-fledged applications for matching, searching, recommending, and much more!
Qdrant is also available as a fully managed Qdrant Cloud ⛅ including a free tier.
Quick Start • Client Libraries • Demo Projects • Integrations • Contact
pip install qdrant-client
The python client offers a convenient way to start with Qdrant locally:
from qdrant_client import QdrantClient
qdrant = QdrantClient(":memory:") # Create in-memory Qdrant instance, for testing, CI/CD
# OR
client = QdrantClient(path="path/to/db") # Persists changes to disk, fast prototypingTo experience the full power of Qdrant locally, run the container with this command:
docker run -p 6333:6333 qdrant/qdrantNow you can connect to this with any client, including Python:
qdrant = QdrantClient("http://localhost:6333") # Connect to existing Qdrant instanceBefore deploying Qdrant to production, be sure to read our installation and security guides.
Qdrant offers the following client libraries to help you integrate it into your application stack with ease:
- Official:
- Community:
- Quick Start Guide
- End to End Colab Notebook demo with SentenceBERT and Qdrant
- Detailed Documentation are great starting points
- Step-by-Step Tutorial to create your first neural network project with Qdrant
Unlock the power of semantic embeddings with Qdrant, transcending keyword-based search to find meaningful connections in short texts. Deploy a neural search in minutes using a pre-trained neural network, and experience the future of text search. Try it online!
There's more to discovery than text search, especially when it comes to food. People often choose meals based on appearance rather than descriptions and ingredients. Let Qdrant help your users find their next delicious meal using visual search, even if they don't know the dish's name. Check it out!
Enter the cutting-edge realm of extreme classification, an emerging machine learning field tackling multi-class and multi-label problems with millions of labels. Harness the potential of similarity learning models, and see how a pre-trained transformer model and Qdrant can revolutionize e-commerce product categorization. Play with it online!
More solutions
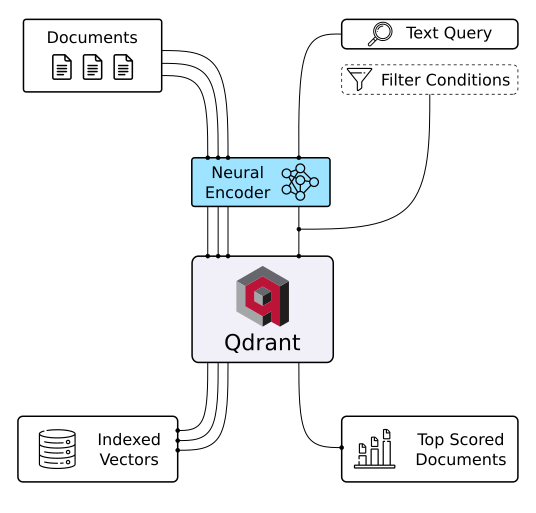
|
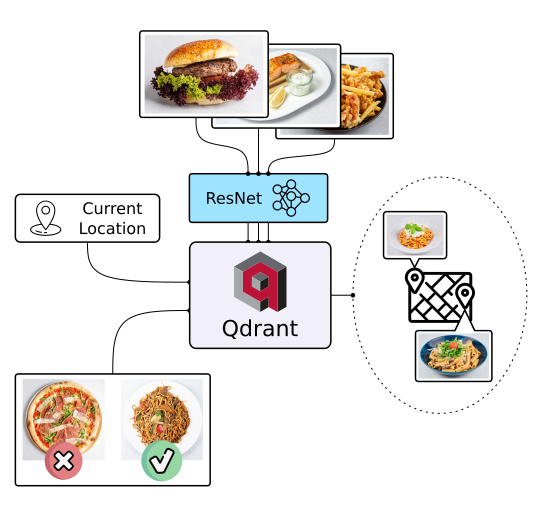
|
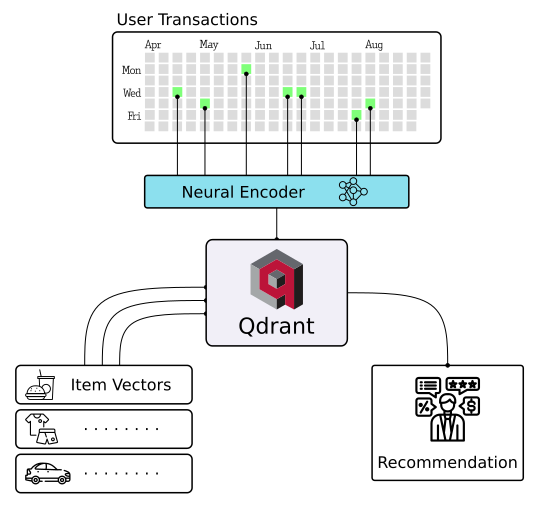
|
| Semantic Text Search | Similar Image Search | Recommendations |
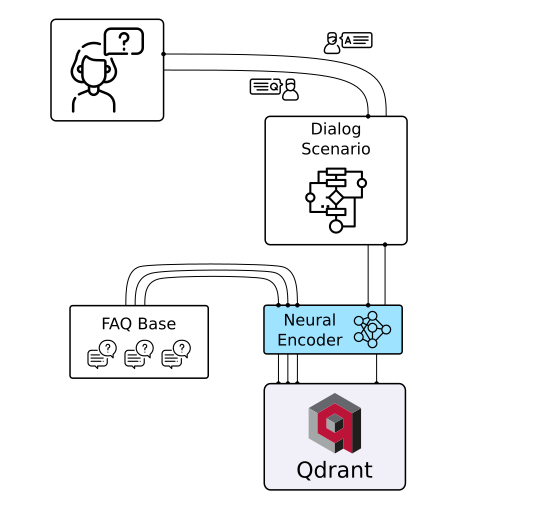
|
|

|
| Chat Bots | Matching Engines | Anomaly Detection |
Online OpenAPI 3.0 documentation is available here. OpenAPI makes it easy to generate a client for virtually any framework or programming language.
You can also download raw OpenAPI definitions.
For faster production-tier searches, Qdrant also provides a gRPC interface. You can find gRPC documentation here.
Qdrant can attach any JSON payloads to vectors, allowing for both the storage and filtering of data based on the values in these payloads. Payload supports a wide range of data types and query conditions, including keyword matching, full-text filtering, numerical ranges, geo-locations, and more.
Filtering conditions can be combined in various ways, including should, must, and must_not clauses,
ensuring that you can implement any desired business logic on top of similarity matching.
To address the limitations of vector embeddings when searching for specific keywords, Qdrant introduces support for sparse vectors in addition to the regular dense ones.
Sparse vectors can be viewed as an generalisation of BM25 or TF-IDF ranking. They enable you to harness the capabilities of transformer-based neural networks to weigh individual tokens effectively.
Qdrant provides multiple options to make vector search cheaper and more resource-efficient. Built-in vector quantization reduces RAM usage by up to 97% and dynamically manages the trade-off between search speed and precision.
Qdrant offers comprehensive horizontal scaling support through two key mechanisms:
- Size expansion via sharding and throughput enhancement via replication
- Zero-downtime rolling updates and seamless dynamic scaling of the collections
- Query Planning and Payload Indexes - leverages stored payload information to optimize query execution strategy.
- SIMD Hardware Acceleration - utilizes modern CPU x86-x64 and Neon architectures to deliver better performance.
- Async I/O - uses
io_uringto maximize disk throughput utilization even on a network-attached storage. - Write-Ahead Logging - ensures data persistence with update confirmation, even during power outages.
Examples and/or documentation of Qdrant integrations:
- Cohere (blogpost on building a QA app with Cohere and Qdrant) - Use Cohere embeddings with Qdrant
- DocArray - Use Qdrant as a document store in DocArray
- Haystack - Use Qdrant as a document store with Haystack (blogpost).
- LangChain (blogpost) - Use Qdrant as a memory backend for LangChain.
- LlamaIndex - Use Qdrant as a Vector Store with LlamaIndex.
- OpenAI - ChatGPT retrieval plugin - Use Qdrant as a memory backend for ChatGPT
- Microsoft Semantic Kernel - Use Qdrant as persistent memory with Semantic Kernel
- Have questions? Join our Discord channel or mention @qdrant_engine on Twitter
- Want to stay in touch with latest releases? Subscribe to our Newsletters
- Looking for a managed cloud? Check pricing, need something personalised? We're at [email protected]
Thanks to the people who contributed to Qdrant:
Qdrant is licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0. View a copy of the License file.





