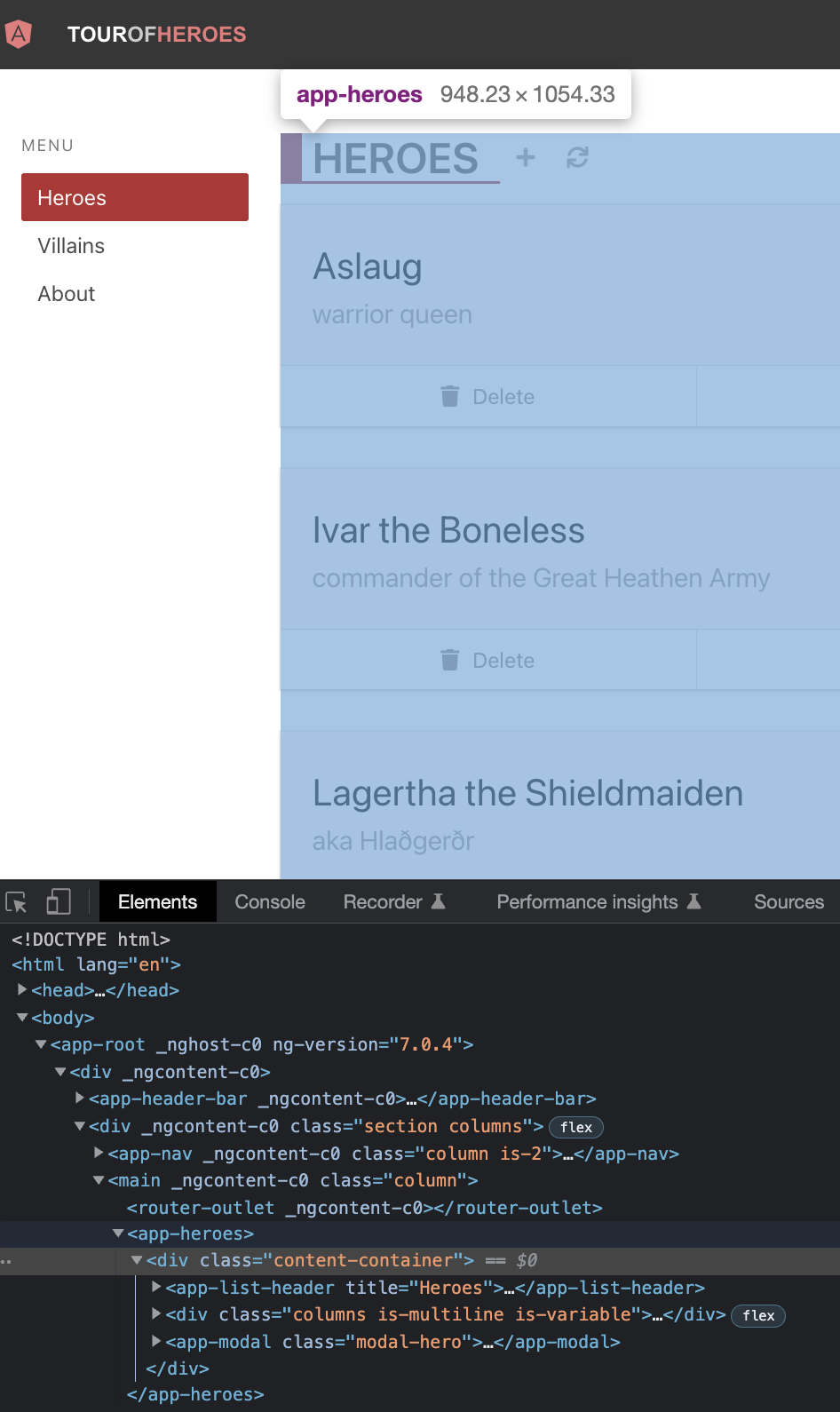
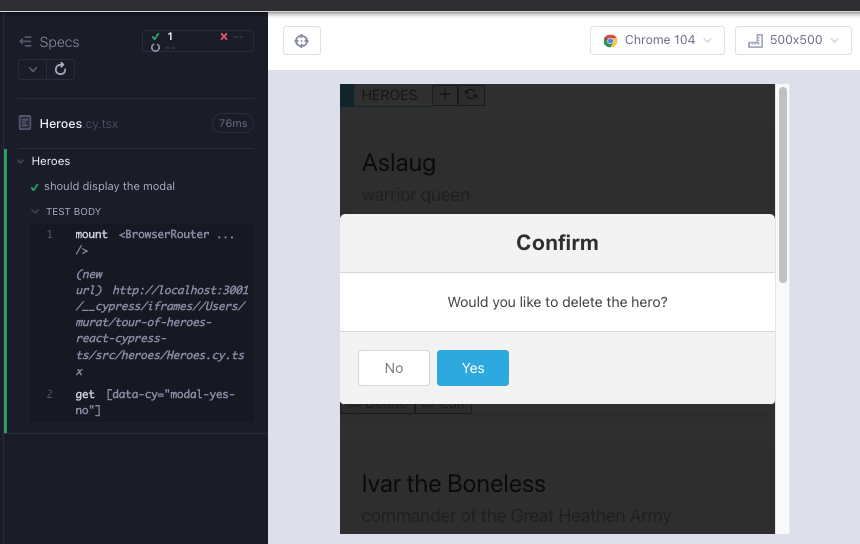
Heroes component utilizes the other hero components and is the most complex so far. Looking at the Angular version of the app, we can come up with a bullet list of the DOM elements.
ListHeaderchild componentdiv- A route that switches between
HeroListandHeroDetail
- A route that switches between
ModalYesNocomponent (for delete operation)
Create a branch feat/Heroes. Create 2 files under src/heroes/ folder; Heroes.cy.tsx, Heroes.tsx. As usual, start minimal with a component rendering; copy the below to the files and execute the test after opening the runner with yarn cy:open-ct.
// src/components/Heroes.cy.tsx
import Heroes from "./Heroes";
import "../styles.scss";
describe("Heroes", () => {
it("should", () => {
cy.mount(<Heroes />);
});
});// src/components/Heroes.tsx
export default function Heroes() {
return <div>hello</div>;
}
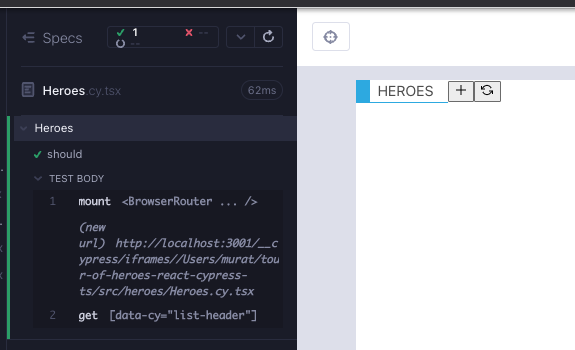
We start with a test that checks for the ListHeader component (Red 1).
// src/components/Heroes.cy.tsx
import Heroes from "./Heroes";
import "../styles.scss";
describe("Heroes", () => {
it("should", () => {
cy.mount(<Heroes />);
cy.getByCy("list-header");
});
});To make the test work, we need to include the child component in the render, and add the necessary attributes; title, handleAdd, handleRefresh. Any value will do for now (Red 1).
// src/components/Heroes.tsx
import ListHeader from "../components/ListHeader";
export default function Heroes() {
return (
<div data-cy="heroes">
<ListHeader title="Heroes" handleAdd={""} handleRefresh={""} />
</div>
);
}We still get a test error, and it is a familiar one about routing. It is because the child component ListHeader is using react-router. Recall from ListHeader and HeaderBarBrand components that any time we are using react-router, we have to wrap the mounted component in BrowserRouter in the component test (Green 1).
// src/components/Heroes.cy.tsx
import Heroes from "./Heroes";
import { BrowserRouter } from "react-router-dom";
import "../styles.scss";
describe("Heroes", () => {
it("should", () => {
cy.mount(
<BrowserRouter>
<Heroes />
</BrowserRouter>
);
cy.getByCy("list-header");
});
});Click the icons and we get type errors. Recall that while testing ListHeader component in isolation, we used cy.stub for handleAdd and handleRefresh. Now the component is being used as a child, and React cannot use cy.stub. The parent / the consumer of the child has to implement this handler function.
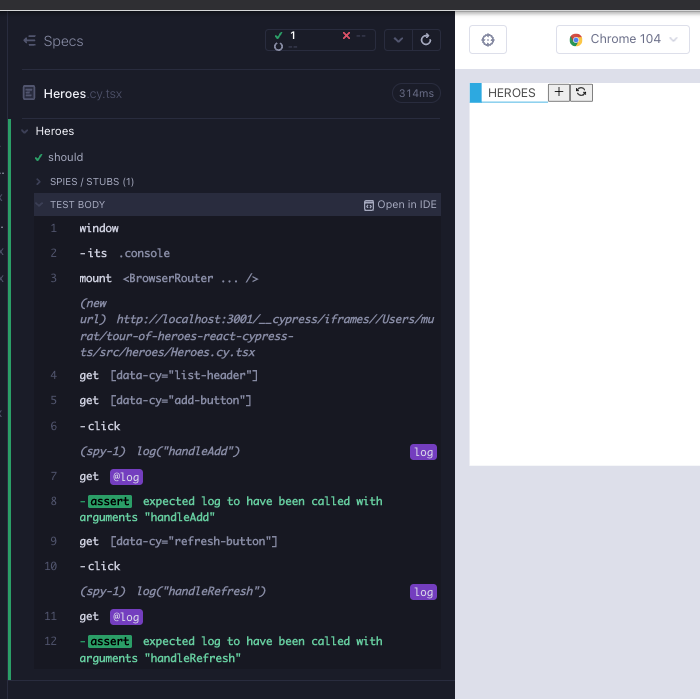
Let's improve the tests with the two clicks that trigger the failures. For now it suffices to spy on console logs as we did in the tests HeroDetail.cy.tsx and HeroList.cy.tsx (Red 2).
// src/components/Heroes.cy.tsx
import Heroes from "./Heroes";
import { BrowserRouter } from "react-router-dom";
import "../styles.scss";
describe("Heroes", () => {
it("should handle hero add and refresh", () => {
cy.window()
.its("console")
.then((console) => cy.spy(console, "log").as("log"));
cy.mount(
<BrowserRouter>
<Heroes />
</BrowserRouter>
);
cy.getByCy("list-header");
cy.getByCy("add-button").click();
cy.get("@log").should("have.been.calledWith", "handleAdd");
cy.getByCy("refresh-button").click();
cy.get("@log").should("have.been.calledWith", "handleRefresh");
});
});To make the test pass, we need to add functions that console.log with the respective strings (Green 2).
// src/components/Heroes.tsx
import ListHeader from "../components/ListHeader";
export default function Heroes() {
return (
<div data-cy="heroes">
<ListHeader
title="Heroes"
handleAdd={() => console.log("handleAdd")}
handleRefresh={() => console.log("handleRefresh")}
/>
</div>
);
}We can refactor those into their own functions and that suffices for the ListHeader for now (Refactor 2).
// src/components/Heroes.tsx
import ListHeader from "../components/ListHeader";
export default function Heroes() {
const addNewHero = () => console.log("handleAdd");
const handleRefresh = () => console.log("handleRefresh");
return (
<div data-cy="heroes">
<ListHeader
title="Heroes"
handleAdd={addNewHero}
handleRefresh={handleRefresh}
/>
</div>
);
}When we render Heroes, at first ListHeader and the HeroList display. If we Edit a hero, the HeroDetail displays. If we Delete a hero, ModalYesNo is shown. We will first focus on the HeroList, then the modal. We will tackle HeroDetail after setting up routing in a later chapter.
We start simple with a test that checks for the HeroList render (Red 3).
// src/components/Heroes.cy.tsx
import Heroes from "./Heroes";
import { BrowserRouter } from "react-router-dom";
import "../styles.scss";
describe("Heroes", () => {
it("should handle hero add and refresh", () => {
cy.window()
.its("console")
.then((console) => cy.spy(console, "log").as("log"));
cy.mount(
<BrowserRouter>
<Heroes />
</BrowserRouter>
);
cy.getByCy("list-header");
cy.getByCy("add-button").click();
cy.get("@log").should("have.been.calledWith", "handleAdd");
cy.getByCy("refresh-button").click();
cy.get("@log").should("have.been.calledWith", "handleRefresh");
});
it("should display hero list on render", () => {
cy.mount(
<BrowserRouter>
<Heroes />
</BrowserRouter>
);
cy.getByCy("hero-list");
});
});We add the child HeroList to our component. It requires a heroes prop. One idea is to look at the component tests for children, see how they are used, and work off of that documentation when writing the tests for the parent component. We do not need to repeat any tests at the parent, but we can use the help to give an idea about how the child should be mounted. Take a look at HeroList.cy.tsx. We are importing a Cypress fixture and passing it as a prop. We can repeat a similar process, and delay the decisions about data and state to a later time until we have to make them (Green 3).
If a component is importing a file from outside the source folder, the component will work in isolation but the greater app will not compile. Make a copy of heroes.json from cypress/fixtures/ in src/heroes and update Heroes component to use this file instead. We will handle this gracefully later when working with network data.
// src/components/Heroes.tsx
import ListHeader from "../components/ListHeader";
import HeroList from "./HeroList";
import heroes from "./heroes.json";
export default function Heroes() {
const addNewHero = () => console.log("handleAdd");
const handleRefresh = () => console.log("handleRefresh");
return (
<div data-cy="heroes">
<ListHeader
title="Heroes"
handleAdd={addNewHero}
handleRefresh={handleRefresh}
/>
<div>
<div>
<HeroList heroes={heroes} />
</div>
</div>
</div>
);
}Once again we can look at the component tests for children, see how they are used, and work off of that documentation when writing the tests for the parent component. ModalYesNo.cy.tsx has props for a message string, onYes and onNo events. It also supports an internal state which allows the modal to be toggled.
Let's write a failing test. For now, we do not have a toggle for the modal, so we should only run the new modal test (Red 4).
// src/components/Heroes.cy.tsx
import Heroes from "./Heroes";
import { BrowserRouter } from "react-router-dom";
import "../styles.scss";
describe("Heroes", () => {
it("should handle hero add and refresh", () => {
cy.window()
.its("console")
.then((console) => cy.spy(console, "log").as("log"));
cy.mount(
<BrowserRouter>
<Heroes />
</BrowserRouter>
);
cy.getByCy("list-header");
cy.getByCy("add-button").click();
cy.get("@log").should("have.been.calledWith", "handleAdd");
cy.getByCy("refresh-button").click();
cy.get("@log").should("have.been.calledWith", "handleRefresh");
});
it("should display hero list on render", () => {
cy.mount(
<BrowserRouter>
<Heroes />
</BrowserRouter>
);
cy.getByCy("hero-list");
});
it.only("should display the modal", () => {
cy.mount(
<BrowserRouter>
<Heroes />
</BrowserRouter>
);
cy.getByCy("modal-yes-no");
});
});To render the child component, we just have to add the props message, onNo, onYes. For now it is all right for them to be empty strings (Green 4).
// src/components/Heroes.tsx
import ListHeader from "../components/ListHeader";
import ModalYesNo from "components/ModalYesNo";
import HeroList from "./HeroList";
import heroes from "./heroes.json";
export default function Heroes() {
const addNewHero = () => console.log("handleAdd");
const handleRefresh = () => console.log("handleRefresh");
return (
<div data-cy="heroes">
<ListHeader
title="Heroes"
handleAdd={addNewHero}
handleRefresh={handleRefresh}
/>
<div>
<div>
<HeroList heroes={heroes} />
</div>
</div>
<ModalYesNo
message="Would you like to delete the hero?"
onNo={""}
onYes={""}
/>
</div>
);
}Having run that test, we really want a way to close that modal and see our Heroes component. Let's write a failing test for this need (Red 5).
From here onwards, for the sake of brevity, when a test is executed with
.onlywe will only be showing the code for the relevant portion.
// src/components/Heroes.cy.tsx
it.only("should display the modal", () => {
cy.mount(
<BrowserRouter>
<Heroes />
</BrowserRouter>
);
cy.getByCy("modal-yes-no");
cy.getByCy("button-no").click();
});We get an error in the Cypress runner func.apply is not a function. Become familiar with this error, it means our event handler isn't doing anything. To resolve it, for now use a function that console.logs (Green 5).
// src/components/Heroes.tsx
import ListHeader from "../components/ListHeader";
import ModalYesNo from "components/ModalYesNo";
import HeroList from "./HeroList";
import heroes from "./heroes.json";
export default function Heroes() {
const addNewHero = () => console.log("handleAdd");
const handleRefresh = () => console.log("handleRefresh");
return (
<div data-cy="heroes">
<ListHeader
title="Heroes"
handleAdd={addNewHero}
handleRefresh={handleRefresh}
/>
<div>
<div>
<HeroList heroes={heroes} />
</div>
</div>
<ModalYesNo
message="Would you like to delete the hero?"
onNo={() => console.log("handleCloseModal")}
onYes={""}
/>
</div>
);
}We can refactor that into its own function (Refactor 5).
// src/components/Heroes.tsx
import ListHeader from "../components/ListHeader";
import ModalYesNo from "components/ModalYesNo";
import HeroList from "./HeroList";
import heroes from "./heroes.json";
export default function Heroes() {
const addNewHero = () => console.log("handleAdd");
const handleRefresh = () => console.log("handleRefresh");
const handleCloseModal = () => () => console.log("handleCloseModal");
return (
<div data-cy="heroes">
<ListHeader
title="Heroes"
handleAdd={addNewHero}
handleRefresh={handleRefresh}
/>
<div>
<div>
<HeroList heroes={heroes} />
</div>
</div>
<ModalYesNo
message="Would you like to delete the hero?"
onNo={handleCloseModal}
onYes={""}
/>
</div>
);
}We covered the useState hook in the HeroDetail function. There were two key takeaways in that chapter. First was that we can simplify our UI state management into two categories:
- UI state: modal is open, item is highlighted, etc.
- Server data.
In the case of the modal, it is category 1; UI state.
The second key takeaway was that we prefer to manage state where it is most relevant. In this case whether the modal is open or closed is most relevant in the Heroes component, and useState hook is the simplest way to satisfy that.
We have 3 requirements about the modal. The flow goes as such:
- We would like the modal to be closed when
Heroesis rendered - When we want to delete a hero, we want to display the modal.
- We would like the modal to go away when clicking No in the modal
Let's write a failing test for the first step of the flow; when rendering the component the modal should be closed. We slightly modify the it block with comments (Red 6).
// src/components/Heroes.cy.tsx
it.only("should display the modal", () => {
cy.mount(
<BrowserRouter>
<Heroes />
</BrowserRouter>
);
cy.getByCy("modal-yes-no").should("not.exist");
// delete the hero
// cy.getByCy('modal-yes-no').should('be.visible')
// select no
// cy.getByCy('button-no').click()
// cy.getByCy('modal-yes-no').should('not.exist')
});To make the test pass, we can just use a false chain before the ModalYesNo component (Green 6).
// src/components/Heroes.tsx
import ListHeader from "../components/ListHeader";
import ModalYesNo from "components/ModalYesNo";
import HeroList from "./HeroList";
import heroes from "./heroes.json";
export default function Heroes() {
const addNewHero = () => console.log("handleAdd");
const handleRefresh = () => console.log("handleRefresh");
const handleCloseModal = () => () => {
console.log("handleCloseModal");
};
return (
<div data-cy="heroes">
<ListHeader
title="Heroes"
handleAdd={addNewHero}
handleRefresh={handleRefresh}
/>
<div>
<div>
<HeroList heroes={heroes} />
</div>
</div>
{false && (
<ModalYesNo
message="Would you like to delete the hero?"
onNo={handleCloseModal}
onYes={""}
/>
)}
</div>
);
}Let's continue writing the test. We need to click the button, and the modal should pop up (Red 7).
// src/components/Heroes.cy.tsx
it.only("should display the modal", () => {
cy.mount(
<BrowserRouter>
<Heroes />
</BrowserRouter>
);
cy.getByCy("modal-yes-no").should("not.exist");
cy.getByCy("delete-button").first().click();
cy.getByCy("modal-yes-no").should("be.visible");
// select no
// cy.getByCy('button-no').click()
// cy.getByCy('modal-yes-no').should('not.exist')
});To make this state toggle work, we need to use useState. We do not like that hard-coded false and it can be used as the initial state of the hook. At this point in time, the test is still expected to fail.
// src/components/Heroes.tsx
import ListHeader from "../components/ListHeader";
import ModalYesNo from "components/ModalYesNo";
import HeroList from "./HeroList";
import heroes from "./heroes.json";
import { useState } from "react";
export default function Heroes() {
const [showModal, setShowModal] = useState(false);
const addNewHero = () => console.log("handleAdd");
const handleRefresh = () => console.log("handleRefresh");
const handleCloseModal = () => () => {
console.log("handleCloseModal");
};
return (
<div data-cy="heroes">
<ListHeader
title="Heroes"
handleAdd={addNewHero}
handleRefresh={handleRefresh}
/>
<div>
<div>
<HeroList heroes={heroes} />
</div>
</div>
{showModal && (
<ModalYesNo
message="Would you like to delete the hero?"
onNo={handleCloseModal}
onYes={() => console.log("handleOnYes")}
/>
)}
</div>
);
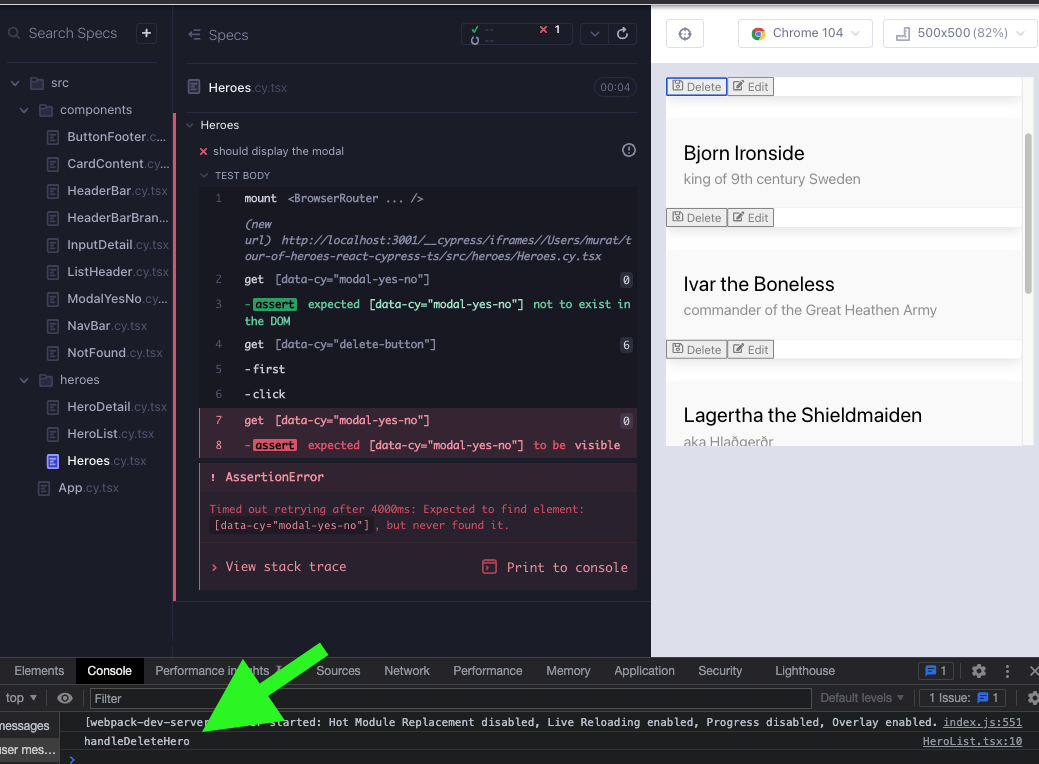
}showModal looks great in there, but we need to be able to setShowModal to true when clicking the Delete button. Take a look at the console, handleDeleteHero is called and this function lives in HeroList component. This is a hint that the two child components are sharing state.
We will reference Kent C. Dodds' Application State Management with React and give you the gist of the article:
- If components are sharing state, lift the state up to their closest common ancestor.
- If the common ancestor is too deep and lifting state results in prop-drilling, use React's context api.
- Beyond that, use state management libraries.
In our case Heroes component hosts two children HeroList and ModalYesNo; lifting state up to the parent is the easiest choice.
ModalYesNo component is already relaying its onYes and onNo onClick handlers above. On the other hand, HeroList implements its own handleDeleteHero onClick handler. Instead we need to pass a prop handleDeleteHero to HeroList which is driven by setShowModal in Heroes component. Therefore we have to make a modification to HeroList component. We remove the self-implemented handleDeleteHero function, and instead pass it as a prop. We leave the prop type generic for the time being.
// src/components/HeroList.tsx
import CardContent from "../components/CardContent";
import ButtonFooter from "../components/ButtonFooter";
import { FaEdit, FaRegSave } from "react-icons/fa";
import { Hero } from "models/Hero";
type HeroListProps = {
heroes: Hero[];
handleDeleteHero: () => void; // TODO: consider better type
};
export default function HeroList({ heroes, handleDeleteHero }: HeroListProps) {
const handleSelectHero = () => console.log("handleSelectHero");
return (
<ul data-cy="hero-list" className="list">
{heroes.map((hero, index) => (
<li data-cy={`hero-list-item-${index}`} key={hero.id}>
<div className="card">
<CardContent name={hero.name} description={hero.description} />
<footer className="card-footer">
<ButtonFooter
label="Delete"
IconClass={FaRegSave}
onClick={handleDeleteHero}
/>
<ButtonFooter
label="Edit"
IconClass={FaEdit}
onClick={handleSelectHero}
/>
</footer>
</div>
</li>
))}
</ul>
);
}We update the matching test to accept the new handleDeleteHero prop. It suffices to use cy.stub to ensure that it is called on click.
// src/components/HeroList.cy.tsx
import HeroList from "./HeroList";
import "../styles.scss";
import heroes from "./heroes.json";
describe("HeroList", () => {
it("should render the item layout", () => {
cy.mount(
<HeroList
heroes={heroes}
handleDeleteHero={cy.stub().as("handleDeleteHero")}
/>
);
cy.getByCyLike("hero-list-item").should("have.length", heroes.length);
cy.getByCy("card-content");
cy.contains(heroes[0].name);
cy.contains(heroes[0].description);
cy.get("footer")
.first()
.within(() => {
cy.getByCy("delete-button");
cy.getByCy("edit-button");
});
});
context("handleDelete, handleEdit", () => {
beforeEach(() => {
cy.window()
.its("console")
.then((console) => cy.spy(console, "log").as("log"));
cy.mount(
<HeroList
heroes={heroes}
handleDeleteHero={cy.stub().as("handleDeleteHero")}
/>
);
});
it("should handle delete", () => {
cy.getByCy("delete-button").first().click();
cy.get("@handleDeleteHero").should("have.been.called");
});
it("should handle edit", () => {
cy.getByCy("edit-button").first().click();
cy.get("@log").should("have.been.calledWith", "handleSelectHero");
});
});
});Back in the parent component Heroes, now we can pass a prop handleDeleteHero. The value of it needs to be a function that returns setShowModal(<a boolean arg>). Why do all the click handlers have to be functions? Per the React docs when using JSX you pass a function as the event handler, rather than a string. After the changes, the test passes. (Green 7).
// src/components/Heroes.tsx
import ListHeader from "../components/ListHeader";
import ModalYesNo from "components/ModalYesNo";
import HeroList from "./HeroList";
import heroes from "./heroes.json";
import { useState } from "react";
export default function Heroes() {
const [showModal, setShowModal] = useState(false);
const addNewHero = () => console.log("handleAdd");
const handleRefresh = () => console.log("handleRefresh");
const handleCloseModal = () => () => {
console.log("handleCloseModal");
};
return (
<div data-cy="heroes">
<ListHeader
title="Heroes"
handleAdd={addNewHero}
handleRefresh={handleRefresh}
/>
<div>
<div>
<HeroList
heroes={heroes}
handleDeleteHero={() => setShowModal(true)}
/>
</div>
</div>
{showModal && (
<ModalYesNo
message="Would you like to delete the hero?"
onNo={handleCloseModal}
onYes={() => console.log("handleOnYes")}
/>
)}
</div>
);
}We can refactor () => setShowModal(true) into its own function. We can also remove the .only in the component test (Refactor 7).
// src/components/Heroes.tsx
import ListHeader from "../components/ListHeader";
import ModalYesNo from "components/ModalYesNo";
import HeroList from "./HeroList";
import heroes from "./heroes.json";
import { useState } from "react";
export default function Heroes() {
const [showModal, setShowModal] = useState<boolean>(false);
const addNewHero = () => console.log("handleAdd");
const handleRefresh = () => console.log("handleRefresh");
const handleCloseModal = () => {
console.log("handleCloseModal");
};
const handleDeleteHero = () => {
setShowModal(true);
};
return (
<div data-cy="heroes">
<ListHeader
title="Heroes"
handleAdd={addNewHero}
handleRefresh={handleRefresh}
/>
<div>
<div>
<HeroList heroes={heroes} handleDeleteHero={handleDeleteHero} />
</div>
</div>
{showModal && (
<ModalYesNo
message="Would you like to delete the hero?"
onNo={handleCloseModal}
onYes={() => console.log("handleOnYes")}
/>
)}
</div>
);
}Time for the next failing test in the modal flow; when button-no is clicked the modal should go away (Red 8).
// src/components/Heroes.cy.tsx
import Heroes from "./Heroes";
import { BrowserRouter } from "react-router-dom";
import "../styles.scss";
describe("Heroes", () => {
it("should handle hero add and refresh", () => {
cy.window()
.its("console")
.then((console) => cy.spy(console, "log").as("log"));
cy.mount(
<BrowserRouter>
<Heroes />
</BrowserRouter>
);
cy.getByCy("list-header");
cy.getByCy("add-button").click();
cy.get("@log").should("have.been.calledWith", "handleAdd");
cy.getByCy("refresh-button").click();
cy.get("@log").should("have.been.calledWith", "handleRefresh");
});
it("should display hero list on render", () => {
cy.mount(
<BrowserRouter>
<Heroes />
</BrowserRouter>
);
cy.getByCy("hero-list");
});
it("should display the modal", () => {
cy.mount(
<BrowserRouter>
<Heroes />
</BrowserRouter>
);
cy.getByCy("modal-yes-no").should("not.exist");
cy.getByCy("delete-button").first().click();
cy.getByCy("modal-yes-no").should("be.visible");
cy.getByCy("button-no").click();
cy.getByCy("modal-yes-no").should("not.exist");
});
});To make this work, we use setShowModal(false) in the already existing handleCloseModal function (Green 8).
// src/components/Heroes.tsx
import ListHeader from "../components/ListHeader";
import ModalYesNo from "components/ModalYesNo";
import HeroList from "./HeroList";
import heroes from "./heroes.json";
import { useState } from "react";
export default function Heroes() {
const [showModal, setShowModal] = useState<boolean>(false);
const addNewHero = () => console.log("handleAdd");
const handleRefresh = () => console.log("handleRefresh");
const handleCloseModal = () => {
setShowModal(false);
};
const handleDeleteHero = () => {
setShowModal(true);
};
return (
<div data-cy="heroes">
<ListHeader
title="Heroes"
handleAdd={addNewHero}
handleRefresh={handleRefresh}
/>
<div>
<div>
<HeroList heroes={heroes} handleDeleteHero={handleDeleteHero} />
</div>
</div>
{showModal && (
<ModalYesNo
message="Would you like to delete the hero?"
onNo={handleCloseModal}
onYes={() => console.log("handleOnYes")}
/>
)}
</div>
);
}While we are here, we can cover the other branch of the modal flow; when clicking yes on the confirmation, we should close the modal and for now at least console.log something (Red 10).
// src/components/Heroes.cy.tsx
import Heroes from "./Heroes";
import { BrowserRouter } from "react-router-dom";
import "../styles.scss";
describe("Heroes", () => {
it("should handle hero add and refresh", () => {
cy.window()
.its("console")
.then((console) => cy.spy(console, "log").as("log"));
cy.mount(
<BrowserRouter>
<Heroes />
</BrowserRouter>
);
cy.getByCy("list-header");
cy.getByCy("add-button").click();
cy.get("@log").should("have.been.calledWith", "handleAdd");
cy.getByCy("refresh-button").click();
cy.get("@log").should("have.been.calledWith", "handleRefresh");
});
it("should display hero list on render", () => {
cy.mount(
<BrowserRouter>
<Heroes />
</BrowserRouter>
);
cy.getByCy("hero-list");
});
const invokeHeroDelete = () => {
cy.getByCy("delete-button").first().click();
cy.getByCy("modal-yes-no").should("be.visible");
};
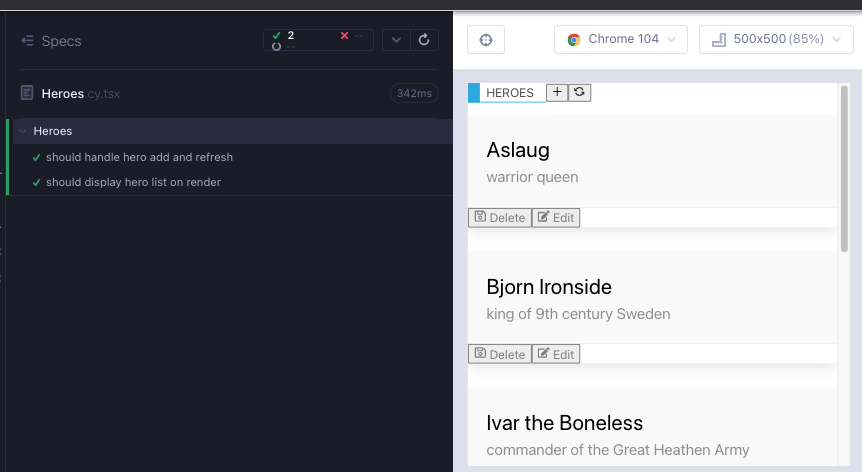
it("should go through the modal flow", () => {
cy.window()
.its("console")
.then((console) => cy.spy(console, "log").as("log"));
cy.mount(
<BrowserRouter>
<Heroes />
</BrowserRouter>
);
cy.getByCy("modal-yes-no").should("not.exist");
cy.log("do not delete flow");
invokeHeroDelete();
cy.getByCy("button-no").click();
cy.getByCy("modal-yes-no").should("not.exist");
cy.log("delete flow");
invokeHeroDelete();
cy.getByCy("button-yes").click();
cy.getByCy("modal-yes-no").should("not.exist");
cy.get("@log").should("have.been.calledWith", "handleDeleteFromModal");
});
});To pass this test, for now we just need function that toggles the modal off and console.logs the string "handleDeleteFromModal" (Green 9).
// src/components/Heroes.tsx
import ListHeader from "../components/ListHeader";
import ModalYesNo from "components/ModalYesNo";
import HeroList from "./HeroList";
import heroes from "./heroes.json";
import { useState } from "react";
export default function Heroes() {
const [showModal, setShowModal] = useState<boolean>(false);
const addNewHero = () => console.log("handleAdd");
const handleRefresh = () => console.log("handleRefresh");
const handleCloseModal = () => {
setShowModal(false);
};
const handleDeleteHero = () => {
setShowModal(true);
};
const handleDeleteFromModal = () => {
setShowModal(false);
console.log("handleDeleteFromModal");
};
return (
<div data-cy="heroes">
<ListHeader
title="Heroes"
handleAdd={addNewHero}
handleRefresh={handleRefresh}
/>
<div>
<div>
<HeroList heroes={heroes} handleDeleteHero={handleDeleteHero} />
</div>
</div>
{showModal && (
<ModalYesNo
message="Would you like to delete the hero?"
onNo={handleCloseModal}
onYes={handleDeleteFromModal}
/>
)}
</div>
);
}Continued after routing chapter.
We added a test to render ListHeader child component (wrapped in BrowserRouter), and added to component with empty props to make the test pass (Red 1, Green 1).
We added tests checking for console.logs upon clicking he add and refresh buttons (Red 2).
We used functions that console.log the function name to make the tests Pass (Green 2, Refactor 2).
We added a failing test for another child HeroList and included the child component in the render (Red 3, Green 3). We used hard coded data for the time being.
We added a failing test for rendering the modal (Red 4). We added mostly empty string props to make the test work (Green 4).
We wrote another test to be able to close the modal and got an error func.apply is not a function, which means our event handler isn't doing anything. To solve it we used console.logging for the event handler functions and refactored them (Green 5, Refactor 5).
We wrote a pseudo test for the modal flow; with the initial step that the modal should be closed (Red 6).
We hard coded a false with a blueprint for conditional rendering to make the test pass (Green 6).
We added a new test to the flow; to check that the modal gets opened on delete button click (Red 7).
We realized that the children HeroList and ModalYesNo components share state, and lifted state up to our Heroes component which is their parent.
HeroList then had a prop handleDeleteHero, and we set its value with () => setShowModal(true), to show the modal when delete is clicked (Green 7).
As before, we refactored the click handler to its own function (Refactor 7).
We wrote the next test in the modal flow, when button-no is clicked the modal should go away (Red 8).
All we needed was to instead use setShowModal(false) instead of the existing console.log in the handleCloseModal function (Green 8).
We added a test for the other branch of the modal; the delete flow (Red 9).
We added a function that toggles the modal off and console.logs the string handleDeleteFromModal and used it on the onYes handler of the modal (Green 9).
- As we repeatedly saw in the previous chapters, while designing the component, you can delay the decisions about network state and use hard coded data. For event handlers we can use functions that console.log. These will help when components that share state get used in other components. Note that per the React docs when using JSX you pass a function as the event handler, rather than a string.
- Look at the component tests for child components, see how they are used, and work off of that documentation when writing the tests for the parent component. We do not need to repeat any tests at the parent, but we can use the help to give an idea about how the child should be mounted.
- In a Cypress component test, the error
func.apply is not a functionusually means the click handlers are not doing anything. - In React, all the click handlers have to be functions. Per the React docs when using JSX you pass a function as the event handler, rather than a string.
- When testing child components in isolation (ex:
ListHeader), we can mock the click events withcy.stub. When the child component is being consumed by a parent, React obviously cannot mock anything. Therefore The parent / the consumer of the child has to implement the handler function and test it. Again,console.logis acceptable until more about the component is known. - From Kent C. Dodds:
- If components are sharing state, lift the state up to their closest common ancestor.
- If the common ancestor is too deep and lifting state results in prop-drilling, use React's context api.
- Beyond that, use state management libraries.