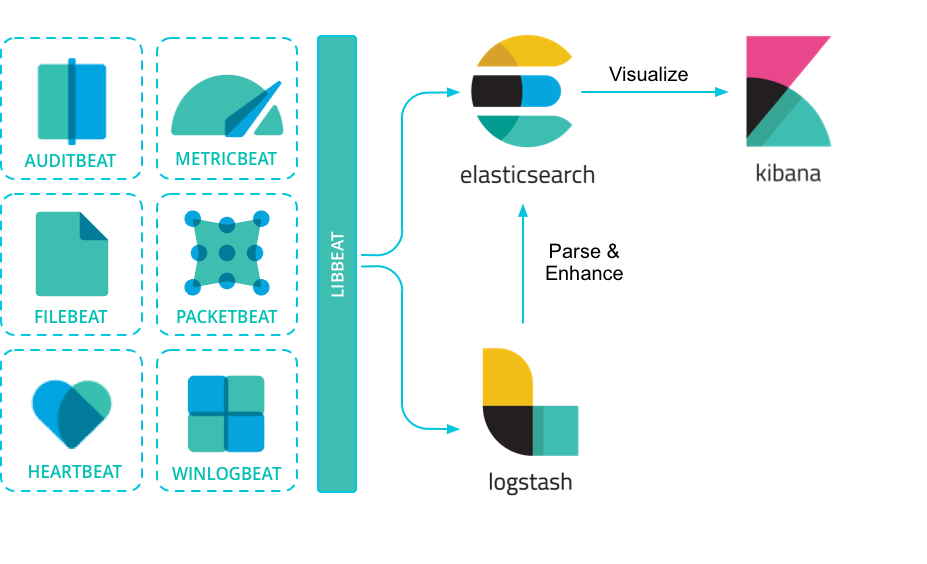
{beats} are open source data shippers that you install as agents on your servers to send operational data to {es}. Elastic provides {beats} for capturing:
| Audit data | |
| Log files | |
| Cloud data | |
| Availability | |
| Systemd journals | |
| Metrics | |
| Network traffic | |
| Windows event logs |
{beats} can send data directly to {es} or via {ls}, where you can further process and enhance the data, before visualizing it in {kib}.
To get started, see [getting-started].
Want to get up and running quickly with infrastructure metrics monitoring and centralized log analytics? Try out the {metrics-app} and the {logs-app} in {kib}. For more details, see {observability-guide}/analyze-metrics.html[Analyze metrics] and {observability-guide}/monitor-logs.html[Monitor logs].
If you have a specific use case to solve, we encourage you to create a community Beat. We’ve created an infrastructure to simplify the process. The libbeat library, written entirely in Go, offers the API that all Beats use to ship data to Elasticsearch, configure the input options, implement logging, and more. To learn how to create a new Beat, see the {beatsdevguide}/index.html[Beats Developer Guide].