SECOND detector.
ONLY support python 3.6+, pytorch 1.0.0+. Tested in Ubuntu 16.04/18.04/Windows 10.
2019-4-1: SECOND V1.6.0alpha released: New Data API, NuScenes support, PointPillars support.
2019-3-21: SECOND V1.5.1 (minor improvement and bug fix) released!
2019-1-20: SECOND V1.5 released! Sparse convolution-based network.
See release notes for more details.
WARNING: you should rerun info generation after every code update.
car.fhd.config + 160 epochs (25 fps in 1080Ti):
Car [email protected], 0.70, 0.70:
bbox AP:90.77, 89.50, 80.80
bev AP:90.28, 87.73, 79.67
3d AP:88.84, 78.43, 76.88
car.fhd.config + 50 epochs + super converge (6.5 hours) + (25 fps in 1080Ti):
Car [email protected], 0.70, 0.70:
bbox AP:90.78, 89.59, 88.42
bev AP:90.12, 87.87, 86.77
3d AP:88.62, 78.31, 76.62
car.fhd.onestage.config + 50 epochs + super converge (6.5 hours) + (25 fps in 1080Ti):
Car [email protected], 0.70, 0.70:
bbox AP:97.65, 89.59, 88.72
bev AP:90.38, 88.20, 86.98
3d AP:89.16, 78.78, 77.41
git clone https://github.com/traveller59/second.pytorch.git
cd ./second.pytorch/secondIt is recommend to use Anaconda package manager.
conda install scikit-image scipy numba pillow matplotlibpip install fire tensorboardX protobuf opencv-pythonIf you don't have Anaconda:
pip install numba scikit-image scipy pillowFollow instructions in spconv to install spconv.
If you want to use NuScenes dataset, you need to install nuscenes-devkit, I recommend to copy nuscenes in python-sdk to second/.. folder (equalivent to add it to PYTHONPATH) and manually install its dependencies, use pip to install devkit will install many fixed-version library.
you need to add following environment variable for numba.cuda, you can add them to ~/.bashrc:
export NUMBAPRO_CUDA_DRIVER=/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libcuda.so
export NUMBAPRO_NVVM=/usr/local/cuda/nvvm/lib64/libnvvm.so
export NUMBAPRO_LIBDEVICE=/usr/local/cuda/nvvm/libdevice- KITTI Dataset preparation
Download KITTI dataset and create some directories first:
└── KITTI_DATASET_ROOT
├── training <-- 7481 train data
| ├── image_2 <-- for visualization
| ├── calib
| ├── label_2
| ├── velodyne
| └── velodyne_reduced <-- empty directory
└── testing <-- 7580 test data
├── image_2 <-- for visualization
├── calib
├── velodyne
└── velodyne_reduced <-- empty directory
Then run
python create_data.py kitti_data_prep --data_path=KITTI_DATASET_ROOT- NuScenes Dataset preparation
Download NuScenes dataset:
└── NUSCENES_TRAINVAL_DATASET_ROOT
├── samples <-- key frames
├── sweeps <-- frames without annotation
├── maps <-- unused
└── v1.0-trainval <-- metadata and annotations
└── NUSCENES_TEST_DATASET_ROOT
├── samples <-- key frames
├── sweeps <-- frames without annotation
├── maps <-- unused
└── v1.0-test <-- metadata
Since the dataset is really large, you can download parts of the dataset.
Then run
python create_data.py nuscenes_data_prep --data_path=NUSCENES_TRAINVAL_DATASET_ROOT --version="v1.0-trainval" --max_sweeps=10
python create_data.py nuscenes_data_prep --data_path=NUSCENES_TEST_DATASET_ROOT --version="v1.0-test" --max_sweeps=10- Modify config file
There is some path need to be configured in config file:
train_input_reader: {
...
database_sampler {
database_info_path: "/path/to/dataset_dbinfos_train.pkl"
...
}
dataset: {
kitti_info_path: "/path/to/dataset_infos_train.pkl"
kitti_root_path: "DATASET_ROOT"
}
}
...
eval_input_reader: {
...
dataset: {
kitti_info_path: "/path/to/dataset_infos_val.pkl"
kitti_root_path: "DATASET_ROOT"
}
}I recommend to use script.py to train and eval. see script.py for more details.
python ./pytorch/train.py train --config_path=./configs/car.fhd.config --model_dir=/path/to/model_dir-
Make sure "/path/to/model_dir" doesn't exist if you want to train new model. A new directory will be created if the model_dir doesn't exist, otherwise will read checkpoints in it.
-
training process use batchsize=6 as default for 1080Ti, you need to reduce batchsize if your GPU has less memory.
-
Currently only support single GPU training, but train a model only needs 20 hours (165 epoch) in a single 1080Ti and only needs 50 epoch to reach 78.3 AP with super converge in car moderate 3D in Kitti validation dateset.
python ./pytorch/train.py evaluate --config_path=./configs/car.fhd.config --model_dir=/path/to/model_dir --measure_time=True --batch_size=1- detection result will saved as a result.pkl file in model_dir/eval_results/step_xxx or save as official KITTI label format if you use --pickle_result=False.
You can download pretrained models in google drive. The car_fhd model is corresponding to car.fhd.config.
Note that this pretrained model is trained before a bug of sparse convolution fixed, so the eval result may slightly worse.
You can use a prebuilt docker for testing:
docker pull scrin/second-pytorch
Then run:
nvidia-docker run -it --rm -v /media/yy/960evo/datasets/:/root/data -v $HOME/pretrained_models:/root/model --ipc=host second-pytorch:latest
python ./pytorch/train.py evaluate --config_path=./configs/car.config --model_dir=/root/model/car
-
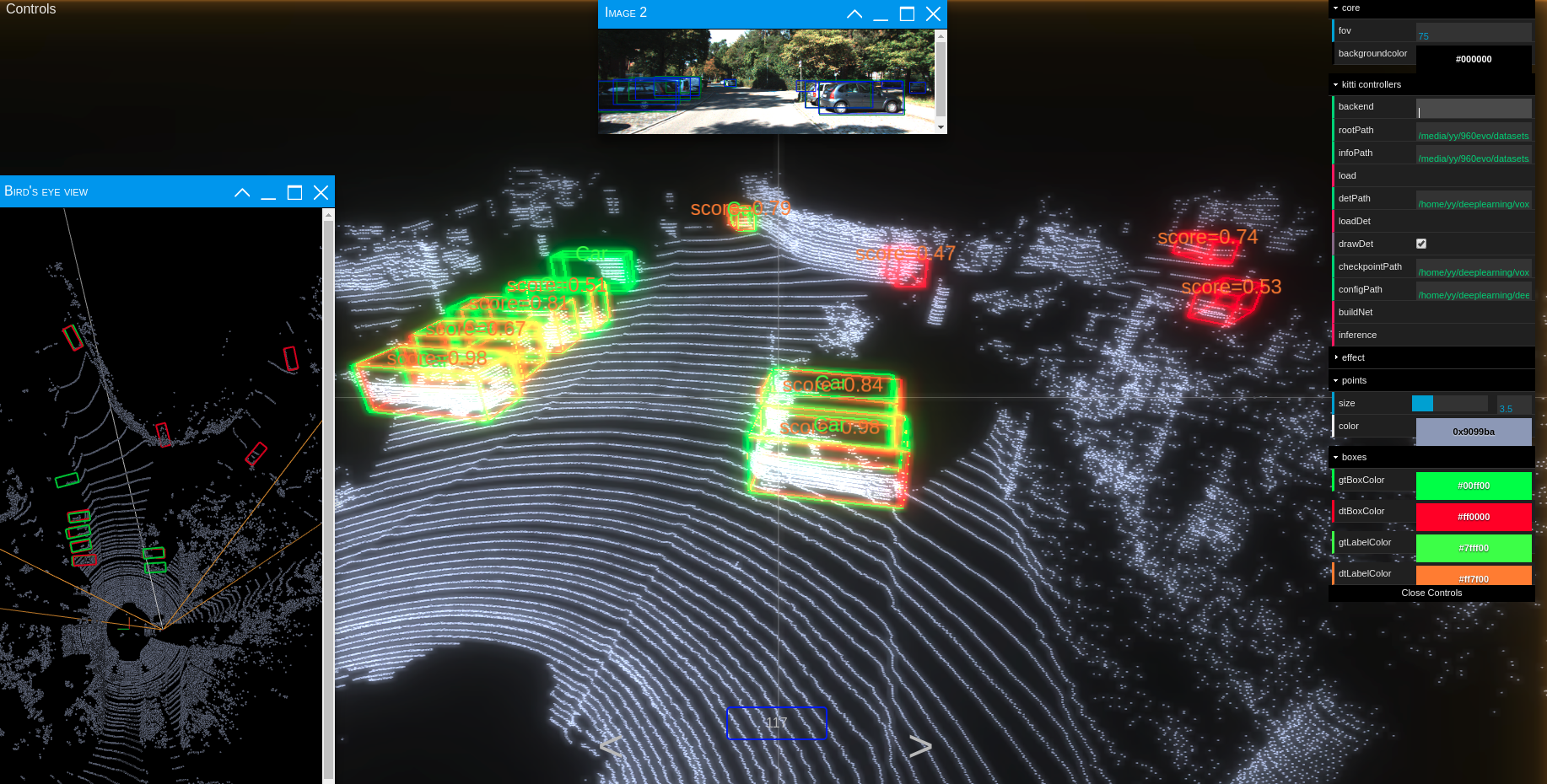
run
python ./kittiviewer/backend/main.py main --port=xxxxin your server/local. -
run
cd ./kittiviewer/frontend && python -m http.serverto launch a local web server. -
open your browser and enter your frontend url (e.g. http://127.0.0.1:8000, default]).
-
input backend url (e.g. http://127.0.0.1:16666)
-
input root path, info path and det path (optional)
-
click load, loadDet (optional), input image index in center bottom of screen and press Enter.
Firstly the load button must be clicked and load successfully.
-
input checkpointPath and configPath.
-
click buildNet.
-
click inference.
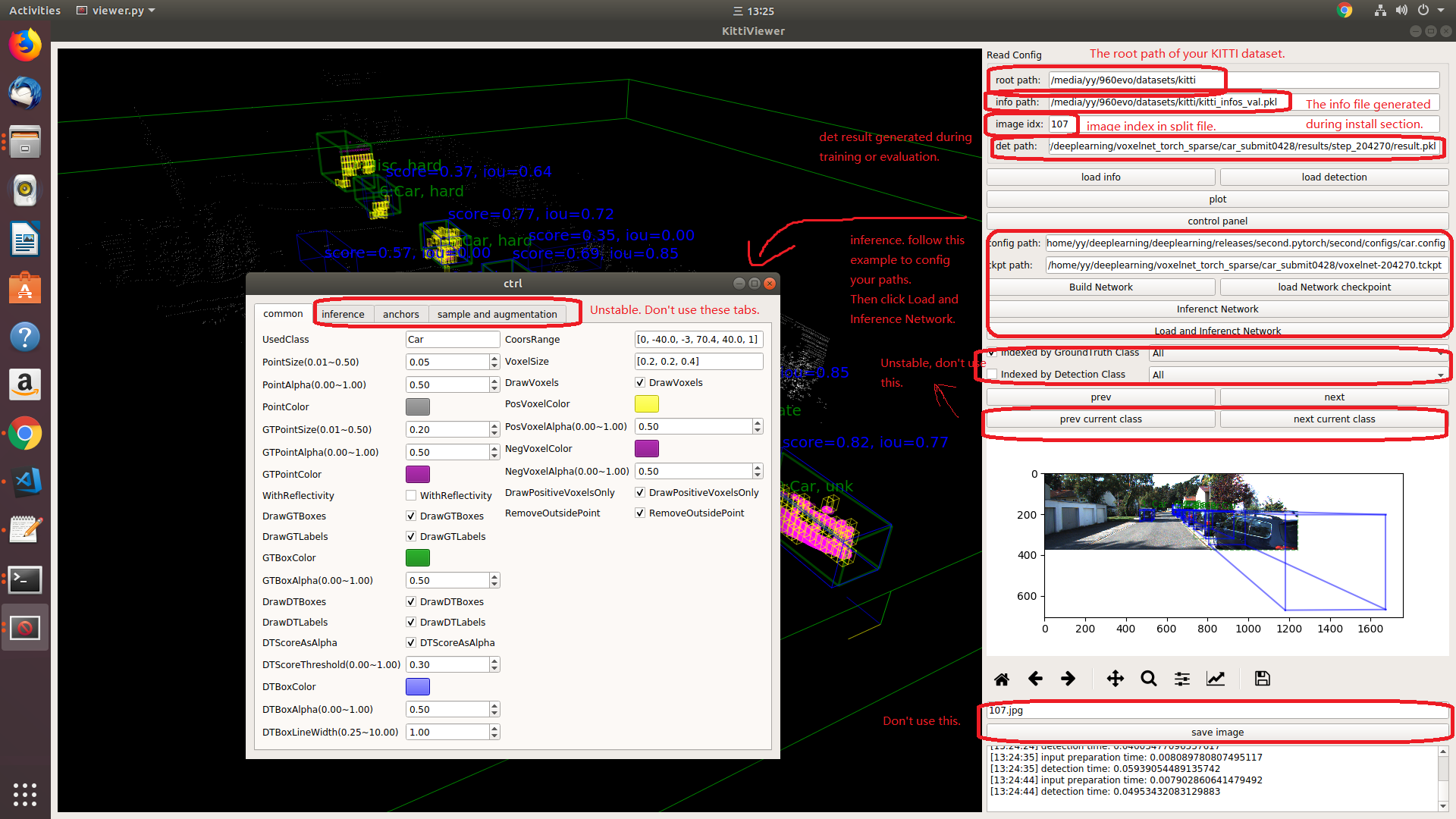
You should use kitti viewer based on pyqt and pyqtgraph to check data before training.
run python ./kittiviewer/viewer.py, check following picture to use kitti viewer:
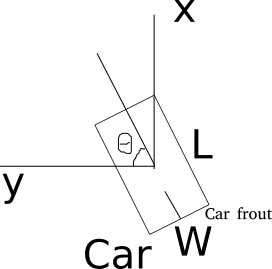
- Kitti lidar box
A kitti lidar box is consist of 7 elements: [x, y, z, w, l, h, rz], see figure.
All training and inference code use kitti box format. So we need to convert other format to KITTI format before training.
- Kitti camera box
A kitti camera box is consist of 7 elements: [x, y, z, l, h, w, ry].