Although QNX has released an official extension for VS Code (QNX Toolkit), that extension only supports QNX SDK 8.0. This leaves the ones unwilling or unable to upgrade with poor tools for interacting with a QNX target. Also, the QNX Toolkit doesn't offer core-dump debugging (for some reason).
This open-source extension gives you the bare minimum, such as a QNX shell, a QNX filesystem explorer and a QNX process list.
For simplicity, this extension assumes you have just a single QNX target you work with.
- QNX Process Explorer
- Filesystem Provider
- Filesystem Explorer
- Context Menu Additions
- QNX Terminal
- Experimental Debugging
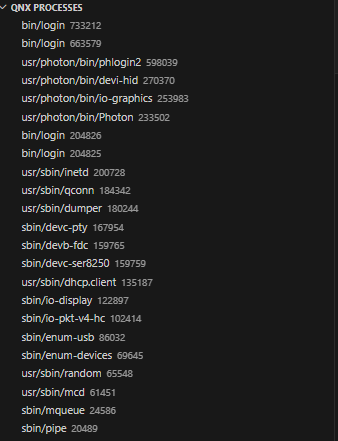
The process explorer lets you see the running processes on the target, and send kill or INT signals to them if needed.
The process explorer is available in the explorer view once the extension is loaded.
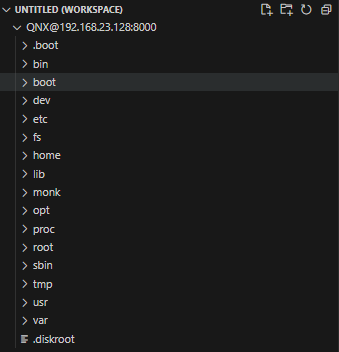
You can add the QNX target file system to your workspace by running the command "Connect to QNX filesystem".
For the ones that don't want to add the QNX filesystem to their workspace, one can do most file operations using the QNX file explorer. The QNX file explorer tries to mimic the regular VSCode filesystem explorer, but because of limitations in the VSCode API, some features are not available, especially drag-and-drop is not supported.
The VSCode filesystem explorer context menu is extended with a "Copy file to QNX target", which will copy the selected file to some directory on the QNX target.
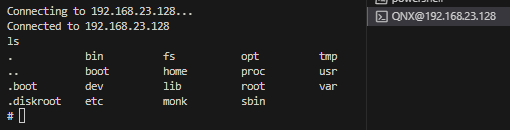
You can spawn a QNX root prompt by running the command "Create QNX terminal" or by selecting the terminal type from the "Terminal" tab.
There are some support for debugging if you have the QNX SDP installed. To enable this, you will need to set the qconn.sdpSearchPath configuration to point to some directory where your QNX SDP is located within. The extension will automatically search subfolders for the right path.
Currently, QNX7.0 and 7.1 from a linux host is mostly supported. Let me know if there are issues.
You will have two new debugging configurations available:
- QNX: Local QNX core dump
- QNX: Remote QNX core dump
The QNX Filesystem Explorer will also feature a "Debug QNX executable" in its context menu, which will allow you to run and debug an executable on the target.
You can also directly debug a QNX core dump from the QNX Filesystem Explorer. It will automatically transfer the file to your host, unzip it (if necessary), resolve dependencies and launch the debugger.
The QNX Process list context menu will also feature a "Attach to QNX process".
When the debugger is launched, the qconn extension will try to resolve the program and the shared library dependencies in the current workspace and in the found SDP paths.
The Local and remote QNX core dump will ask for the location of a core dump file. "remote" will look on the target in the /var/dumps directory by default.
QConn must be running on the target QNX system
This extension contributes the following settings:
qConn.target.host: The hostname or IP of the target QNX system.qConn.target.port: The port of the target QNX system (defaults to 8000).qConn.sdpSearchPaths: A list of paths to search for QNX SDPsqconn.additionalSOLibSearchPaths: A list of paths to search for additional shared objects
The current host and port of QNX can also be set by clicking on the statusbar
Contributions to this extension are much welcome.
To develop and test the extension, the VMWare image downloadable from the QNX website is used. It contains a QNX image v 6.3 running qconn. Thus, the extension is tested with that version.
For performance reasons, the extension tries as much as possible to use the native qconn protocol.
However, given the fact that we can basically spawn a root shell on the target and remote control that, the options are practically limitless as to what can be done :)
The QNX documentation has helped quite a bit with deciphering the output coming from qconn. However, there has also been a lot of guesswork involved with reverse engineering the protocol :)
Connection to qconn is done using the qConn npm package (https://www.npmjs.com/package/qconn). The development of that library goes hand-in-hand with the development of this extension.
Thanks goes out to https://github.com/zayfod/qcl for initial hints on how to interface with qconn.
- Added debugging support
- Initial release