Visual Studio Tools for Apache Cordova allow you to build cross-platform, multi-device hybrid apps based on Apache Cordova. In other tutorials, we’ve shown how to Build a Cordova app for iOS using Parallels so you can use the tools from your Mac. In this tutorial, we will show how to speed up Android emulation by running the Android emulator on OSX rather than inside Parallels running Windows using a SSH tunnel. The instructions here use the Android emulator as an example, but you should be able to do this with other emulators like GenyMotion as well.
Most of the steps in this section show how to install and configure Java and the Android SDK on your Mac. If you have already installed and configured Java and the Android SDK on your Mac, all you need to do is enable Remote Login in the OSX Sharing settings, and then you can skip to the Windows setup. If not, follow the complete step-by-step instructions in this section.
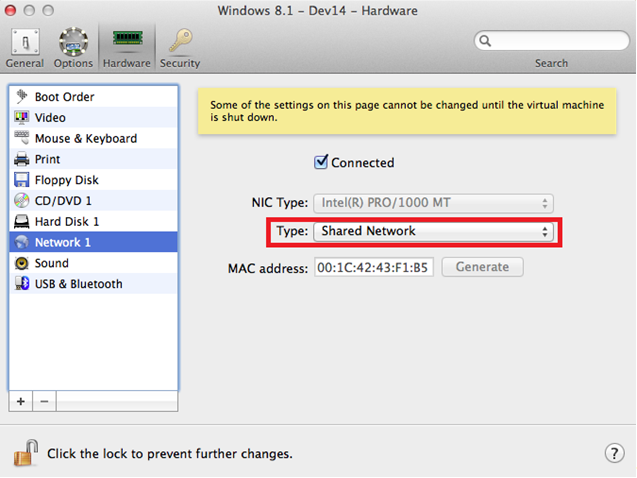
First, make sure that you have configured your Parallels VM setup to run in Shared Networking mode (it is the default setting).
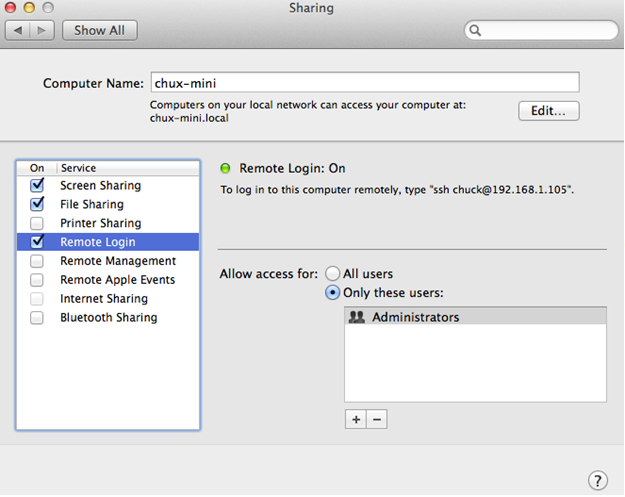
Because you will be setting up an SSH tunnel, you will need to enable SSH logins for your Mac. Start the Settings app then go to Sharing and Check Remote Login.
Next, install and configure Java and the Android SDK.
-
Download and install JDK 7 for Mac. 2. Download the Android SDK tools for Mac.
Note: You can choose the download under Get the SDK for an existing IDE if you don’t intend to use the Android IDE directly.
-
Unzip the Android tools.
In this tutorial, we will assume you’ve unzipped it to your Documents folder (~/Documents/android-sdk-macosx).
-
Open the Terminal app and type the following command:
~/Documents/android-sdk-macosx/tools/tools/android -
Deselect anything you do not want to install, but make sure the following are selected:
-
Android 4.4.2 (API 19)
-
Extras/Intel x86 Emulator Accelerator (HAXM installer)
-
-
Choose Install packages…
-
After the installation has completed, make sure you close the Android SDK Manager.
-
Install the Intel HAXM driver.
-
In Finder, go to Documents, android-sdk-macosx, extras, Intel, and then Hardware_Accelerated_Execution_Manager.
-
Open
IntelHAXM_x.x.x.dmg. -
Open the
.mpkgfile in the folder window that appears. -
Follow the installation instructions.
-
-
In the Terminal app, type:
~/Documents/android-sdk-macosx/tools/android avd -
Create an AVD image, start it, and verify that it runs. Make sure to select the following options:
-
Set CPU/ABI to an Intel Atom (x86) system image.
-
Select Use Host GPU.
-
To start up your Android emulator images in the future, use the android avd command.
Next, start Parallels and configure Windows.
-
Download plink from the Putty website and place it in a folder. Next, you will create two scripts. The scripts will shut down the “Android Debug Bridge (adb)” if it is running and setup an SSH tunnel from Windows to OSX.
-
For the first script, create a new file in this same folder called “connect-to-mac.cmd” and copy the following script into the file.
@echo off adb.exe kill-server plink -L 5554:localhost:5554 -L 5555:localhost:5555 -m mac-script.sh -l johndoe123 -pw johnspassword johnsmac.microsoft.com -
In the preceding script, replace:
-
jondoe123with your Mac user name -
johnspasswordwith your Mac password -
johnsmac.microsoft.comwith either the IP address or the host name of your Mac
-
For the second script, create another file in this same folder called
mac-script.shand copy the following script into the file:#!/bin/sh ~/Documents/android-sdk-macosx/platform-tools/adb kill-server read -p "Press any key to terminate SSH tunnel" anykey -
In the preceding script, replace ``~/Documents/android-sdk-macosx` with the location where you unzipped the Android SDK.
Windows is now configured and ready to go.
Follow these instructions each time you startup your Mac and Parallels.
-
In OSX, open the Terminal app and type:
~/Documents/android-sdk-macosx/tools/android avd -
Use the AVD Manager to start the Android emulator that you want to use.
-
On Windows in Parallels, take the following steps:
- Go to the location where you created
connect-to-mac.cmd. - Open
connect-to-mac.cmd. - Leave the window open!
- Go to the location where you created
After you do this, you should connect any attached Android devices to the Mac side not the Windows side if prompted by Parallels.
That’s it! You can now start Visual Studio and run your app on the Android Emulator in the same way that you normally run it.