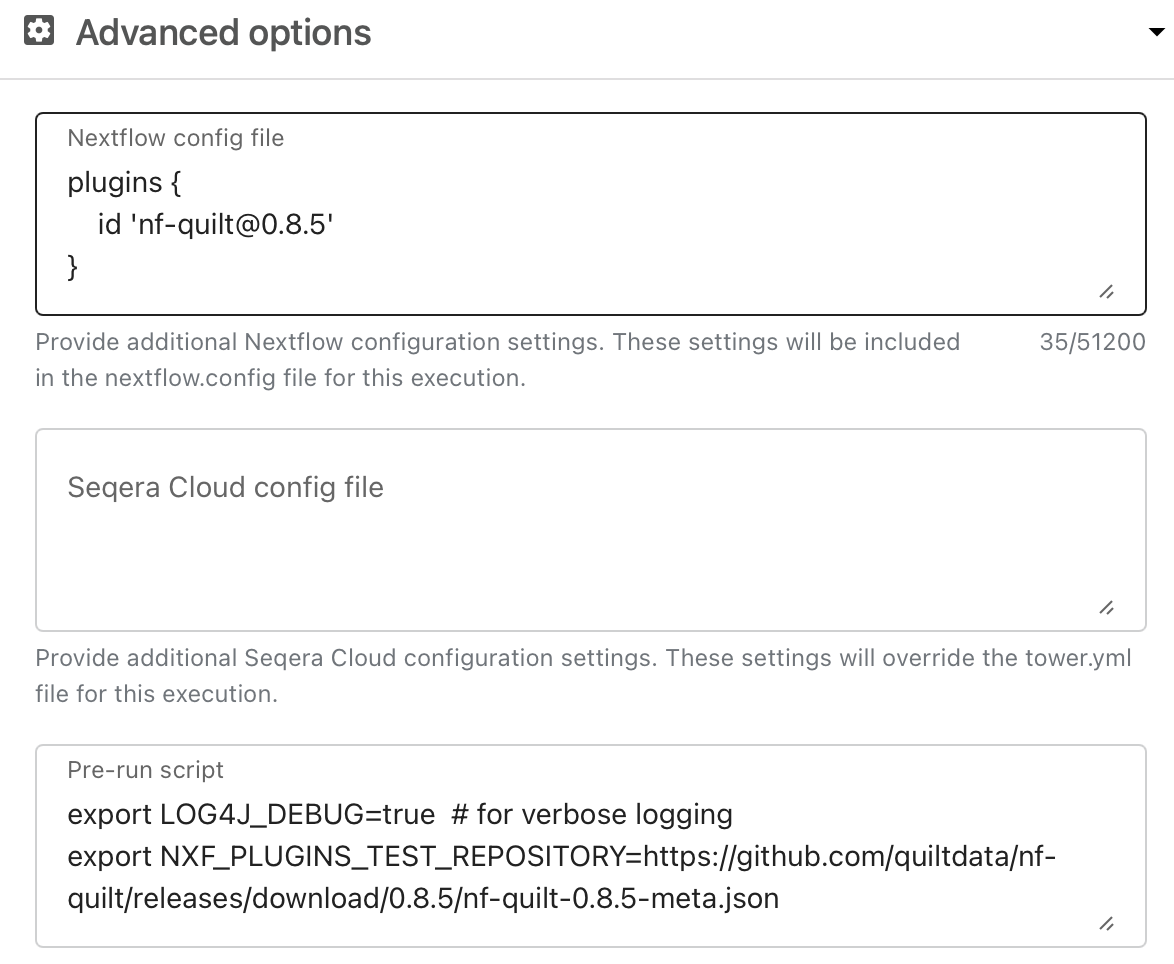
Occasionally we will release beta versions of the plugin that are not yet available in the Nextflow plugin registry. You can help test these versions as follows:
- Set the
NXF_PLUGINS_TEST_REPOSITORYenvironment variable to the URL of the plugin's metadata file - Specify the plugin version in the
pluginssection of yournextflow.configfile
From the command-line, do, e.g.:
export LOG4J_DEBUG=true # for verbose logging
export NXF_PLUGINS_TEST_REPOSITORY=https://github.com/quiltdata/nf-quilt/releases/download/0.9.0/nf-quilt-0.9.0-meta.json
nextflow run main.nf -plugins [email protected]For Tower, you set the environment variables in the "Pre-run script".
If you want to use edge versions of nf-quilt, you must run it with a development
version of nextflow. The simplest way to do that is to pull them both directly
from GitHub:
git clone https://github.com/nextflow.io/nextflow.git
git clone https://github.com/quiltdata/nf-quilt.git
cd ./nf-quiltIf this is your first time using Nextflow, you may also need to install a recent version of Java for your platform. Nextflow itself will take care of all the other dependencies.
You can verify and compile Nextflow with:
make nextflowTo quickly run nf-quilt from this GitHub repository:
# install and compiles dependencies, then test
make test-all
# create "test/hurdat" package on s3://$WRITE_BUCKET
make pkg-test WRITE_BUCKET=your-writeablebucketThis ensures you have properly installed Nextflow and configured your local <--markdownlint-disable-next-line MD041--> AWS credentials.
You can also set WRITE_BUCKET and other parameters in a .env file in the
project root, and they will be automatically read by the Makefile.
From inside the nf-quilt directory, call ./launch.sh with a path to your
pipeline.
For example, with a standard nf-core pipeline like sarek:
./launch.sh run nf-core/sarek -profile test,docker -plugins nf-quilt --outdir "quilt+s3://bucket#package=nf-quilt/sarek"Otherwise, replace nf-core/sarek with the local path to your pipeline's .nf
file (be sure to rename the outdir parameter if you use different convention).
For example:
./launch.sh run ./main.nf -profile standard -plugins $(PROJECT) --outdir "quilt+s3://bucket#package=test/hurdat"You can cleanly compile and run all unit tests with:
make checkTo show the output of the tests, use:
make verifyTo fast-fail on the first failing test, use:
make fastIf your system is properly configured, use make publish to package, upload,
and publish the plugin.
Otherwise, follow these steps:
-
Create a file named
gradle.propertiesin the user's home (NOT project) directory containing the following attributes:github_organization: the GitHub organisation where the plugin repository is hosted.github_username: The GitHub username granting access to the plugin repository.github_access_token: The GitHub access token required to upload and commit changes to the plugin repository.github_commit_email: The email address associated with your GitHub account.
-
Use the following command to package and create a release for your plugin on GitHub:
./gradlew :plugins:nf-quilt:upload
-
Fork the nextflow-io/plugins repository to one you can write to
-
Use the following command to publish your plugin to your fork:
./gradlew :plugins:publishIndex
-
Create a pull request to push your changes back to nextflow-io/plugins