B-Trees are version of 2-3 trees, which are self-balancing. They are used to improve Disk reads and have a complexity of O(log(n)), for every tree operations.The number of Childrens/Keys a particular node has, is determined by the Branching Factor/Degree of that tree. B-Trees will always have sorted keys.
- Branching Factor(B) / Degree (D): If B = n, n <= Children per Node < 2(n), n-1 <= Keys per Node < 2(n) - 1
Properties
- Worst/Average case performance for all operations O(log n)
- Space complexity O(n)
Sources to read:
An AVL Tree is a self-balancing binary search tree. The heights of any two sibling nodes must differ by at most one; the tree may rebalance itself after insertion or deletion to uphold this property.
Properties
- Worst/Average time complexity for basic operations: O(log n)
- Worst/Average space complexity: O(n)
Sources to read:
A linked list is also a linear data structure, and each element in the linked list is actually a separate object while all the objects are linked together by the reference filed in each element. In a doubly linked list, each node contains, besides the next node link, a second link field pointing to the previous node in the sequence. The two links may be called next and prev. And many modern operating systems use doubly linked lists to maintain references to active processes, threads and other dynamic objects.
Properties
- Indexing O(n)
- Insertion O(1)
- Beginning O(1)
- Middle (Indexing time+O(1))
- End O(n)
- Deletion O(1)
- Beginning O(1)
- Middle (Indexing time+O(1))
- End O(n)
- Search O(n)
Source to read:
From Wikipedia, a stack is an abstract data type that serves as a collection of elements, with two main principal operations, Push and Pop.
Properties
- Push O(1)
- Pop head.data O(1) tail.data O(n)
- Peek O(1)
Source to read:
When backed by a vector (or other contiguous data structure), a stack can keep tabs of its size and change that size.
Properties
- Push O(1)
- Pop O(1)
- Peek O(1)
Sources to read:
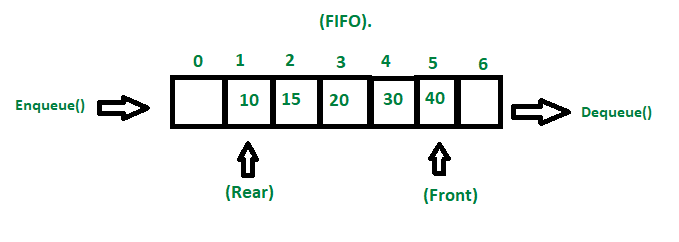
- A queue is a
lineardata structure that is open at both ends with operations performed in First in first out (FIFO) or Last in Last out (LILO) - A queue is considered a list where all additions are made on one end and all deletions on the opposite end to adhere to the FIFO principle
- The
frontis considered the location where the first entry will be removed from the queue - The
rearis considered the location of the latest entry and will be the last entry removed from the queue
Enqueue(): items are added to the rear, returns the value of the node or item addedDequeue(): items are removed from the front, returns the value of the node or item removedPeek(): returns the value of the front, throws an exception if emptyisEmpty(): check if there is a node or item in queue returns a boolean
- If the underlying data structure of a queue is a linked list:
- enqueue: O(1)
- peek: O(1)
- dequeue: O(1)*
- search O(n)
*Depends on capacity, if capacity is gone over for vector it is reallocated to different point in memory which can reduce efficiency