Scans ethereum for ERC-721 Non-Fungible Tokens and replicates all assets by saving them on nft.storage.
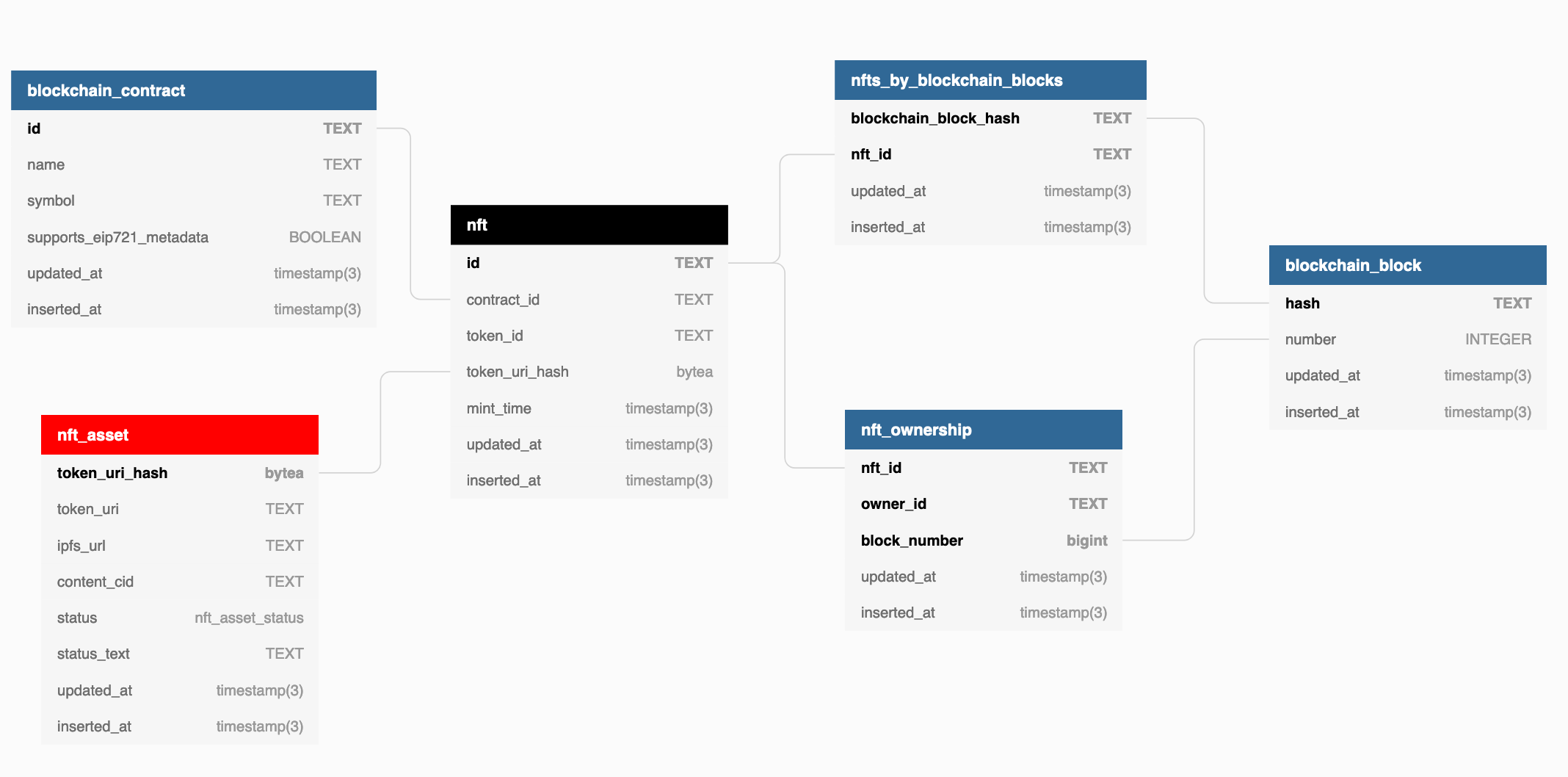
Module ingest.js continuously runs on heroku pulling data from the EIP721 Subgraph and writing it into Postgres DB on Heroku through hasura graphql-engine.
Process runs two concurrent tasks:
- Reader task pulls new data in batches from EIP721 Subgraph and queues it in memory for writer to flush.
- Writer pull one nft from graph at a time and writes it into Postgres DB through hasura graphql-engine.
Postgres SQL function exposed as GraphQL mutation does most of the heavy lifting. It takes apart received data and distributes it across relevant tables.
Module analyze.js continuously runs on heroku pulling queued nft_asset records (created by ingestion) and performing analysis. Every pulled nft_asset is updated to either
Linkedstate in which it is linked with correspondingmetadataandresourcesrecords.*Failedstate with information about the failure.
Analyzer performs following tasks:
- Parse
token_urias a valid URL. - Infer
ipfs://URL from the parsedtoken_uri, by recognizing gateway URLs (e.g. https://ipfs.io/ipfs/Qm..) and malformed ipfs:// URLs. - Fetch content for the resource. From IPFS if ipfs:// URL can be inferred or from web otherwise.
- Parse content as JSON.
- Extract all the URLS from the (metadata) JSON.
- Derive CID from content.
- Submit content pin request.
If analyzer succesfully completes above steps it will link nft_asset with metadata, it's content and extracted resources.
Otherwise nft_asset status is updated to *Failed state with a corresponding failure attached.
Moudle pin.js continuously runs on heroku pulling queued resource records (created by analyzer) and attempts to pin their content on IPFS.
It performs following tasks:
- Parse
urias a valid URL. - Infer
ipfs://URL from the parseduri, by recognizing gateway URLs (e.g. https://ipfs.io/ipfs/Qm..) and malformed ipfs:// URLs. - If IPFS URL is derived submit a pin request to an IPFS cluster.
- If IPFS URL can not be derived, fetch resource from the web and pin by uploading to IPFS Cluster.
If all tasks succeed it will link resource with corresponding content and pin records.
Otherwise resource status is updated to *Failed state with acorresponding failure attached.