This <- command basically takes anything on the right hand side
and puts it into the left hand side. Like an equation. This is
called variable assignment.
df <- read.csv('train.csv')head checks only the first few rows of the dataset.
head(df)## PassengerId Survived Pclass
## 1 1 0 3
## 2 2 1 1
## 3 3 1 3
## 4 4 1 1
## 5 5 0 3
## 6 6 0 3
## Name Sex Age SibSp
## 1 Braund, Mr. Owen Harris male 22 1
## 2 Cumings, Mrs. John Bradley (Florence Briggs Thayer) female 38 1
## 3 Heikkinen, Miss. Laina female 26 0
## 4 Futrelle, Mrs. Jacques Heath (Lily May Peel) female 35 1
## 5 Allen, Mr. William Henry male 35 0
## 6 Moran, Mr. James male NA 0
## Parch Ticket Fare Cabin Embarked
## 1 0 A/5 21171 7.2500 S
## 2 0 PC 17599 71.2833 C85 C
## 3 0 STON/O2. 3101282 7.9250 S
## 4 0 113803 53.1000 C123 S
## 5 0 373450 8.0500 S
## 6 0 330877 8.4583 Q
dim checks the dimensions of the dataset (number of rows and
number of columns, in that order).
dim(df)## [1] 891 12
str checks the structure of the dataset, showing what the df
object is, what each item (or column) in the dataset is, such as
numeric, factor, etc. This is pretty useful as it can give you a
quick overview of what the variables have been classified as and
if there are any problems.
str(df)## 'data.frame': 891 obs. of 12 variables:
## $ PassengerId: int 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 ...
## $ Survived : int 0 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 1 1 ...
## $ Pclass : int 3 1 3 1 3 3 1 3 3 2 ...
## $ Name : Factor w/ 891 levels "Abbing, Mr. Anthony",..: 109 191 358 277 16 559 520 629 416 581 ...
## $ Sex : Factor w/ 2 levels "female","male": 2 1 1 1 2 2 2 2 1 1 ...
## $ Age : num 22 38 26 35 35 NA 54 2 27 14 ...
## $ SibSp : int 1 1 0 1 0 0 0 3 0 1 ...
## $ Parch : int 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 2 0 ...
## $ Ticket : Factor w/ 681 levels "110152","110413",..: 525 596 662 50 473 276 86 396 345 133 ...
## $ Fare : num 7.25 71.28 7.92 53.1 8.05 ...
## $ Cabin : Factor w/ 148 levels "","A10","A14",..: 1 83 1 57 1 1 131 1 1 1 ...
## $ Embarked : Factor w/ 4 levels "","C","Q","S": 4 2 4 4 4 3 4 4 4 2 ...
class checks only the type of object you are asking, not the
contents (unlike str).
class(df)## [1] "data.frame"
summary is an extremely useful command to check the basic
descriptive statistics (mean, median, range, count for factors).
I usually use this anytime I want to quickly look at my dataset,
to get a sense of it.
summary(df)## PassengerId Survived Pclass
## Min. : 1.0 Min. :0.0000 Min. :1.000
## 1st Qu.:223.5 1st Qu.:0.0000 1st Qu.:2.000
## Median :446.0 Median :0.0000 Median :3.000
## Mean :446.0 Mean :0.3838 Mean :2.309
## 3rd Qu.:668.5 3rd Qu.:1.0000 3rd Qu.:3.000
## Max. :891.0 Max. :1.0000 Max. :3.000
##
## Name Sex Age
## Abbing, Mr. Anthony : 1 female:314 Min. : 0.42
## Abbott, Mr. Rossmore Edward : 1 male :577 1st Qu.:20.12
## Abbott, Mrs. Stanton (Rosa Hunt) : 1 Median :28.00
## Abelson, Mr. Samuel : 1 Mean :29.70
## Abelson, Mrs. Samuel (Hannah Wizosky): 1 3rd Qu.:38.00
## Adahl, Mr. Mauritz Nils Martin : 1 Max. :80.00
## (Other) :885 NA's :177
## SibSp Parch Ticket Fare
## Min. :0.000 Min. :0.0000 1601 : 7 Min. : 0.00
## 1st Qu.:0.000 1st Qu.:0.0000 347082 : 7 1st Qu.: 7.91
## Median :0.000 Median :0.0000 CA. 2343: 7 Median : 14.45
## Mean :0.523 Mean :0.3816 3101295 : 6 Mean : 32.20
## 3rd Qu.:1.000 3rd Qu.:0.0000 347088 : 6 3rd Qu.: 31.00
## Max. :8.000 Max. :6.0000 CA 2144 : 6 Max. :512.33
## (Other) :852
## Cabin Embarked
## :687 : 2
## B96 B98 : 4 C:168
## C23 C25 C27: 4 Q: 77
## G6 : 4 S:644
## C22 C26 : 3
## D : 3
## (Other) :186
If you want to see specific columns or rows, you can use the [
command. The first number is the row [row, ], and the second
number is the column [, column]. So together: [row, column].
df[1:2, 1:5]## PassengerId Survived Pclass
## 1 1 0 3
## 2 2 1 1
## Name Sex
## 1 Braund, Mr. Owen Harris male
## 2 Cumings, Mrs. John Bradley (Florence Briggs Thayer) female
Also, numbers can be put together like so:
1:10## [1] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
-1:10## [1] -1 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
1:-10## [1] 1 0 -1 -2 -3 -4 -5 -6 -7 -8 -9 -10
-10:1## [1] -10 -9 -8 -7 -6 -5 -4 -3 -2 -1 0 1
In dataframes, a negative number means remove:
df[1:2, ]## PassengerId Survived Pclass
## 1 1 0 3
## 2 2 1 1
## Name Sex Age SibSp
## 1 Braund, Mr. Owen Harris male 22 1
## 2 Cumings, Mrs. John Bradley (Florence Briggs Thayer) female 38 1
## Parch Ticket Fare Cabin Embarked
## 1 0 A/5 21171 7.2500 S
## 2 0 PC 17599 71.2833 C85 C
df[1:2, -2:-4]## PassengerId Sex Age SibSp Parch Ticket Fare Cabin Embarked
## 1 1 male 22 1 0 A/5 21171 7.2500 S
## 2 2 female 38 1 0 PC 17599 71.2833 C85 C
You can use strings (real words) to select a specific column.
df[1:2, 'Age']## [1] 22 38
You can use the combine command c() to put two strings or
numbers together.
df[c(1, 4), c('Age', 'Sex')]## Age Sex
## 1 22 male
## 4 35 female
You can also subset the data using these commands:
head(df[df$Sex == 'male', ])## PassengerId Survived Pclass Name Sex Age
## 1 1 0 3 Braund, Mr. Owen Harris male 22
## 5 5 0 3 Allen, Mr. William Henry male 35
## 6 6 0 3 Moran, Mr. James male NA
## 7 7 0 1 McCarthy, Mr. Timothy J male 54
## 8 8 0 3 Palsson, Master. Gosta Leonard male 2
## 13 13 0 3 Saundercock, Mr. William Henry male 20
## SibSp Parch Ticket Fare Cabin Embarked
## 1 1 0 A/5 21171 7.2500 S
## 5 0 0 373450 8.0500 S
## 6 0 0 330877 8.4583 Q
## 7 0 0 17463 51.8625 E46 S
## 8 3 1 349909 21.0750 S
## 13 0 0 A/5. 2151 8.0500 S
head(df[c(df$Sex == 'male', df$Age < 40), ])## PassengerId Survived Pclass Name Sex Age
## 1 1 0 3 Braund, Mr. Owen Harris male 22
## 5 5 0 3 Allen, Mr. William Henry male 35
## 6 6 0 3 Moran, Mr. James male NA
## 7 7 0 1 McCarthy, Mr. Timothy J male 54
## 8 8 0 3 Palsson, Master. Gosta Leonard male 2
## 13 13 0 3 Saundercock, Mr. William Henry male 20
## SibSp Parch Ticket Fare Cabin Embarked
## 1 1 0 A/5 21171 7.2500 S
## 5 0 0 373450 8.0500 S
## 6 0 0 330877 8.4583 Q
## 7 0 0 17463 51.8625 E46 S
## 8 3 1 349909 21.0750 S
## 13 0 0 A/5. 2151 8.0500 S
However, these are a bit complicated, and hard to read! There is a better way. Install and/or load these packages:
install.packages('dplyr')
install.packages('tidyr')library(dplyr)
library(tidyr)To do the same as the above, use:
df %>%
filter(Sex == 'male', Age < 40) %>%
## You can keep chaining
tbl_df() %>%
## ... and chaining
select(Sex, Age, Pclass, Parch) %>%
## ... and chaining
summary()## Sex Age Pclass Parch
## female: 0 Min. : 0.42 Min. :1.000 Min. :0.0000
## male :344 1st Qu.:19.00 1st Qu.:2.000 1st Qu.:0.0000
## Median :25.00 Median :3.000 Median :0.0000
## Mean :24.28 Mean :2.494 Mean :0.2878
## 3rd Qu.:31.00 3rd Qu.:3.000 3rd Qu.:0.0000
## Max. :39.00 Max. :3.000 Max. :5.0000
The extremely useful %>% chain, or pipe command, is just like in
the shell/terminal. It takes the output of the previous command
and inputs it into the next command. Otherwise, without the %>%
pipe, it looks like:
summary(select(tbl_df(filter(df, Sex == 'male', Age < 40)), Sex, Age, Pclass, Parch))## Sex Age Pclass Parch
## female: 0 Min. : 0.42 Min. :1.000 Min. :0.0000
## male :344 1st Qu.:19.00 1st Qu.:2.000 1st Qu.:0.0000
## Median :25.00 Median :3.000 Median :0.0000
## Mean :24.28 Mean :2.494 Mean :0.2878
## 3rd Qu.:31.00 3rd Qu.:3.000 3rd Qu.:0.0000
## Max. :39.00 Max. :3.000 Max. :5.0000
The pipe does this by basically making the output be named ., so
really, the pipe is doing this:
df %>% select(., Fare, Sex) %>%
filter(., Sex == 'male') %>%
select(., Fare) %>%
round(., 3) %>%
head(.)## Fare
## 1 7.250
## 2 8.050
## 3 8.458
## 4 51.862
## 5 21.075
## 6 8.050
tbl_df makes the dataframe also a tbl object, so that the outout
can be printed easily. The verbs for dplyr are:
- select
- filter
- mutate
- summarise
- arrange
- group_by
For more explanation of dplyr, check the documentation:
https://github.com/hadley/dplyr or run this command
vignette('introduction', package = 'dplyr')
The tbl_df() function makes the printing prettier.
df <- tbl_df(df)
df %>% summary## PassengerId Survived Pclass
## Min. : 1.0 Min. :0.0000 Min. :1.000
## 1st Qu.:223.5 1st Qu.:0.0000 1st Qu.:2.000
## Median :446.0 Median :0.0000 Median :3.000
## Mean :446.0 Mean :0.3838 Mean :2.309
## 3rd Qu.:668.5 3rd Qu.:1.0000 3rd Qu.:3.000
## Max. :891.0 Max. :1.0000 Max. :3.000
##
## Name Sex Age
## Abbing, Mr. Anthony : 1 female:314 Min. : 0.42
## Abbott, Mr. Rossmore Edward : 1 male :577 1st Qu.:20.12
## Abbott, Mrs. Stanton (Rosa Hunt) : 1 Median :28.00
## Abelson, Mr. Samuel : 1 Mean :29.70
## Abelson, Mrs. Samuel (Hannah Wizosky): 1 3rd Qu.:38.00
## Adahl, Mr. Mauritz Nils Martin : 1 Max. :80.00
## (Other) :885 NA's :177
## SibSp Parch Ticket Fare
## Min. :0.000 Min. :0.0000 1601 : 7 Min. : 0.00
## 1st Qu.:0.000 1st Qu.:0.0000 347082 : 7 1st Qu.: 7.91
## Median :0.000 Median :0.0000 CA. 2343: 7 Median : 14.45
## Mean :0.523 Mean :0.3816 3101295 : 6 Mean : 32.20
## 3rd Qu.:1.000 3rd Qu.:0.0000 347088 : 6 3rd Qu.: 31.00
## Max. :8.000 Max. :6.0000 CA 2144 : 6 Max. :512.33
## (Other) :852
## Cabin Embarked
## :687 : 2
## B96 B98 : 4 C:168
## C23 C25 C27: 4 Q: 77
## G6 : 4 S:644
## C22 C26 : 3
## D : 3
## (Other) :186
df %>%
## subset the data by SibSp
filter(SibSp >= 2) %>%
## select only the relevant columns
select(Age, Sex, Survived, Cabin, Fare) %>%
## order the data (in descending) by Age
arrange(Age) %>%
## create a new column
mutate(d.Fare = cut(Fare, 3, labels = c('Low', 'Middle', 'High')))## Source: local data frame [74 x 6]
##
## Age Sex Survived Cabin Fare d.Fare
## 1 0.75 female 1 19.2583 Low
## 2 0.75 female 1 19.2583 Low
## 3 1.00 male 0 39.6875 Low
## 4 1.00 male 1 F4 39.0000 Low
## 5 1.00 male 0 46.9000 Low
## 6 2.00 male 0 21.0750 Low
## 7 2.00 male 0 29.1250 Low
## 8 2.00 female 0 31.2750 Low
## 9 2.00 female 0 27.9000 Low
## 10 2.00 male 0 39.6875 Low
## .. ... ... ... ... ... ...
To do even more interesting things, we can combine the dplyr package with the tidyr package. The tidyr has basically two main verbs:
- gather
- spread
df %>%
filter(SibSp >= 2) %>%
select(Age, Sex, Survived, Cabin, Fare) %>%
## convert the data into a very long format
gather(Measure, Value, -Sex) %>%
## make each summarise command run on the groups Sex and Measure
group_by(Sex, Measure) %>%
## create summary statistics, in this cause the sample in each group
## (Sex and Measure)
summarise(n = n()) %>%
## convert the data into a wide format
spread(Sex, n)## Warning: attributes are not identical across measure variables; they will
## be dropped
## Source: local data frame [4 x 3]
##
## Measure female male
## 1 Age 34 40
## 2 Survived 34 40
## 3 Cabin 34 40
## 4 Fare 34 40
Check the content again:
df %>% summary## PassengerId Survived Pclass
## Min. : 1.0 Min. :0.0000 Min. :1.000
## 1st Qu.:223.5 1st Qu.:0.0000 1st Qu.:2.000
## Median :446.0 Median :0.0000 Median :3.000
## Mean :446.0 Mean :0.3838 Mean :2.309
## 3rd Qu.:668.5 3rd Qu.:1.0000 3rd Qu.:3.000
## Max. :891.0 Max. :1.0000 Max. :3.000
##
## Name Sex Age
## Abbing, Mr. Anthony : 1 female:314 Min. : 0.42
## Abbott, Mr. Rossmore Edward : 1 male :577 1st Qu.:20.12
## Abbott, Mrs. Stanton (Rosa Hunt) : 1 Median :28.00
## Abelson, Mr. Samuel : 1 Mean :29.70
## Abelson, Mrs. Samuel (Hannah Wizosky): 1 3rd Qu.:38.00
## Adahl, Mr. Mauritz Nils Martin : 1 Max. :80.00
## (Other) :885 NA's :177
## SibSp Parch Ticket Fare
## Min. :0.000 Min. :0.0000 1601 : 7 Min. : 0.00
## 1st Qu.:0.000 1st Qu.:0.0000 347082 : 7 1st Qu.: 7.91
## Median :0.000 Median :0.0000 CA. 2343: 7 Median : 14.45
## Mean :0.523 Mean :0.3816 3101295 : 6 Mean : 32.20
## 3rd Qu.:1.000 3rd Qu.:0.0000 347088 : 6 3rd Qu.: 31.00
## Max. :8.000 Max. :6.0000 CA 2144 : 6 Max. :512.33
## (Other) :852
## Cabin Embarked
## :687 : 2
## B96 B98 : 4 C:168
## C23 C25 C27: 4 Q: 77
## G6 : 4 S:644
## C22 C26 : 3
## D : 3
## (Other) :186
Compare the means of continuous variables of those who survived and those who didn't.
prep.table <- df %>%
select(Survived, Age, Pclass, SibSp, Parch, Fare) %>%
gather(Measure, Value, -Survived) %>%
group_by(Survived, Measure) %>%
## remove missing values
na.omit() %>%
## create a summary statistic (means)
summarise(mean = mean(Value) %>% round(2)) %>%
spread(Survived, mean)
prep.table## Source: local data frame [5 x 3]
##
## Measure 0 1
## 1 Age 30.63 28.34
## 2 Pclass 2.53 1.95
## 3 SibSp 0.55 0.47
## 4 Parch 0.33 0.46
## 5 Fare 22.12 48.40
This can be created into a markdown table, so that it can be
easily put into a manuscript or report. A very useful package is
called pander which allows you to create markdown tables.
install.packages('pander')library(pander)
prep.table %>% pander(style = 'rmarkdown')| Measure | 0 | 1 |
|---|---|---|
| Age | 30.63 | 28.34 |
| Pclass | 2.53 | 1.95 |
| SibSp | 0.55 | 0.47 |
| Parch | 0.33 | 0.46 |
| Fare | 22.12 | 48.4 |
There is also join commands from dplyr:
- left_join
- outer_join
- inner_join
- anti_join
Exact code used in the workshop
ds <- df
ds %>% select(., Sex, Cabin, Fare) %>%
filter(., Sex == 'female', Fare > 10)## Source: local data frame [250 x 3]
##
## Sex Cabin Fare
## 1 female C85 71.2833
## 2 female C123 53.1000
## 3 female 11.1333
## 4 female 30.0708
## 5 female G6 16.7000
## 6 female C103 26.5500
## 7 female 16.0000
## 8 female 18.0000
## 9 female 21.0750
## 10 female 31.3875
## .. ... ... ...
filter(select(ds, Sex, Cabin, Fare),
Sex == 'female')## Source: local data frame [314 x 3]
##
## Sex Cabin Fare
## 1 female C85 71.2833
## 2 female 7.9250
## 3 female C123 53.1000
## 4 female 11.1333
## 5 female 30.0708
## 6 female G6 16.7000
## 7 female C103 26.5500
## 8 female 7.8542
## 9 female 16.0000
## 10 female 18.0000
## .. ... ... ...
ds %>%
select(Sex, Cabin, Fare) %>%
mutate(newcol = 10 * Fare) %>%
arrange(Fare)## Source: local data frame [891 x 4]
##
## Sex Cabin Fare newcol
## 1 male 0 0
## 2 male B94 0 0
## 3 male 0 0
## 4 male 0 0
## 5 male 0 0
## 6 male 0 0
## 7 male 0 0
## 8 male 0 0
## 9 male 0 0
## 10 male 0 0
## .. ... ... ... ...
ds %>%
select(Sex, Age, Fare) %>%
group_by(Sex) %>%
na.omit() %>%
summarise(n = n(),
mean = mean(Age))## Source: local data frame [2 x 3]
##
## Sex n mean
## 1 female 261 27.91571
## 2 male 453 30.72664
Remove a column using the - sign.
ds %>% select(-Age)## Source: local data frame [891 x 11]
##
## PassengerId Survived Pclass
## 1 1 0 3
## 2 2 1 1
## 3 3 1 3
## 4 4 1 1
## 5 5 0 3
## 6 6 0 3
## 7 7 0 1
## 8 8 0 3
## 9 9 1 3
## 10 10 1 2
## .. ... ... ...
## Variables not shown: Name (fctr), Sex (fctr), SibSp (int), Parch (int),
## Ticket (fctr), Fare (dbl), Cabin (fctr), Embarked (fctr)
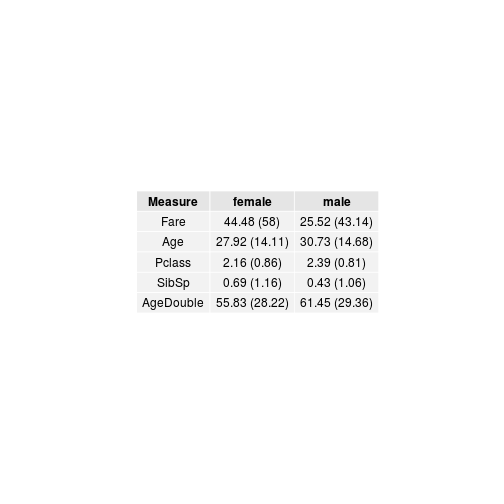
prep.table2 <- ds %>%
select(Sex, Fare, Age, Pclass, SibSp) %>%
mutate(AgeDouble = Age * 2) %>%
gather(Measure, Value, -Sex) %>%
na.omit() %>%
group_by(Sex, Measure) %>%
## create a column with the mean and standard deviation
summarise(meanSD = paste0(mean(Value) %>% round(2),
' (', sd(Value) %>% round(2),
')')) %>%
spread(Sex, meanSD)
prep.table2## Source: local data frame [5 x 3]
##
## Measure female male
## 1 Fare 44.48 (58) 25.52 (43.14)
## 2 Age 27.92 (14.11) 30.73 (14.68)
## 3 Pclass 2.16 (0.86) 2.39 (0.81)
## 4 SibSp 0.69 (1.16) 0.43 (1.06)
## 5 AgeDouble 55.83 (28.22) 61.45 (29.36)
Create a table, with a caption!
pander(prep.table2, style = 'rmarkdown',
caption = 'Testing caption for this table!')| Measure | female | male |
|---|---|---|
| Fare | 44.48 (58) | 25.52 (43.14) |
| Age | 27.92 (14.11) | 30.73 (14.68) |
| Pclass | 2.16 (0.86) | 2.39 (0.81) |
| SibSp | 0.69 (1.16) | 0.43 (1.06) |
| AgeDouble | 55.83 (28.22) | 61.45 (29.36) |
Table: Testing caption for this table!
To use the grid.table function instead of pander, load the
gridExtra package. You may need to install first
(install.packages('gridExtra')).
library(gridExtra)
grid.table(prep.table2, rows = NULL)A package that does a tutorial within R! I've heard good things from it.
install.packages('swirl')To see help files, you can run the vignette command.
vignette('introduction', package = 'dplyr')