SPIFFE Demo application is a simple demo app that uses SPIFFE Workload API. The app consists of two parts: frontend and backend. Frontend provides simple functionality to view the content of SPIFFE X509-SVID, JWT-SVID, and SPIFFE Trust Bundle through simple UI.
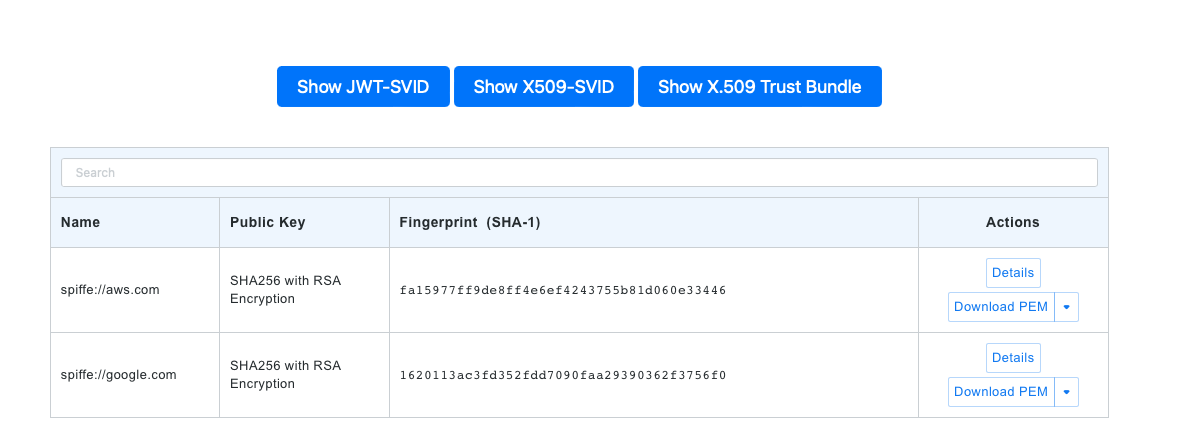
You can use it to troubleshoot things like SPIFFE federation (because you can see the trust bundle content):
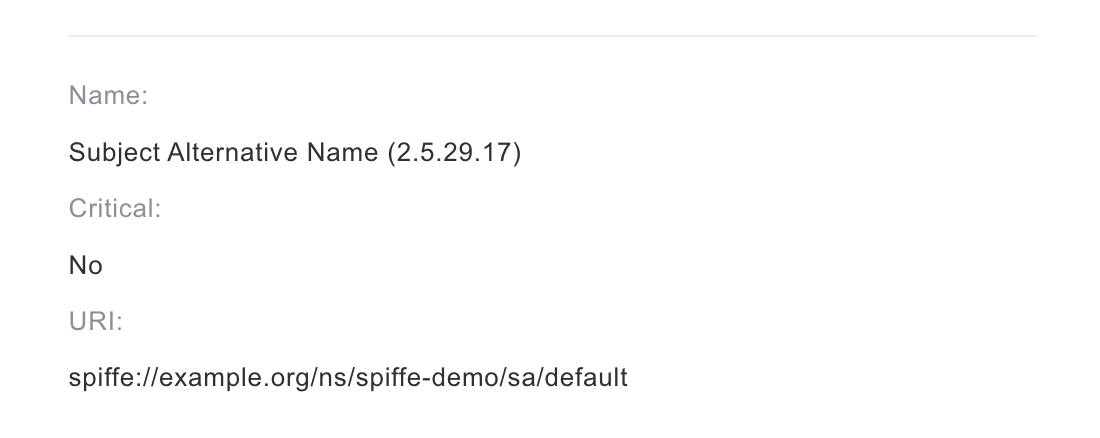
Or easily view X509-SVID or JWT-SVID details:
You'll need kubectl and helm installed. Follow the official documentation for both projects on how to install them:
helm repo add spiffe-demo https://elinesterov.github.io/spiffe-demo-app$ helm install spiffe-demo spiffe-demo/spiffe-demo-app
NAME: spiffe-demo
LAST DEPLOYED: Wed May 24 10:34:58 2023
NAMESPACE: default
STATUS: deployed
REVISION: 1
TEST SUITE: NoneThat will install the app in the default namespace. If you want to install to a different namespace, you need to create it first via kubectl create namespace foo' and then add --namespace` flag to the above command:
$ helm install spiffe-demo spiffe-demo/spiffe-demo-app --namespace foo
NAME: spiffe-demo
LAST DEPLOYED: Wed May 24 10:39:28 2023
NAMESPACE: foo
STATUS: deployed
REVISION: 1
TEST SUITE: NoneThe easiest way to use kubernetes port forwarding:
$ kubectl port-forward svc/spiffe-demo-service 8080:80
Forwarding from 127.0.0.1:8080 -> 8080
Forwarding from [::1]:8080 -> 8080If you installed a specific namespace - don't forget about `--namespace flag.
Now you can point your browser to http://localhost:8080 to reach a frontend.
> helm delete spiffe-demoSPIFFE community recently released a verison SPIRE Helm Chart which provides a really easy way of starting and playing with SPIRE. Instructions below are for the SPIRE Helm Chart Version v0.8.0.
I'll use kind as an example but you can use any other k8s distribution with a little bit of adjusment (e.g. don't use port-forwarding)
$ kind create cluster --name spire-demo
Creating cluster "spire-demo" ...
✓ Ensuring node image (kindest/node:v1.26.3) 🖼
✓ Preparing nodes 📦
✓ Writing configuration 📜
✓ Starting control-plane 🕹️
✓ Installing CNI 🔌
✓ Installing StorageClass 💾
Set kubectl context to "kind-spire-demo"
You can now use your cluster with:
kubectl cluster-info --context kind-spire-demoWe need two namespaces: one for SPIRE deployment and another one for the spiffe-demo-app
$ kubectl create namespace spire
$ kubectl create namespace spiffe-demoFirst of all add SPIFFE repo:
$ helm repo add spiffe https://spiffe.github.io/helm-charts/
If you already have it, make sure you updated it via helm repo update command.
Now add spiffe-demo-app Helm Chart:
$ helm repo add spiffe-demo https://elinesterov.github.io/spiffe-demo-appWe don't do any changes to default values. SPIRE chart at this point enables spire-controller-manager and spiffe-csi-driver by default, so you don't need to do anything.
$ helm -n spire install spire spiffe/spire --version 0.8.0SPIRE Helm Chart by default uses spire-agent.socketPath with a value /run/spire/agent-sockets/spire-agent.sock that in combination with a SPIFFE CSI Driver creates SPIFFE Workload API socket with a name spire-agent.sock. However, spiffe-demo-app by default expects the name for a socket agent.sock. Therefore we need to change it.
Also, since SPIRE Helm Chart installs SPIFFE CSI Driver we need to disable it in spiffe-demo-app.
You can use the following command with a few parameters or you may choose to set them in your values.yaml for a helm chart.
$ helm -n spiffe-demo install spiffe-demo spiffe-demo/spiffe-demo-app --set app.spiffeSocketName=spire-agent.sockSince we use kind cluster in this example, the easiest way to connect to a frontend is by using kubectl port-frowarding feature. If you use minikube, eks or any other flavour of k8s you might be able to use node port or LoadBalancer.
With kind run the following command to enable port-frwarding to the spiffe-demo-app frontend:
$ kubectl -n spiffe-demo port-forward svc/spiffe-demo-service 8080:80
Forwarding from 127.0.0.1:8080 -> 8080
Forwarding from [::1]:8080 -> 8080Now you can point your browser to http://localhost:8080 to connect to the frontend. Clock buttons to see JWT-SVID, X509-SVID and expore SPIFFE Trust Bundle in a very simple way.
Sometimes you need to run a few simple shell commands to list mounted agent socket content or for any other reason. We have busybox container withtin the spiffe-demo-app deployemnt that is disabled by default. In order to enable it you can add --set app.enableBusybox=true when installing spiffe-demo-app helm chart.
Cleaning up is simple:
$ helm -n spiffe-demo delete spiffe-demo
$ helm -n spire delete spire
$ kubectl delete namespace spire
$ kubectl delete namespace spiffe-demo
$ kind delete cluster --name spire-demor you can just execute the lates command in case of kind.