A Doubly Linked List is a linked data structure that consists of a set of sequentially linked records called nodes. Each node contains three fields: two link fields (references to the previous and to the next node in the sequence of nodes) and one data/key field. The beginning and ending nodes' previous and next links, respectively, point to some kind of terminator, typically a sentinel node or null, to facilitate traversal of the list.
The head or starter pointer points to the beginning of the doubly linked list.
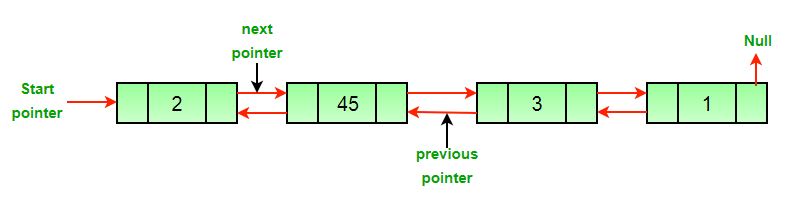
An example of a doubly linked list:
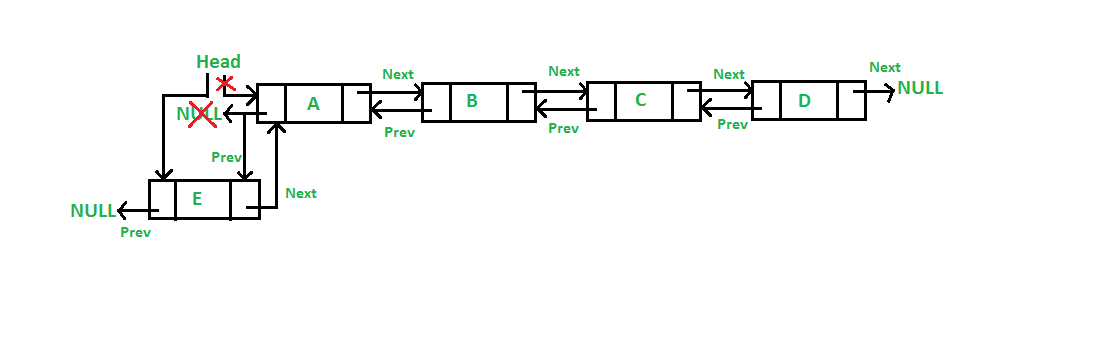
In a prepend operation - a node is added to the beginning of the doubly linked list. The newly added node becomes the head of the doubly linked list.
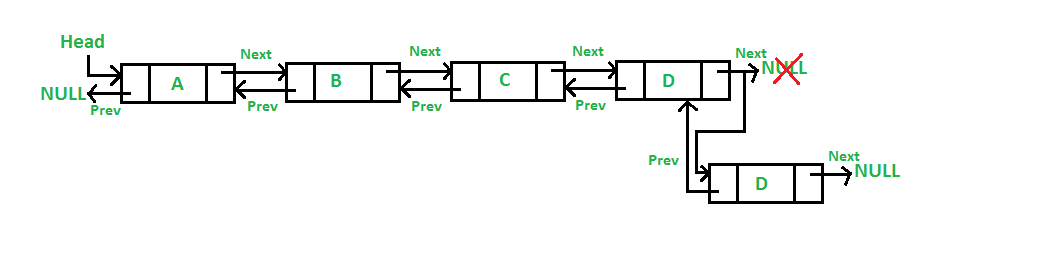
In an append operation - a node is added to the end of the doubly linked list.
If the doubly linked list is empty - a node can be added via an append operation to create a new doubly linked list with a single item.
Otherwise we traverse the list and the new node is added after the given node.
If the doubly linked list is empty - a node can be added via a prepend operation to create a new doubly linked list with a single item.
Otherwise we traverse the list and the new node is added before the given node.
[Courtesy: geeksforgeeks.org] (https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/doubly-linked-list/)
[Courtesy: geeksforgeeks.org] (https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/delete-a-node-in-a-doubly-linked-list/)