Houdini add-on for Sublime Text
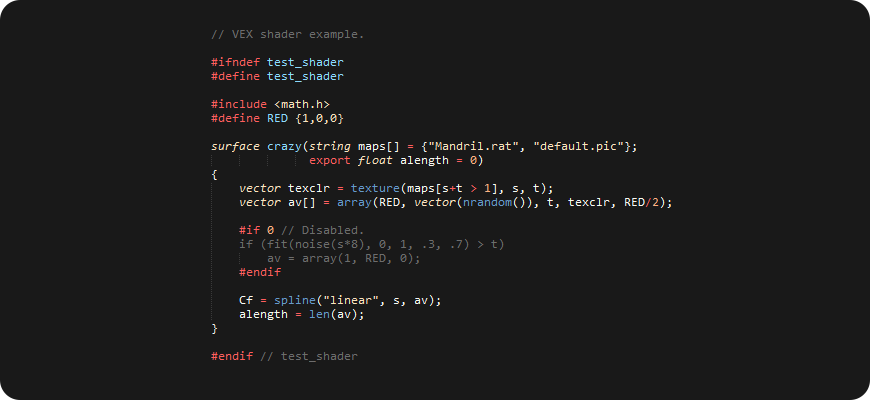
- VEX and VEX Expressions syntax.
- VCC-based syntax checker with formatted errors output.
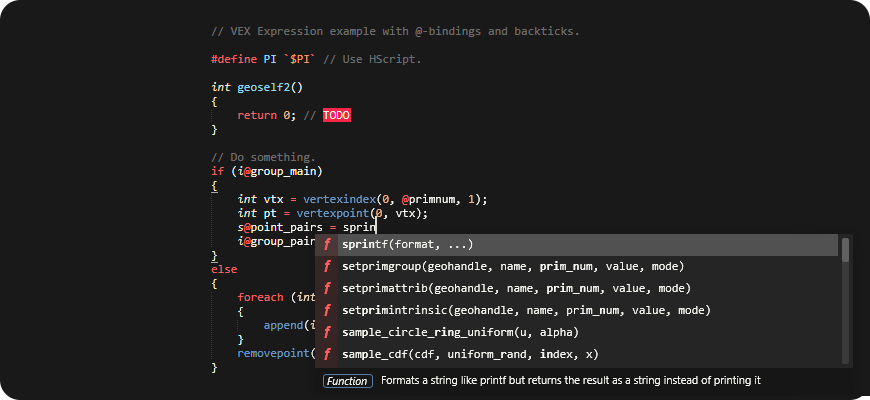
- Function auto-completions with arguments.
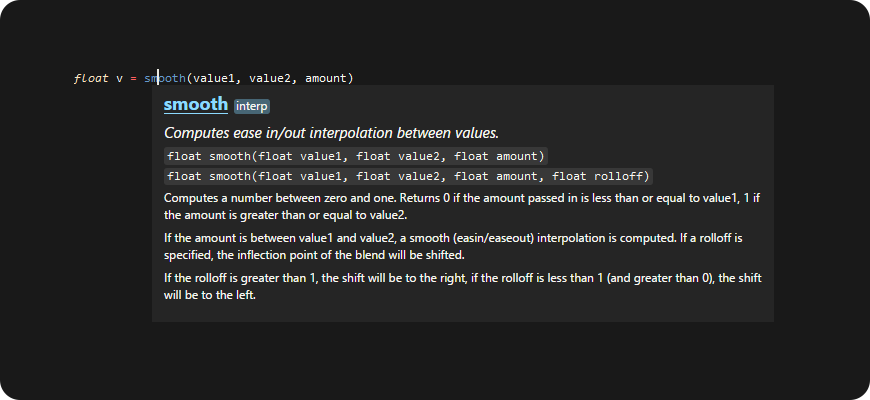
- Function documentation via styled popups.
- Special support for HScript add-on.
Open issues for bug reports, requests, suggestions, etc.
Preferences → Package Control → Install Package → VEX
Requirements:
-
Recent version of Sublime Text.
-
Tools → Install Package Control
You should be able to use the add-on now. Skip all "Optional" sections below if you are first-time user. Read them if you want to use more advanced features.
Create EDITOR variable in your houdini.env and set it to Sublime Text
executable path.
Example file location on Windows:
C:\Users\teared\Documents\houdini20.0\houdini.env
Example line to add to houdini.env (use forward slashes):
EDITOR = "C:/Program Files/Sublime Text/sublime_text.exe"
Place cursor in any parameter field and press Alt+E,
then place cursor inside the built-in editor
and press Alt+E again to launch Sublime Text from Houdini.
-
Tools → Build System → New Build System…
-
Remove default contents and copy-paste VEX Build file here.
-
Change value of
executablesetting to existing VCC executable path.Example setting for Windows:
"executable": "C:\Program Files\Side Effects Software\Houdini 20.0.506\bin\vcc.exe", -
Save to Data/Packages/User/
Any Name.sublime-buildTo override default, save it to Data/Packages/VEX/prefs/VEX Build.sublime-build
Alternatively, add Houdini binaries dir to the PATH
environment variable. By default, the add-on uses vcc command.
See "Syntax Check" section of this readme.
Optional: HScript add-on
Similar add-on for HScript and HScript Expressions languages. Syntax, auto-completions, documentation popups. It used by the VEX add-on for backtick-expressions embedded inside snippets.
Some tools I use to work on Houdini projects using Sublime Text.
- Monolit — Sublime Text 3.0 latest "Monokai" turned into "1337" color scheme. Better scopes from Monokai and greater color palette from 1337. Greatly affects default Markdown syntax highlighting.
- SublimeAStyleFormatter — format messy code for easier reading. My settings.
Open any VEX code and choose VEX using menu at the right bottom corner of
the editor. By default, it will be automatically set on all .vfl files.
If you don't want to change from ANSI C to VEX every time you open some VEX
library with .h extension, there is "Open all with current extension as..."
action in the same menu.
When you start to type VEX function name, it will prompt you with suggestions.
You can choose one and use Tab and Shift+Tab keys to navigate back and
forth. Snippets are also available for common keywords: if, else, for,
foreach, while.
To show docs for the function:
Tools → Command Pallette → VEX: Show Documentation for Function Under Cursor
Shortcut: Ctrl+Alt+D.
For the rest, check Sublime Text Documentation, it has many small features that make textual editing easy and powerful.
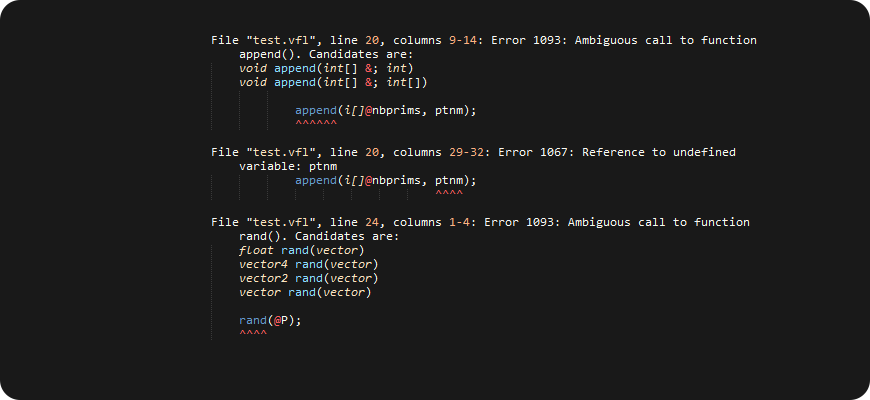
If you configured VCC path, you can do syntax check in the editor and see errors. It doesn't require Houdini to run on background.
Tools → Build With... →
-
VEX Build
Use this variant if you write a custom shader and define context function with return type like: surface, displace, cvex, etc. This is what VCC expects by default, and probably least useful for Houdini user this days.
-
VEX Build — As a Library
If you write a custom library to include it in your code.
-
VEX Build — As a Snippet
If you write wrangle. Most common choice.
See some code examples in the add-on development repo.
VCC has no idea about attribute bindings, libraries got automatically compiled within CVEX context, snippets are just functions internally, and VCC does not expect to see a surface shader there. Therefore three variants. So, if you try to do syntax check and error messages make a little sense, like this:
Error 1092: Cannot compile VEX library; source file's context 'surface' does not match required context 'cvex'.
Error 1040: Invalid return type (surface) for function my_function_name.
Error 1091: Invalid context name 'float'
Error 1088: Syntax error, unexpected '=', expecting '('
Error 1088: Syntax error, unexpected identifier, expecting ';'
Check if correct build variant is used. Error 1088 is a common error, but in case of wrong build variant chosen, there won't be visible syntax problems.
Public domain.