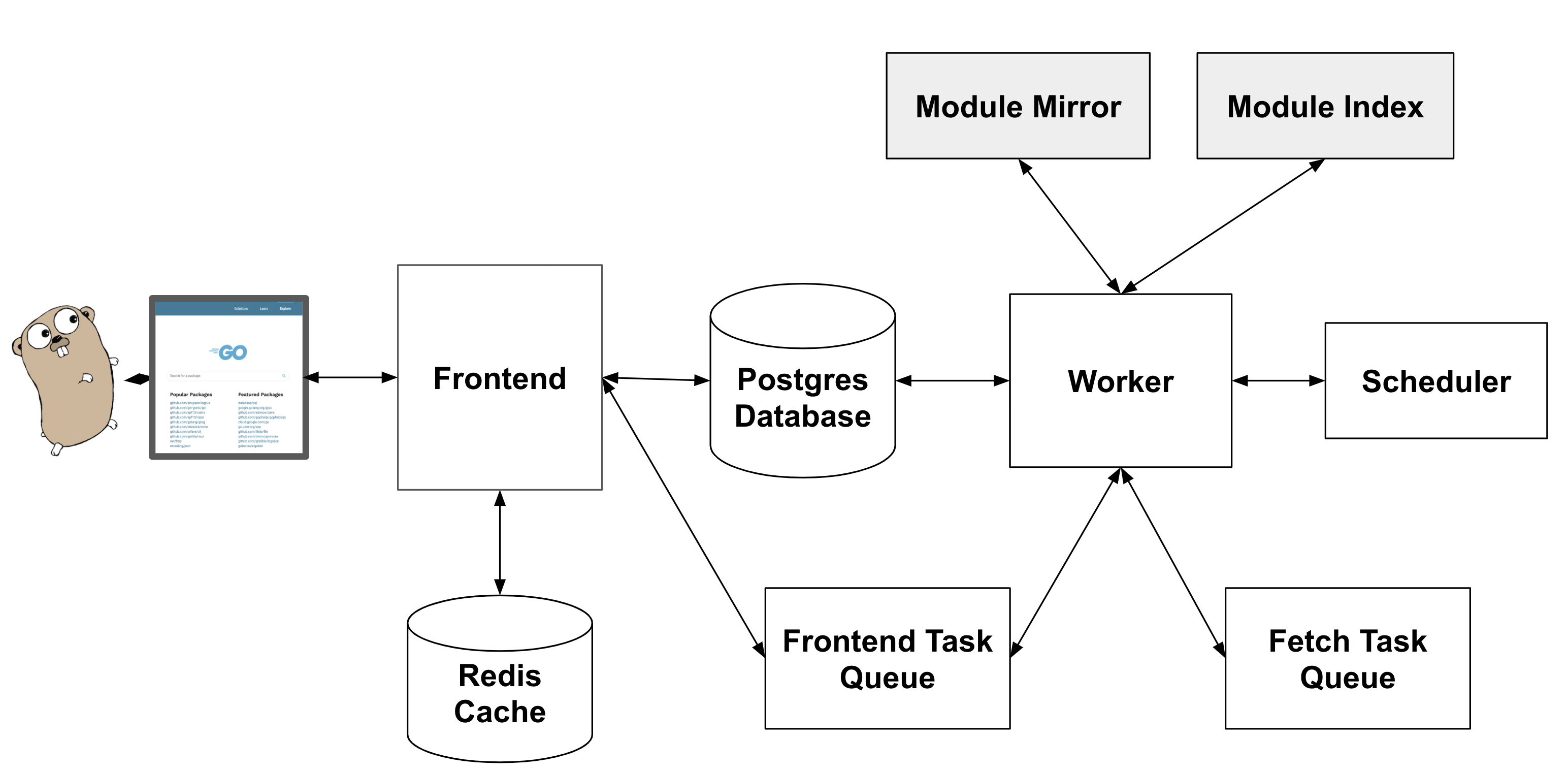
Pkg.go.dev consists of the following high-level pieces:
-
A frontend that presents user-facing web pages on pkg.go.dev.
-
A worker that populates the database with information about new modules. Data about new modules come from the Go Module Index, and the contents of these modules are downloaded from the Go Module Mirror.
-
A database that stores all information served on the site.
Both services are hosted on App Engine Standard and run Go 1.13. We use a Postgres database managed by Google Cloud SQL.
The frontend is a straightforward HTTP server that composes HTML pages by populating templates with information retrieved from the database. For search, it uses Postgres's special text-search features to run a query over a table prepared by the worker.
The frontend has the following dependencies:
- The Postgres DB, to retrieve information about modules and packages.
- A Redis instance, as a cache.
- Frontend task queue (future)
See documentation for frontend development for details on how to run the frontend locally.
The worker's main job is to download new modules as they are discovered, process
them, and write the information to the database for the frontend to serve. It
extracts README files, license files and documentation and writes them to the
database. It also writes data relevant for search to its own table
(search_documents). In addition to search information available directly in
the module zip, it also computes the number of importers of each package.
To smooth out the work of processing new modules and to take advantage of its rate-limiting and retry features, the worker uses a Google Cloud Tasks queue to manage the list of modules to be processed. The worker adds tasks to the queue when it finds new modules in the index. The queue pushes tasks to the worker at a fixed maximum rate.
Because it must be a stateless HTTP server, the worker cannot run background tasks. Instead, we use Google Cloud Scheduler to run activities periodically. The activities, which typically run once a minute, are:
- Poll the index to enqueue new modules.
- Re-enqueue transient module-processing failures.
- Update the count of importers for each package.
The worker has the following dependencies:
- The index (index.golang.org by default) to learn about new modules.
- The proxy (proxy.golang.org by default) to fetch the module zip files.
- The Postgres database.
See documentation for worker development for details on how to run the worker locally.