Graylog is transparently managing a set of indices to optimize search and analysis operations for speed and low resource utilisation.
The system is maintaining an index alias called
graylog_deflector which is always pointing to the current write-active index.
There is always exactly one index to which new messages are written until the configured rotation criterion
(number of documents, index size, or index age) has been reached.
A background task checks regularly if the rotation criterion has been reached and a new
index is created and prepared when that happens. Once the index is considered to be ready
to be written to, the graylog_deflector index alias is atomically switched to the it. That means that
all writing nodes can always write to the deflector alias without even knowing what the
currently write-active index is.
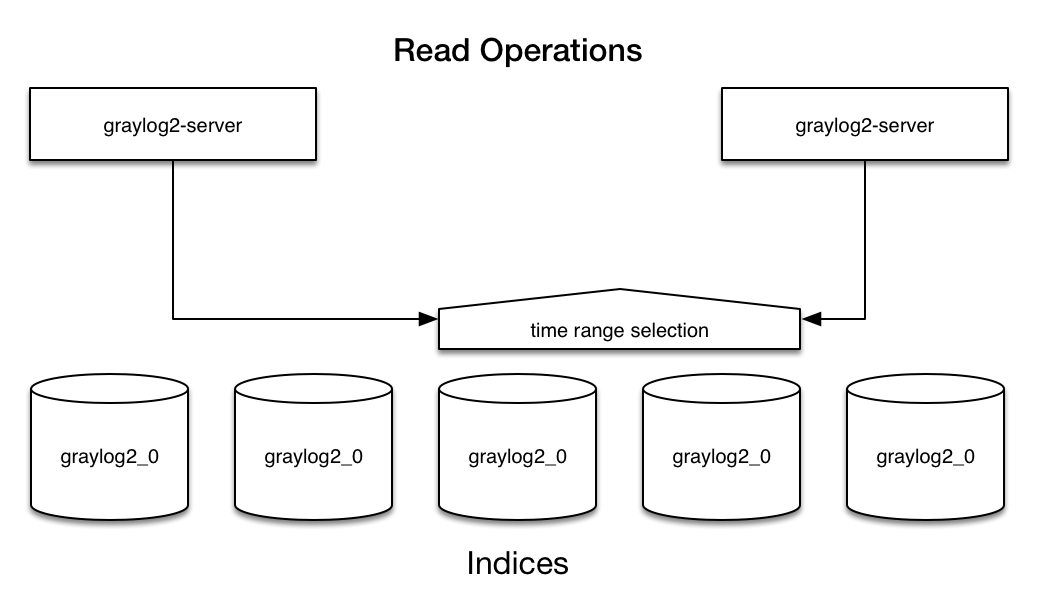
Almost every read operation is performed with a given time range. Because Graylog is only writing sequentially it can keep a cached collection of information about which index starts at what point in time. It selects a lists of indices to query when having a time range provided. If no time range is provided it will search in all indices it knows.
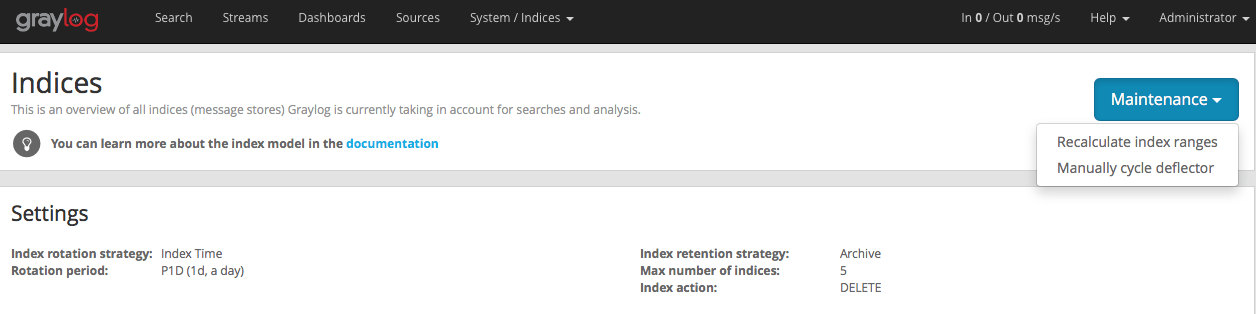
There's a configuration setting for the maximum number of indices Graylog is managing. Depending on the configured retention strategy, the oldest indices will automatically closed, deleted, or exported when the maximum number of indices has been reached. The deletion is performed by the Graylog master node in a background thread that is continuously comparing the number of indices with the configured maximum.
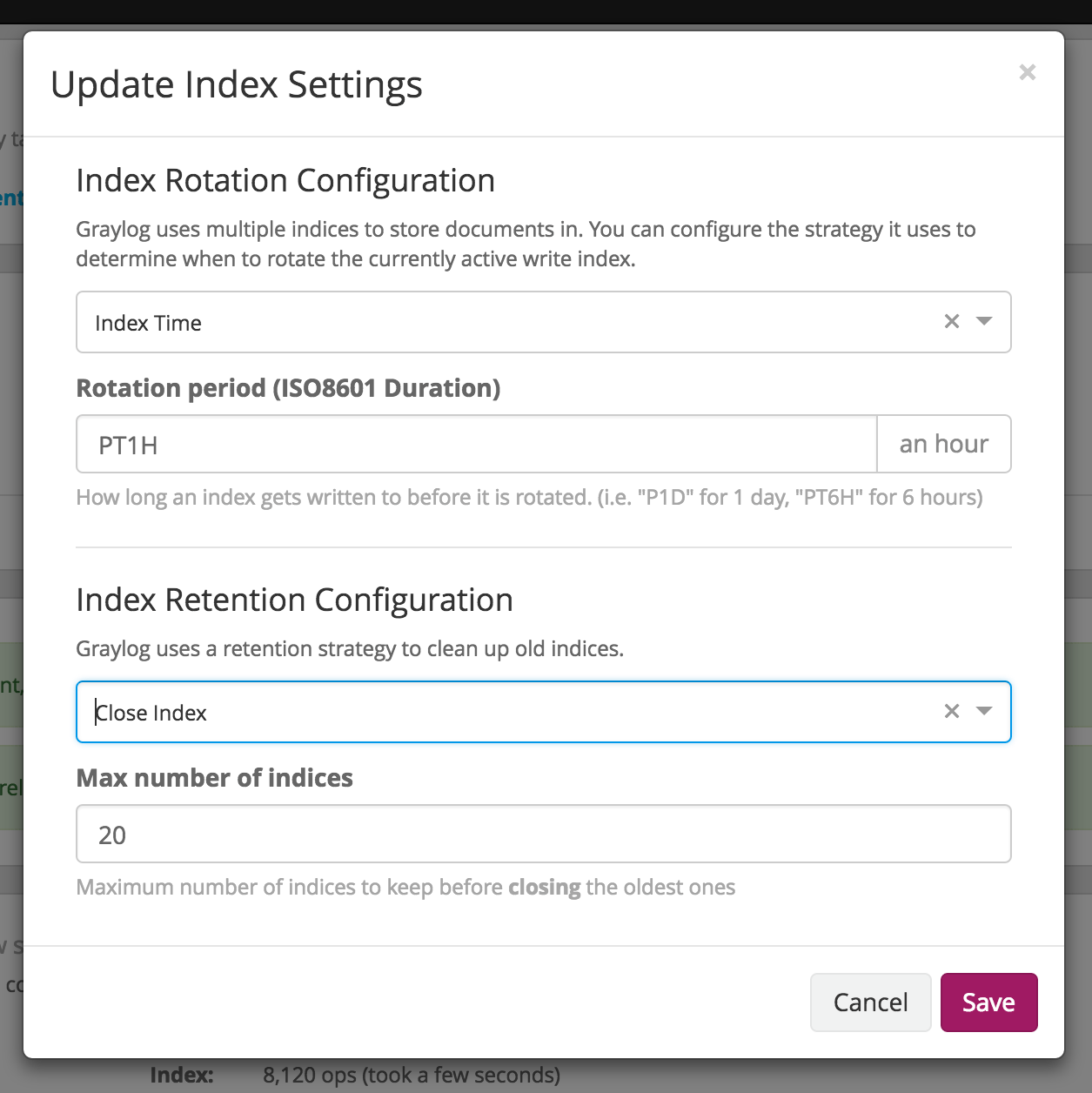
The following index rotation settings are available:
- Message count: Rotates the index after a specific number of messages have been written.
- Index size: Rotates the index after an approximate size (before optimization) has been reached.
- Index time: Rotates the index after a specific time (e. g. 1 hour or 1 week).
The following index retention settings are available:
- Delete: Delete indices in Elasticsearch to minimize resource consumption.
- Close: Close indices in Elasticsearch to reduce resource consumption.
- Do nothing
- Archive: Commercial feature, see :doc:`archiving`.
Graylog will notify you when the stored metadata about index time ranges has run out of sync. This can for example happen when you delete indices by hand or delete messages from already "closed" indices. The system will offer you to just re-generate all time range information. This may take a few seconds but is an easy task for Graylog.
You can easily re-build the information yourself after manually deleting indices or doing other changes that might cause synchronisation problems:
$ curl -XPOST http://127.0.0.1:9000/api/system/indices/ranges/rebuild
This will trigger a systemjob:
INFO : org.graylog2.system.jobs.SystemJobManager - Submitted SystemJob <ef7057c0-5ae3-11e3-b935-4c8d79f2b596> [org.graylog2.indexer.ranges.RebuildIndexRangesJob] INFO : org.graylog2.indexer.ranges.RebuildIndexRangesJob - Re-calculating index ranges. INFO : org.graylog2.indexer.ranges.RebuildIndexRangesJob - Calculated range of [graylog2_56] in [640ms]. INFO : org.graylog2.indexer.ranges.RebuildIndexRangesJob - Calculated range of [graylog2_18] in [66ms]. ... INFO : org.graylog2.indexer.ranges.RebuildIndexRangesJob - Done calculating index ranges for 88 indices. Took 4744ms. INFO : org.graylog2.system.jobs.SystemJobManager - SystemJob <ef7057c0-5ae3-11e3-b935-4c8d79f2b596> [org.graylog2.indexer.ranges.RebuildIndexRangesJob] finished in 4758ms.
Sometimes you might want to cycle the deflector manually and not wait until the configured rotation criterion for in the latest index has been reached. You can do this either via an HTTP request against the REST API of the Graylog master node or via the web interface:
$ curl -XPOST http://127.0.0.1:9000/api/system/deflector/cycle
This triggers the following log output:
INFO : org.graylog2.rest.resources.system.DeflectorResource - Cycling deflector. Reason: REST request. INFO : org.graylog2.indexer.Deflector - Cycling deflector to next index now. INFO : org.graylog2.indexer.Deflector - Cycling from <graylog2_90> to <graylog2_91> INFO : org.graylog2.indexer.Deflector - Creating index target <graylog2_91>... INFO : org.graylog2.indexer.Deflector - Done! INFO : org.graylog2.indexer.Deflector - Pointing deflector to new target index.... INFO : org.graylog2.indexer.Deflector - Flushing old index <graylog2_90>. INFO : org.graylog2.indexer.Deflector - Setting old index <graylog2_90> to read-only. INFO : org.graylog2.system.jobs.SystemJobManager - Submitted SystemJob <a05e0d60-5c34-11e3-8df7-4c8d79f2b596> [org.graylog2.indexer.indices.jobs.OptimizeIndexJob] INFO : org.graylog2.indexer.Deflector - Done! INFO : org.graylog2.indexer.indices.jobs.OptimizeIndexJob - Optimizing index <graylog2_90>. INFO : org.graylog2.system.jobs.SystemJobManager - SystemJob <a05e0d60-5c34-11e3-8df7-4c8d79f2b596> [org.graylog2.indexer.indices.jobs.OptimizeIndexJob] finished in 334ms.