A VS Code extension providing the basic support for editing and debugging programs running on GraalVM. As of version 0.0.8 this extension replaces the original GraalVM Python, GraalVM R, GraalVM Ruby, and GraalVM Extension Pack extensions so those can be safely uninstalled from your VS Code. The extension is Technology Preview.
Upon the extension installation, the user is requested to provide a path to the GraalVM home directory.
To that purpose, the following commands can be used:
-
Select GraalVM Installation - Provides the UI to select an already installed GraalVM.
By default, the following locations are searched for an already installed GraalVM:
- the extension's global storage
/optfolder as the default RPM install locationPATHenvironment variable contentGRAALVM_HOMEenvironment variable contentJAVA_HOMEenvironment variable content
-
Install GraalVM - Downloads the latest GraalVM release from Github and installs it within the extension's global storage. If you are behind a proxy, do not forget to setup your proxy configuration in
File -> Preferences -> Settings, or run your VS Code instance with thehttp_proxyandhttps_proxyenvironment variables exported.
Once the path to the GraalVM home directory is provided, the GraalVM is checked for presence of the optional components:
User is provided with an option of an automatic installation of the missing components.
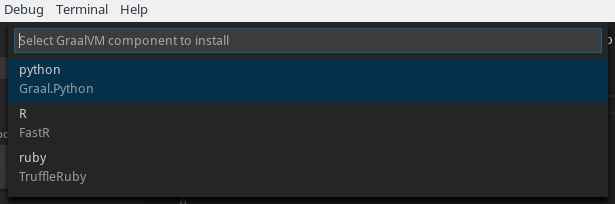
The folowing command can be used to install any missing GraalVM component manually:
- Install GraalVM Component
All three commands can be invoked at any time from the Command Palette (Ctrl+Shift+P)
To debug a JavaScript or Node.js application running on GraalVM, creating a launch configuration for the application is necessary. To do so, open the application project folder in VS Code (File > Open Folder), switch to the Debug view by clicking on the "bug" icon in the left side panel, and then select the Configure "gear" icon on the Debug view top bar. If debugging is not yet configured (no launch.json has been created), select GraalVM from the list of available debug environmnets. Once the launch.json file is opened in the editor, one of the following techniques can be used to add a new configuration:
- Use IntelliSense if your cursor is located inside the configurations array.
- Press the Add Configuration button to invoke snippet IntelliSense at the start of the array.
- Choose Add Configuration option in the Debug menu.
The GraalVM extension provides the following debug configurations that can be used to debug an applications running on GraalVM:
- Launch Node.js Application - Launches a Node.js Application using GraalVM in a debug mode.
- Launch JavaScript - Launches a JavaScript using GraalVM in a debug mode.
- Attach - Attaches debugger to a locally running GraalVM.
- Attach to Remote - Attaches debugger to the debug port of a remote GraalVM.
Note that the attributes available in launch configurations vary from configuration to configuration. You can use IntelliSense suggestions (Ctrl+Space) to find out which attributes exist for a specific debug configuration. Hover help is also available for all attributes.
In order to start a debug session, first select the proper configuration using the Configuration drop-down in the Debug view. Once you have your launch configuration set, start your debug session with F5. Alternatively you can run your configuration through the Command Palette (Ctrl+Shift+P), by filtering on Debug: Select and Start Debugging or typing 'debug ', and selecting the configuration you want to debug.
To run a polyglot application using the GraalVM, user has to either pass the --polyglot option to any of the existing application lauchers (e.g. js --polyglot, node --polyglot) or use an experimental launcher called polyglot that runs code for JavaScript, Ruby, and R without requiring the selection of a primary language. The polyglot launcher does not require the --polyglot option, it is enabled by default. For more information see the GraalVM polyglot documentation.
To debug a polyglot application using the GraalVM, creating a launch configuration for the application is necessary. To do so, open the application project folder in VS Code (File > Open Folder), switch to the Debug view by clicking on the "bug" icon in the left side panel, and then select the Configure "gear" icon on the Debug view top bar. If debugging is not yet configured (no launch.json has been created), select GraalVM from the list of available debug environmnets. Once the launch.json file is opened in the editor, one of the following techniques can be used to add a new configuration:
- Use IntelliSense if your cursor is located inside the configurations array.
- Press the Add Configuration button to invoke snippet IntelliSense at the start of the array.
- Choose Add Configuration option in the Debug menu.
The GraalVM extension provides the following debug configuration that can be used to debug an applications running on GraalVM using the polyglot launcher:
- Launch Polyglot Application - Launches a Polyglot Application in debug mode.
Alternatively, to pass the --polyglot option to any of the existing application lauchers, add the runtimeArgs attribute containing the --polyglot value to their respective debug configurations. Note that in some cases (polyglot application calls Java or R, or native launcher accesses languages installed with gu without rebuilding images), passing also the --jvm option is necessary.
To debug a Python application running on GraalVM, creating a launch configuration for the application is necessary. To do so, open the application project folder in VS Code (File > Open Folder), switch to the Debug view by clicking on the "bug" icon in the left side panel, and then select the Configure "gear" icon on the Debug view top bar. If debugging is not yet configured (no launch.json has been created), select GraalVM from the list of available debug environmnets. Once the launch.json file is opened in the editor, one of the following techniques can be used to add a new configuration:
- Use IntelliSense if your cursor is located inside the configurations array.
- Press the Add Configuration button to invoke snippet IntelliSense at the start of the array.
- Choose Add Configuration option in the Debug menu.
The GraalVM Pyton extension provides the following debug configuration that can be used to debug a Python applications/scripts running on GraalVM:
- Launch Python Script - Launches a Python script using GraalVM in a debug mode.
When editing debug configurations, you can use IntelliSense suggestions (Ctrl+Space) to find out which attributes exist for a specific debug configuration. Hover help is also available for all attributes.
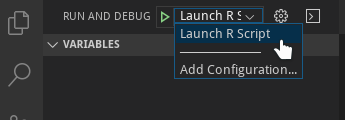
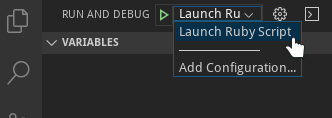
In order to start a debug session, first select the proper configuration using the Configuration drop-down in the Debug view. Once you have your launch configuration set, start your debug session with F5. Alternatively you can run your configuration through the Command Palette (Ctrl+Shift+P), by filtering on Debug: Select and Start Debugging or typing 'debug ', and selecting the configuration you want to debug.
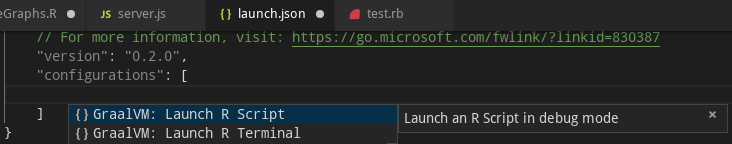
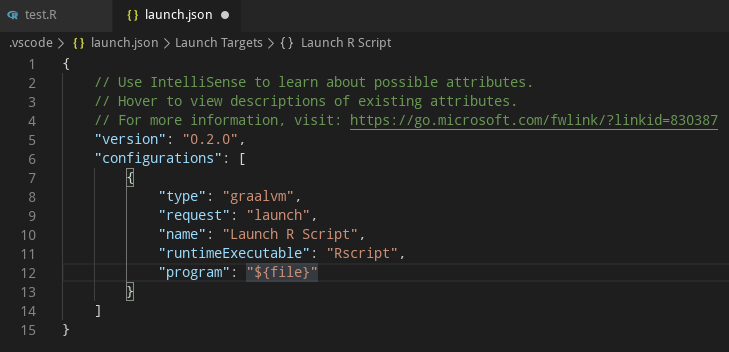
To debug an R application running on GraalVM, creating a launch configuration for the application is necessary. To do so, open the application project folder in VS Code (File > Open Folder), switch to the Debug view by clicking on the "bug" icon in the left side panel, and then select the Configure "gear" icon on the Debug view top bar. If debugging is not yet configured (no launch.json has been created), select GraalVM from the list of available debug environmnets. Once the launch.json file is opened in the editor, one of the following techniques can be used to add a new configuration:
- Use IntelliSense if your cursor is located inside the configurations array.
- Press the Add Configuration button to invoke snippet IntelliSense at the start of the array.
- Choose Add Configuration option in the Debug menu.
The GraalVM R extension provides the following debug configurations that can be used to debug an R applications/scripts running on GraalVM:
- Launch R Script - Launches an R script using GraalVM in a debug mode.
- Launch R Terminal - Launches an integrated R terminal running on GraalVM in a debug mode.
When editing debug configurations, you can use IntelliSense suggestions (Ctrl+Space) to find out which attributes exist for a specific debug configuration. Hover help is also available for all attributes.
In order to start a debug session, first select the proper configuration using the Configuration drop-down in the Debug view. Once you have your launch configuration set, start your debug session with F5. Alternatively you can run your configuration through the Command Palette (Ctrl+Shift+P), by filtering on Debug: Select and Start Debugging or typing 'debug ', and selecting the configuration you want to debug.
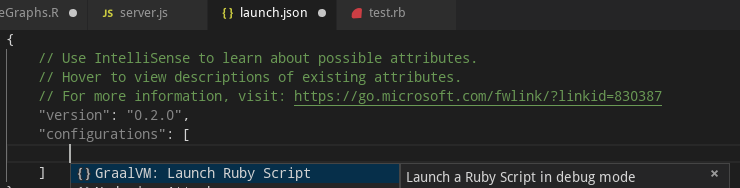
To debug a Ruby application running on GraalVM, creating a launch configuration for the application is necessary. To do so, open the application project folder in VS Code (File > Open Folder), switch to the Debug view by clicking on the "bug" icon in the left side panel, and then select the Configure "gear" icon on the Debug view top bar. If debugging is not yet configured (no launch.json has been created), select GraalVM from the list of available debug environmnets. Once the launch.json file is opened in the editor, one of the following techniques can be used to add a new configuration:
- Use IntelliSense if your cursor is located inside the configurations array.
- Press the Add Configuration button to invoke snippet IntelliSense at the start of the array.
- Choose Add Configuration option in the Debug menu.
The GraalVM Ruby extension provides the following debug configuration that can be used to debug a Ruby applications/scripts running on GraalVM:
- Launch Ruby Script - Launches a Ruby script using GraalVM in a debug mode.
When editing debug configurations, you can use IntelliSense suggestions (Ctrl+Space) to find out which attributes exist for a specific debug configuration. Hover help is also available for all attributes.
In order to start a debug session, first select the proper configuration using the Configuration drop-down in the Debug view. Once you have your launch configuration set, start your debug session with F5. Alternatively you can run your configuration through the Command Palette (Ctrl+Shift+P), by filtering on Debug: Select and Start Debugging or typing 'debug ', and selecting the configuration you want to debug.
GraalVM supports smart editing features of development tools used to create guest language applications by providing a built-in implementation of the Language Server Protocol. This allows you to attach compatible development tools such as VS Code to GraalVM and to get features like auto complete, go to declaration, or documentation on hover.
Currently, the GraalVM Language Server implementation supports the following services:
- Text Document Synchronization
- Hover Provider
- Completion Provider
- Signature Help Provider
- Document Highlight Provider
- Code Action Provider
- Code Lens Provider
- Execute Command Provider
Note: GraalVM Language Server is offered as a technology preview and requires to pass the --experimental-options option for its activation.
To start the GraalVM Language Server, pass the --lsp option to the command-line launcher as in the following example with a Node.js application:
$ node --experimental-options --lsp app.js
[Graal LSP] Starting server and listening on localhost/127.0.0.1:8123
Example app listening on port 3000!
Note that the GraalVM Language Server itself does not provide the static data usually gathered by parsing the application sources (as these data are sometimes fuzzy in case of dynamic languages). Instead, the GraalVM Language Server was designed to provide the accurate dynamic data gathered form the application runtime.
However, the GraalVM Language Server could delegate to the existing language servers written specially for the particular languages (using the --lsp.Delegates launcher option) and merge the static data returned from these servers with its own dynamic data to a single result.
This extension works as a client to the GraalVM Language Server. By default, a language server is started as a part of every process being executed or debugged via VS Code UI. The other possibility (available on option) is a language server started as a separated process that gets informed about every application being executed or debugged. It tries to "dry-run" the same code as the original application and serve the runetime data afterwards. Currently, both approaches start the language server providing the smart editing features for the following Truffle Languages - JavaScript, Python, R, Ruby, and SimpleLanguage.
This extension provides an option to automatically install and run the languageserver which is an implementation of the Language Server Protocol for the language of R. Enabling this option, the GraalVM R installation is checked for presence of the languageserver package and user is provided with an option of an automatic installation of the missing package.
Once the languageserver package is installed, the R Language Server is automatically started and passed to the GraalVM Language Server as delegate when necessary.
This extension provides an option to automatically install and run the solargraph which is an implementation of the Language Server Protocol for the language of Ruby. Enabling this option, the GraalVM Ruby installation is checked for presence of the solargraph gem and user is provided with an option of an automatic installation of the missing gem.
Once the solargraph gem is installed, the Ruby Language Server is automatically started and passed to the GraalVM Language Server as delegate when necessary.
Since an easy writing of polyglot applications is one of the defining features of GraalVM, the code completion invoked inside JavaScript sources provides items for Polyglot.eval(...), Polyglot.evalFile(...) and Java.type(...) calls.
Similarly, the code completion invoked inside Python sources provides items for Polyglot.eval(...), Polyglot.eval_file(...) and Java.type(...) calls.
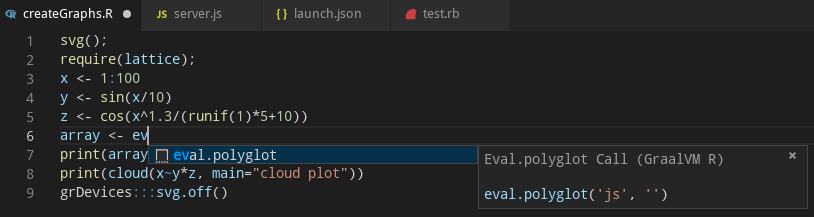
The code completion invoked inside R sources provides items for eval.polyglot(...) and new("<Java type>", ...) calls.
And finally, the code completion invoked inside Ruby sources provides items for Polyglot.eval(...), Polyglot.eval_file(...) and Java.type(...) calls.
For JavaScript, Python, R, and Ruby sources opened in editor, all the Polyglot.eval(...) calls are detected and the respective embedded languages are injected to their locations. For example, having an R code snippet called via the Polyglot API from inside a JavaScript source, the R language code is embedded inside the corresponding JavaScript string and all VS Code's editing features (syntax highlighting, bracket matching, auto closing pairs, code completion, etc.) treat the content of the string as the R source code.
This extension contributes the following settings:
- graalvm.home - Path to GraalVM installation.
- graalvm.languageServer.currentWorkDir - Absolute path to the working directory of the GraalVM Language Server.
- graalvm.languageServer.inProcessServer - Start GraalVM Language Server within processes being run or debugged.
- graalvm.languageServer.delegateServers - Comma-separated list of language@[host:]port where other language servers run.
- graalvm.languageServer.startRLanguageServer - Start R Language Server.
- graalvm.languageServer.startRubyLanguageServer - Start Ruby Language Server.
This extension depends on the following extensions:
Please read the Oracle Privacy Policy to learn more.