判断在一个矩阵中是否存在一条包含某字符串所有字符的路径。路径可以从矩阵中的任意一个格子开始,每一步可以在矩阵中向上下左右移动一个格子。如果一条路径经过了矩阵中的某一个格子,则该路径不能再进入该格子。
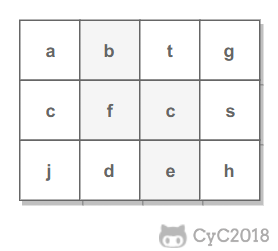
例如下面的矩阵包含了一条 bfce 路径。
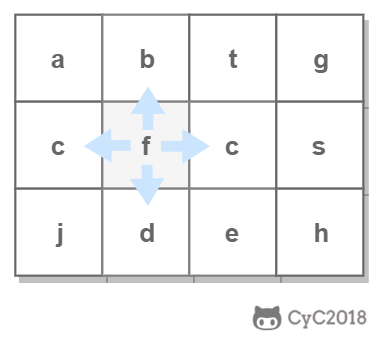
使用回溯法(backtracking)进行求解,它是一种暴力搜索方法,通过搜索所有可能的结果来求解问题。回溯法在一次搜索结束时需要进行回溯(回退),将这一次搜索过程中设置的状态进行清除,从而开始一次新的搜索过程。例如下图示例中,从 f 开始,下一步有 4 种搜索可能,如果先搜索 b,需要将 b 标记为已经使用,防止重复使用。在这一次搜索结束之后,需要将 b 的已经使用状态清除,并搜索 c。
本题的输入是数组而不是矩阵(二维数组),因此需要先将数组转换成矩阵。
public class Solution {
private final static int[][] next = {{0, -1}, {0, 1}, {-1, 0}, {1, 0}};
private int rows;
private int cols;
public boolean hasPath (String val, int rows, int cols, String path) {
if (rows == 0 || cols == 0) return false;
this.rows = rows;
this.cols = cols;
char[] array = val.toCharArray();
char[][] matrix = buildMatrix(array);
char[] pathList = path.toCharArray();
boolean[][] marked = new boolean[rows][cols];
for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < cols; j++)
if (backtracking(matrix, pathList, marked, 0, i, j))
return true;
return false;
}
private boolean backtracking(char[][] matrix, char[] pathList,
boolean[][] marked, int pathLen, int r, int c) {
if (pathLen == pathList.length) return true;
if (r < 0 || r >= rows || c < 0 || c >= cols
|| matrix[r][c] != pathList[pathLen] || marked[r][c]) {
return false;
}
marked[r][c] = true;
for (int[] n : next)
if (backtracking(matrix, pathList, marked, pathLen + 1, r + n[0], c + n[1]))
return true;
marked[r][c] = false;
return false;
}
private char[][] buildMatrix(char[] array) {
char[][] matrix = new char[rows][cols];
for (int r = 0, idx = 0; r < rows; r++)
for (int c = 0; c < cols; c++)
matrix[r][c] = array[idx++];
return matrix;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Solution solution = new Solution();
String val = "ABCESFCSADEE";
int rows = 3;
int cols = 4;
String path = "ABCCED";
boolean res = solution.hasPath(val, rows, cols, path);
System.out.println(res);
}
}