Azure Blob storage is a service for storing large amounts of unstructured data, such as text or binary data, that can be accessed from anywhere in the world via HTTP or HTTPS. You can use Blob storage to expose data publicly to the world, or to store application data privately.
Common uses of Blob storage include:
- Serving images or documents directly to a browser
- Storing files for distributed access
- Streaming video and audio
- Performing secure backup and disaster recovery
- Storing data for analysis by an on-premises or Azure-hosted service
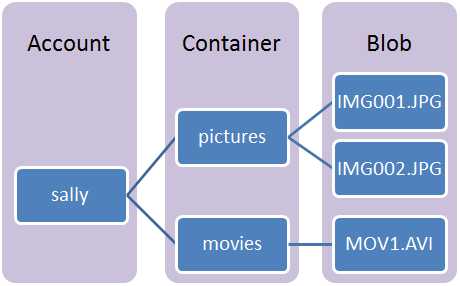
The Blob service contains the following components:
-
Storage Account: All access to Azure Storage is done through a storage account. See Azure Storage Scalability and Performance Targets for details about storage account capacity.
-
Container: A container provides a grouping of a set of blobs. All blobs must be in a container. An account can contain an unlimited number of containers. A container can store an unlimited number of blobs.
-
Blob: A file of any type and size. There are two types of blobs that can be stored in Azure Storage: block and page blobs. Most files are block blobs. A single block blob can be up to 200 GB in size. This tutorial uses block blobs. Page blobs, another blob type, can be up to 1 TB in size, and are more efficient when ranges of bytes in a file are modified frequently. For more information about blobs, see [Understanding Block Blobs and Page Blobs][].
-
URL format: Blobs are addressable using the following URL format:
http://<storage account>.blob.core.windows.net/<container>/<blob>The following example URL could be used to address one of the blobs in the diagram above:
http://sally.blob.core.windows.net/movies/MOV1.AVI