Excelize is a library written in pure Go providing a set of functions that allow you to write to and read from XLSX files. Supports reading and writing XLSX file generated by Microsoft Excel™ 2007 and later. Supports saving a file without losing original charts of XLSX. This library needs Go version 1.10 or later. The full API docs can be seen using go's built-in documentation tool, or online at godoc.org and docs reference.
go get github.com/360EntSecGroup-Skylar/excelizeHere is a minimal example usage that will create XLSX file.
package main
import (
"fmt"
"github.com/360EntSecGroup-Skylar/excelize"
)
func main() {
f := excelize.NewFile()
// Create a new sheet.
index := f.NewSheet("Sheet2")
// Set value of a cell.
f.SetCellValue("Sheet2", "A2", "Hello world.")
f.SetCellValue("Sheet1", "B2", 100)
// Set active sheet of the workbook.
f.SetActiveSheet(index)
// Save xlsx file by the given path.
err := f.SaveAs("./Book1.xlsx")
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
}
}The following constitutes the bare to read a XLSX document.
package main
import (
"fmt"
"github.com/360EntSecGroup-Skylar/excelize"
)
func main() {
f, err := excelize.OpenFile("./Book1.xlsx")
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
return
}
// Get value from cell by given worksheet name and axis.
cell, err := f.GetCellValue("Sheet1", "B2")
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
return
}
fmt.Println(cell)
// Get all the rows in the Sheet1.
rows, err := f.GetRows("Sheet1")
for _, row := range rows {
for _, colCell := range row {
fmt.Print(colCell, "\t")
}
fmt.Println()
}
}With Excelize chart generation and management is as easy as a few lines of code. You can build charts based off data in your worksheet or generate charts without any data in your worksheet at all.
package main
import (
"fmt"
"github.com/360EntSecGroup-Skylar/excelize"
)
func main() {
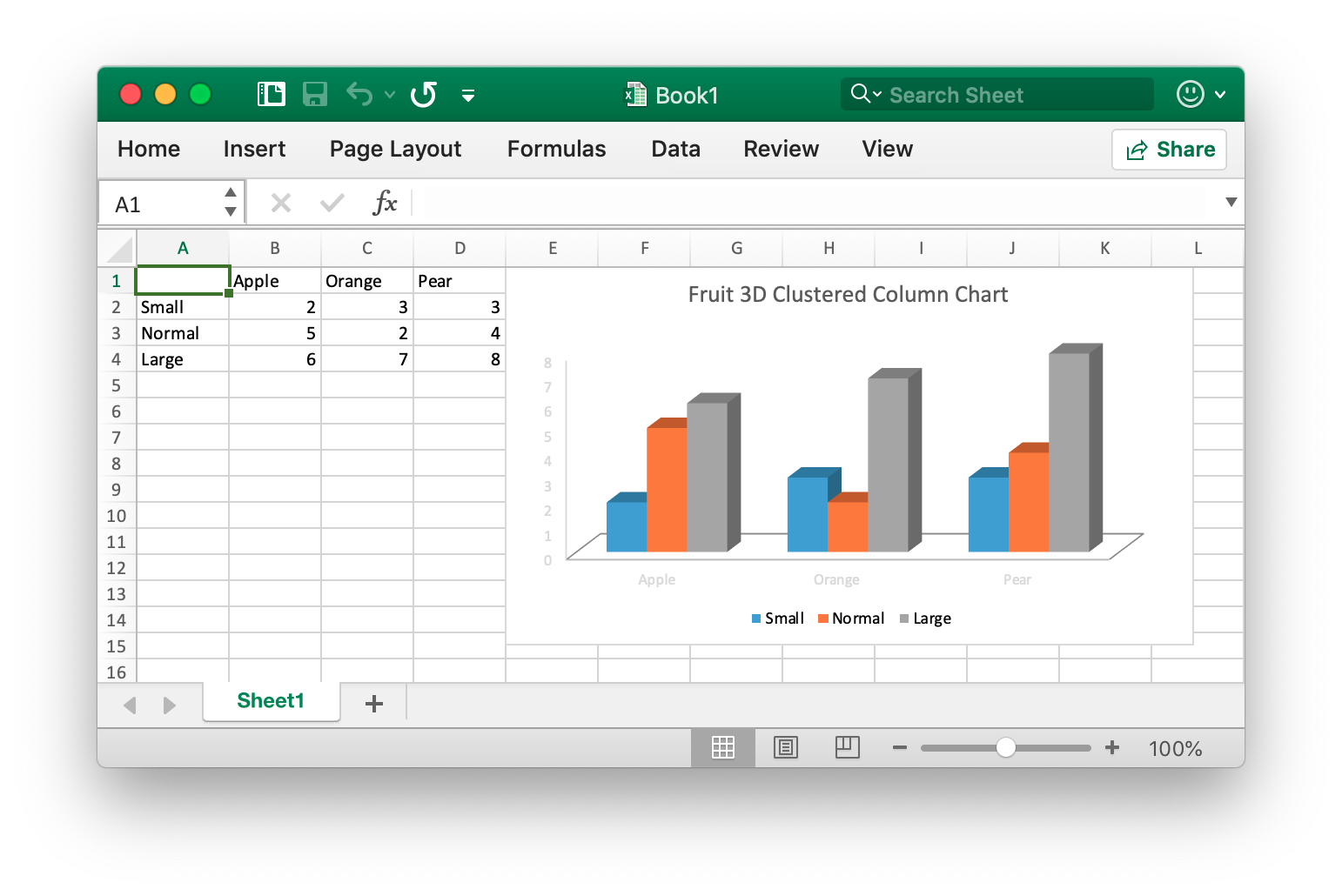
categories := map[string]string{"A2": "Small", "A3": "Normal", "A4": "Large", "B1": "Apple", "C1": "Orange", "D1": "Pear"}
values := map[string]int{"B2": 2, "C2": 3, "D2": 3, "B3": 5, "C3": 2, "D3": 4, "B4": 6, "C4": 7, "D4": 8}
f := excelize.NewFile()
for k, v := range categories {
f.SetCellValue("Sheet1", k, v)
}
for k, v := range values {
f.SetCellValue("Sheet1", k, v)
}
err := f.AddChart("Sheet1", "E1", `{"type":"col3DClustered","series":[{"name":"Sheet1!$A$2","categories":"Sheet1!$B$1:$D$1","values":"Sheet1!$B$2:$D$2"},{"name":"Sheet1!$A$3","categories":"Sheet1!$B$1:$D$1","values":"Sheet1!$B$3:$D$3"},{"name":"Sheet1!$A$4","categories":"Sheet1!$B$1:$D$1","values":"Sheet1!$B$4:$D$4"}],"title":{"name":"Fruit 3D Clustered Column Chart"}}`)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
return
}
// Save xlsx file by the given path.
err = f.SaveAs("./Book1.xlsx")
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
}
}package main
import (
"fmt"
_ "image/gif"
_ "image/jpeg"
_ "image/png"
"github.com/360EntSecGroup-Skylar/excelize"
)
func main() {
f, err := excelize.OpenFile("./Book1.xlsx")
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
return
}
// Insert a picture.
err = f.AddPicture("Sheet1", "A2", "./image1.png", "")
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
}
// Insert a picture to worksheet with scaling.
err = f.AddPicture("Sheet1", "D2", "./image2.jpg", `{"x_scale": 0.5, "y_scale": 0.5}`)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
}
// Insert a picture offset in the cell with printing support.
err = f.AddPicture("Sheet1", "H2", "./image3.gif", `{"x_offset": 15, "y_offset": 10, "print_obj": true, "lock_aspect_ratio": false, "locked": false}`)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
}
// Save the xlsx file with the origin path.
err = f.Save()
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
}
}Contributions are welcome! Open a pull request to fix a bug, or open an issue to discuss a new feature or change. XML is compliant with part 1 of the 5th edition of the ECMA-376 Standard for Office Open XML.
This program is under the terms of the BSD 3-Clause License. See https://opensource.org/licenses/BSD-3-Clause.
The Excel logo is a trademark of Microsoft Corporation. This artwork is an adaptation.
gopher.{ai,svg,png} was created by Takuya Ueda. Licensed under the Creative Commons 3.0 Attributions license.