| layout | title | folder | permalink | categories | tags | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
pattern |
Strategy |
strategy |
/patterns/strategy/ |
Behavioral |
|
Policy
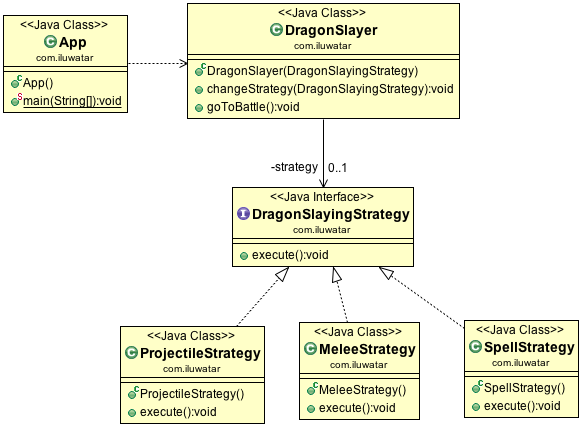
Define a family of algorithms, encapsulate each one, and make them interchangeable. Strategy lets the algorithm vary independently from clients that use it.
Use the Strategy pattern when
- many related classes differ only in their behavior. Strategies provide a way to configure a class either one of many behaviors
- you need different variants of an algorithm. for example, you might define algorithms reflecting different space/time trade-offs. Strategies can be used when these variants are implemented as a class hierarchy of algorithms
- an algorithm uses data that clients shouldn't know about. Use the Strategy pattern to avoid exposing complex, algorithm-specific data structures
- a class defines many behaviors, and these appear as multiple conditional statements in its operations. Instead of many conditionals, move related conditional branches into their own Strategy class