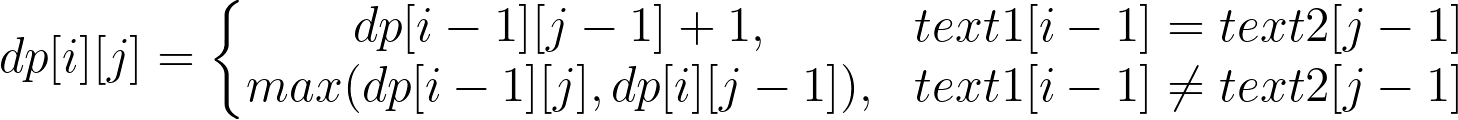给定两个字符串 text1 和 text2,返回这两个字符串的最长 公共子序列 的长度。如果不存在 公共子序列 ,返回 0 。
一个字符串的 子序列 是指这样一个新的字符串:它是由原字符串在不改变字符的相对顺序的情况下删除某些字符(也可以不删除任何字符)后组成的新字符串。
- 例如,
"ace"是"abcde"的子序列,但"aec"不是"abcde"的子序列。
两个字符串的 公共子序列 是这两个字符串所共同拥有的子序列。
示例 1:
输入:text1 = "abcde", text2 = "ace" 输出:3 解释:最长公共子序列是 "ace" ,它的长度为 3 。
示例 2:
输入:text1 = "abc", text2 = "abc" 输出:3 解释:最长公共子序列是 "abc" ,它的长度为 3 。
示例 3:
输入:text1 = "abc", text2 = "def" 输出:0 解释:两个字符串没有公共子序列,返回 0 。
提示:
1 <= text1.length, text2.length <= 1000text1和text2仅由小写英文字符组成。
方法一:动态规划
定义 dp[i][j] 表示 text1[0:i-1] 和 text2[0:j-1] 的最长公共子序列(闭区间)。
递推公式如下:
时间复杂度:$O(mn)$。
class Solution:
def longestCommonSubsequence(self, text1: str, text2: str) -> int:
m, n = len(text1), len(text2)
dp = [[0] * (n + 1) for _ in range(m + 1)]
for i in range(1, m + 1):
for j in range(1, n + 1):
if text1[i - 1] == text2[j - 1]:
dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j - 1] + 1
else:
dp[i][j] = max(dp[i - 1][j], dp[i][j - 1])
return dp[-1][-1]class Solution {
public int longestCommonSubsequence(String text1, String text2) {
int m = text1.length(), n = text2.length();
int[][] dp = new int[m + 1][n + 1];
for (int i = 1; i <= m; ++i) {
for (int j = 1; j <= n; ++j) {
if (text1.charAt(i - 1) == text2.charAt(j - 1)) {
dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j - 1] + 1;
} else {
dp[i][j] = Math.max(dp[i - 1][j], dp[i][j - 1]);
}
}
}
return dp[m][n];
}
}class Solution {
public:
int longestCommonSubsequence(string text1, string text2) {
int m = text1.size(), n = text2.size();
vector<vector<int>> dp(m + 1, vector<int>(n + 1));
for (int i = 1; i <= m; ++i)
{
for (int j = 1; j <= n; ++j)
{
if (text1[i - 1] == text2[j - 1]) dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j - 1] + 1;
else dp[i][j] = max(dp[i - 1][j], dp[i][j - 1]);
}
}
return dp[m][n];
}
};func longestCommonSubsequence(text1 string, text2 string) int {
m, n := len(text1), len(text2)
dp := make([][]int, m+1)
for i := 0; i <= m; i++ {
dp[i] = make([]int, n+1)
}
for i := 1; i <= m; i++ {
for j := 1; j <= n; j++ {
if text1[i-1] == text2[j-1] {
dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j-1] + 1
} else {
dp[i][j] = max(dp[i-1][j], dp[i][j-1])
}
}
}
return dp[m][n]
}
func max(a, b int) int {
if a > b {
return a
}
return b
}/**
* @param {string} text1
* @param {string} text2
* @return {number}
*/
var longestCommonSubsequence = function (text1, text2) {
const m = text1.length;
const n = text2.length;
const dp = new Array(m + 1).fill(0).map(() => new Array(n + 1).fill(0));
for (let i = 1; i <= m; ++i) {
for (let j = 1; j <= n; ++j) {
if (text1[i - 1] == text2[j - 1]) {
dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j - 1] + 1;
} else {
dp[i][j] = Math.max(dp[i - 1][j], dp[i][j - 1]);
}
}
}
return dp[m][n];
};function longestCommonSubsequence(text1: string, text2: string): number {
const m = text1.length;
const n = text2.length;
const dp = Array.from({ length: m + 1 }, () => Array(n + 1).fill(0));
for (let i = 1; i <= m; i++) {
for (let j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
if (text1[i - 1] === text2[j - 1]) {
dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j - 1] + 1;
} else {
dp[i][j] = Math.max(dp[i - 1][j], dp[i][j - 1]);
}
}
}
return dp[m][n];
}impl Solution {
pub fn longest_common_subsequence(text1: String, text2: String) -> i32 {
let (m, n) = (text1.len(), text2.len());
let (text1, text2) = (text1.as_bytes(), text2.as_bytes());
let mut dp = vec![vec![0; n + 1]; m + 1];
for i in 1..=m {
for j in 1..=n {
dp[i][j] = if text1[i - 1] == text2[j - 1] {
dp[i - 1][j - 1] + 1
} else {
dp[i - 1][j].max(dp[i][j - 1])
}
}
}
dp[m][n]
}
}