BertViz 是一种交互式工具,用于可视化Transformer语言模型(例如 BERT、GPT2 或 T5)中的注意力。它可以通过支持大多数Huggingface 模型的简单 Python API 在 Jupyter 或 Colab 笔记本中运行。 BertViz 扩展了 Llion Jones 的Tensor2Tensor 可视化工具,提供了多个视图,每个视图都为注意力机制提供了独特的视角。
在Twitter

头部视图可视化同一层中一个或多个注意力头的注意力。它基于Llion Jones出色的Tensor2Tensor 可视化工具。
🕹 尝试交互式 Colab 教程中的头部视图(所有可视化效果均已预加载)。
<span data-target="animated-image.imageContainer">
<img data-target="animated-image.replacedImage" alt="head-view.gif" class="AnimatedImagePlayer-animatedImage" src="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/jessevig/bertviz/master/images/head-view.gif" style="display: block; opacity: 1;">
<canvas class="AnimatedImagePlayer-stillImage" aria-hidden="true" width="425" height="374"></canvas></span></a>
<button data-target="animated-image.imageButton" class="AnimatedImagePlayer-images" tabindex="-1" aria-label="Play head-view.gif" hidden=""></button>
<span class="AnimatedImagePlayer-controls" data-target="animated-image.controls" hidden="">
<button data-target="animated-image.playButton" class="AnimatedImagePlayer-button" aria-label="Play head-view.gif">
<svg aria-hidden="true" focusable="false" class="octicon icon-play" width="16" height="16" viewBox="0 0 16 16" fill="none" xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg">
<path d="M4 13.5427V2.45734C4 1.82607 4.69692 1.4435 5.2295 1.78241L13.9394 7.32507C14.4334 7.63943 14.4334 8.36057 13.9394 8.67493L5.2295 14.2176C4.69692 14.5565 4 14.1739 4 13.5427Z">
</path></svg>
<svg aria-hidden="true" focusable="false" class="octicon icon-pause" width="16" height="16" viewBox="0 0 16 16" xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg">
<rect x="4" y="2" width="3" height="12" rx="1"></rect>
<rect x="9" y="2" width="3" height="12" rx="1"></rect>
</svg>
</button>
<a data-target="animated-image.openButton" aria-label="Open head-view.gif in new window" class="AnimatedImagePlayer-button" href="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/jessevig/bertviz/master/images/head-view.gif" target="_blank">
<svg aria-hidden="true" class="octicon" xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg" viewBox="0 0 16 16" width="16" height="16">
<path fill-rule="evenodd" d="M10.604 1h4.146a.25.25 0 01.25.25v4.146a.25.25 0 01-.427.177L13.03 4.03 9.28 7.78a.75.75 0 01-1.06-1.06l3.75-3.75-1.543-1.543A.25.25 0 0110.604 1zM3.75 2A1.75 1.75 0 002 3.75v8.5c0 .966.784 1.75 1.75 1.75h8.5A1.75 1.75 0 0014 12.25v-3.5a.75.75 0 00-1.5 0v3.5a.25.25 0 01-.25.25h-8.5a.25.25 0 01-.25-.25v-8.5a.25.25 0 01.25-.25h3.5a.75.75 0 000-1.5h-3.5z"></path>
</svg>
</a>
</span>
</span></animated-image>
模型视图显示了所有层和头的注意力的鸟瞰图。
🕹 尝试交互式 Colab 教程中的模型视图(所有可视化均已预加载)。
<span data-target="animated-image.imageContainer">
<img data-target="animated-image.replacedImage" alt="model view" class="AnimatedImagePlayer-animatedImage" src="https://github.com/jessevig/bertviz/raw/master/images/model-view-noscroll.gif" style="display: block; opacity: 1;">
<canvas class="AnimatedImagePlayer-stillImage" aria-hidden="true" width="814" height="757"></canvas></span></a>
<button data-target="animated-image.imageButton" class="AnimatedImagePlayer-images" tabindex="-1" aria-label="Play model view" hidden=""></button>
<span class="AnimatedImagePlayer-controls" data-target="animated-image.controls" hidden="">
<button data-target="animated-image.playButton" class="AnimatedImagePlayer-button" aria-label="Play model view">
<svg aria-hidden="true" focusable="false" class="octicon icon-play" width="16" height="16" viewBox="0 0 16 16" fill="none" xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg">
<path d="M4 13.5427V2.45734C4 1.82607 4.69692 1.4435 5.2295 1.78241L13.9394 7.32507C14.4334 7.63943 14.4334 8.36057 13.9394 8.67493L5.2295 14.2176C4.69692 14.5565 4 14.1739 4 13.5427Z">
</path></svg>
<svg aria-hidden="true" focusable="false" class="octicon icon-pause" width="16" height="16" viewBox="0 0 16 16" xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg">
<rect x="4" y="2" width="3" height="12" rx="1"></rect>
<rect x="9" y="2" width="3" height="12" rx="1"></rect>
</svg>
</button>
<a data-target="animated-image.openButton" aria-label="Open model view in new window" class="AnimatedImagePlayer-button" href="https://github.com/jessevig/bertviz/blob/master/images/model-view-noscroll.gif" target="_blank">
<svg aria-hidden="true" class="octicon" xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg" viewBox="0 0 16 16" width="16" height="16">
<path fill-rule="evenodd" d="M10.604 1h4.146a.25.25 0 01.25.25v4.146a.25.25 0 01-.427.177L13.03 4.03 9.28 7.78a.75.75 0 01-1.06-1.06l3.75-3.75-1.543-1.543A.25.25 0 0110.604 1zM3.75 2A1.75 1.75 0 002 3.75v8.5c0 .966.784 1.75 1.75 1.75h8.5A1.75 1.75 0 0014 12.25v-3.5a.75.75 0 00-1.5 0v3.5a.25.25 0 01-.25.25h-8.5a.25.25 0 01-.25-.25v-8.5a.25.25 0 01.25-.25h3.5a.75.75 0 000-1.5h-3.5z"></path>
</svg>
</a>
</span>
</span></animated-image></p>
神经元视图可视化查询和关键向量中的各个神经元,并显示它们如何用于计算注意力。
🕹 尝试交互式 Colab 教程中的神经元视图(所有可视化均已预加载)。
<span data-target="animated-image.imageContainer">
<img data-target="animated-image.replacedImage" alt="neuron view" class="AnimatedImagePlayer-animatedImage" src="https://github.com/jessevig/bertviz/raw/master/images/neuron-view-dark.gif" style="display: block; opacity: 1;">
<canvas class="AnimatedImagePlayer-stillImage" aria-hidden="true" width="814" height="403"></canvas></span></a>
<button data-target="animated-image.imageButton" class="AnimatedImagePlayer-images" tabindex="-1" aria-label="Play neuron view" hidden=""></button>
<span class="AnimatedImagePlayer-controls" data-target="animated-image.controls" hidden="">
<button data-target="animated-image.playButton" class="AnimatedImagePlayer-button" aria-label="Play neuron view">
<svg aria-hidden="true" focusable="false" class="octicon icon-play" width="16" height="16" viewBox="0 0 16 16" fill="none" xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg">
<path d="M4 13.5427V2.45734C4 1.82607 4.69692 1.4435 5.2295 1.78241L13.9394 7.32507C14.4334 7.63943 14.4334 8.36057 13.9394 8.67493L5.2295 14.2176C4.69692 14.5565 4 14.1739 4 13.5427Z">
</path></svg>
<svg aria-hidden="true" focusable="false" class="octicon icon-pause" width="16" height="16" viewBox="0 0 16 16" xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg">
<rect x="4" y="2" width="3" height="12" rx="1"></rect>
<rect x="9" y="2" width="3" height="12" rx="1"></rect>
</svg>
</button>
<a data-target="animated-image.openButton" aria-label="在新窗口中打开神经元视图" class="AnimatedImagePlayer-button" href="https://github.com/jessevig/bertviz/blob/master/images/neuron-view-dark.gif" target="_blank">
<svg aria-hidden="true" class="octicon" xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg" viewBox="0 0 16 16" width="16" height="16">
<path fill-rule="evenodd" d="M10.604 1h4.146a.25.25 0 01.25.25v4.146a.25.25 0 01-.427.177L13.03 4.03 9.28 7.78a.75.75 0 01-1.06-1.06l3.75-3.75-1.543-1.543A.25.25 0 0110.604 1zM3.75 2A1.75 1.75 0 002 3.75v8.5c0 .966.784 1.75 1.75 1.75h8.5A1.75 1.75 0 0014 12.25v-3.5a.75.75 0 00-1.5 0v3.5a.25.25 0 01-.25.25h-8.5a.25.25 0 01-.25-.25v-8.5a.25.25 0 01.25-.25h3.5a.75.75 0 000-1.5h-3.5z"></path>
</svg>
</a>
</span>
</span></animated-image></p>
从命令行:
pip install bertviz
您还必须安装 Jupyter Notebook 和 ipywidgets:
pip install jupyterlab pip install ipywidgets
(如果您在安装 Jupyter 或 ipywidgets 时遇到任何问题,请参阅此处和此处的文档。)
要创建新的 Jupyter 笔记本,只需运行:
jupyter notebook
然后如果出现提示,请单击New并选择Python 3 (ipykernel)。
To run in Colab, simply add the following cell at the beginning of your Colab notebook:
!pip install bertviz
Run the following code to load the xtremedistil-l12-h384-uncased model and display it in the model view:
from transformers import AutoTokenizer, AutoModel, utils from bertviz import model_view utils.logging.set_verbosity_error() # Suppress standard warningsmodel_name = "microsoft/xtremedistil-l12-h384-uncased" # Find popular HuggingFace models here: https://huggingface.co/models input_text = "The cat sat on the mat"
model = AutoModel.from_pretrained(model_name, output_attentions=True) # Configure model to return attention values tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_name) inputs = tokenizer.encode(input_text, return_tensors='pt') # Tokenize input text outputs = model(inputs) # Run model attention = outputs[-1] # Retrieve attention from model outputs tokens = tokenizer.convert_ids_to_tokens(inputs[0]) # Convert input ids to token strings model_view(attention, tokens) # Display model view
model_name = "microsoft/xtremedistil-l12-h384-uncased" # Find popular HuggingFace models here: https://huggingface.co/models
input_text = "The cat sat on the mat"
model = AutoModel.from_pretrained(model_name, output_attentions=True) # Configure model to return attention values
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_name)
inputs = tokenizer.encode(input_text, return_tensors='pt') # Tokenize input text
outputs = model(inputs) # Run model
attention = outputs[-1] # Retrieve attention from model outputs
tokens = tokenizer.convert_ids_to_tokens(inputs[0]) # Convert input ids to token strings
model_view(attention, tokens) # Display model view" tabindex="0" role="button">
The visualization may take a few seconds to load. Feel free to experiment with different input texts and models. See Documentation for additional use cases and examples, e.g., encoder-decoder models.
You may also run any of the sample notebooks included with BertViz:
git clone --depth 1 [email protected]:jessevig/bertviz.git cd bertviz/notebooks jupyter notebook
Check out the Interactive Colab Tutorial to learn more about BertViz and try out the tool. Note: all visualizations are pre-loaded, so there is no need to execute any cells.
- Self-attention models (BERT, GPT-2, etc.)
- Encoder-decoder models (BART, T5, etc.)
- Installing from source
- Additional options
- Limitations
First load a Huggingface model, either a pre-trained model as shown below, or your own fine-tuned model.
Be sure to set output_attentions=True.
from transformers import AutoTokenizer, AutoModel, utils utils.logging.set_verbosity_error() # Suppress standard warnings tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("bert-base-uncased") model = AutoModel.from_pretrained("bert-base-uncased", output_attentions=True)
Then prepare inputs and compute attention:
inputs = tokenizer.encode("The cat sat on the mat", return_tensors='pt') outputs = model(inputs) attention = outputs[-1] # Output includes attention weights when output_attentions=True tokens = tokenizer.convert_ids_to_tokens(inputs[0])
Finally, display the attention weights using the head_view or model_view
functions:
from bertviz import head_view head_view(attention, tokens)
Examples: DistilBERT (Model View Notebook, Head View Notebook)
For full API, please refer to the source code for the head view or model view.
The neuron view is invoked differently than the head view or model view, due to requiring access to the model's query/key vectors, which are not returned through the Huggingface API. It is currently limited to custom versions of BERT, GPT-2, and RoBERTa included with BertViz.
# Import specialized versions of models (that return query/key vectors) from bertviz.transformers_neuron_view import BertModel, BertTokenizer from bertviz.neuron_view import showmodel_type = 'bert' model_version = 'bert-base-uncased' do_lower_case = True sentence_a = "The cat sat on the mat" sentence_b = "The cat lay on the rug" model = BertModel.from_pretrained(model_version, output_attentions=True) tokenizer = BertTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_version, do_lower_case=do_lower_case) show(model, model_type, tokenizer, sentence_a, sentence_b, layer=2, head=0)
model_type = 'bert' model_version = 'bert-base-uncased' do_lower_case = True sentence_a = "The cat sat on the mat" sentence_b = "The cat lay on the rug" model = BertModel.from_pretrained(model_version, output_attentions=True) tokenizer = BertTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_version, do_lower_case=do_lower_case) show(model, model_type, tokenizer, sentence_a, sentence_b, layer=2, head=0)" tabindex="0" role="button">
Examples: BERT (Notebook, Colab) • GPT-2 (Notebook, Colab) • RoBERTa (Notebook)
For full API, please refer to the source.
The head view and model view both support encoder-decoder models.
First, load an encoder-decoder model:
from transformers import AutoTokenizer, AutoModeltokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("Helsinki-NLP/opus-mt-en-de") model = AutoModel.from_pretrained("Helsinki-NLP/opus-mt-en-de", output_attentions=True)
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("Helsinki-NLP/opus-mt-en-de") model = AutoModel.from_pretrained("Helsinki-NLP/opus-mt-en-de", output_attentions=True)" tabindex="0" role="button">
Then prepare the inputs and compute attention:
encoder_input_ids = tokenizer("She sees the small elephant.", return_tensors="pt", add_special_tokens=True).input_ids with tokenizer.as_target_tokenizer(): decoder_input_ids = tokenizer("Sie sieht den kleinen Elefanten.", return_tensors="pt", add_special_tokens=True).input_idsoutputs = model(input_ids=encoder_input_ids, decoder_input_ids=decoder_input_ids)
encoder_text = tokenizer.convert_ids_to_tokens(encoder_input_ids[0]) decoder_text = tokenizer.convert_ids_to_tokens(decoder_input_ids[0])
outputs = model(input_ids=encoder_input_ids, decoder_input_ids=decoder_input_ids)
encoder_text = tokenizer.convert_ids_to_tokens(encoder_input_ids[0]) decoder_text = tokenizer.convert_ids_to_tokens(decoder_input_ids[0])" tabindex="0" role="button">
Finally, display the visualization using either head_view or model_view.
from bertviz import model_view model_view( encoder_attention=outputs.encoder_attentions, decoder_attention=outputs.decoder_attentions, cross_attention=outputs.cross_attentions, encoder_tokens= encoder_text, decoder_tokens = decoder_text )
You may select Encoder, Decoder, or Cross attention from the drop-down in the upper left corner of the visualization.
Examples: MarianMT (Notebook) • BART (Notebook)
For full API, please refer to the source code for the head view or model view.
git clone https://github.com/jessevig/bertviz.git
cd bertviz
python setup.py developThe model view and neuron view support dark (default) and light modes. You may set the mode using
the display_mode parameter:
model_view(attention, tokens, display_mode="light")
To improve the responsiveness of the tool when visualizing larger models or inputs, you may set the include_layers
parameter to restrict the visualization to a subset of layers (zero-indexed). This option is available in the head view and model
view.
Example: Render model view with only layers 5 and 6 displayed
model_view(attention, tokens, include_layers=[5, 6])
For the model view, you may also restrict the visualization to a subset of attention heads (zero-indexed) by setting the
include_heads parameter.
In the head view, you may choose a specific layer and collection of heads as the default selection when the
visualization first renders. Note: this is different from the include_heads/include_layers parameter (above), which
removes layers and heads from the visualization completely.
Example: Render head view with layer 2 and heads 3 and 5 pre-selected
head_view(attention, tokens, layer=2, heads=[3,5])
You may also pre-select a specific layer and single head for the neuron view.
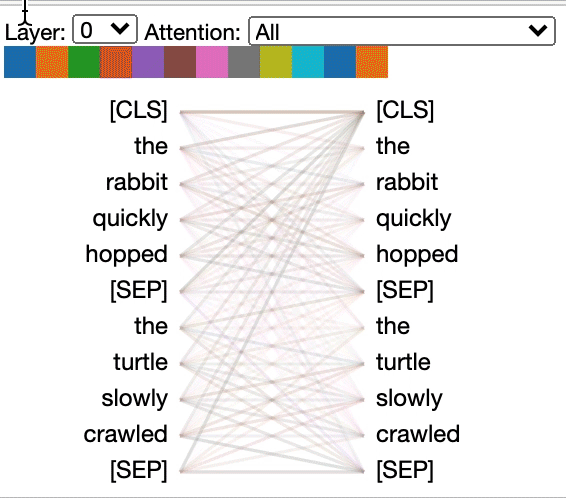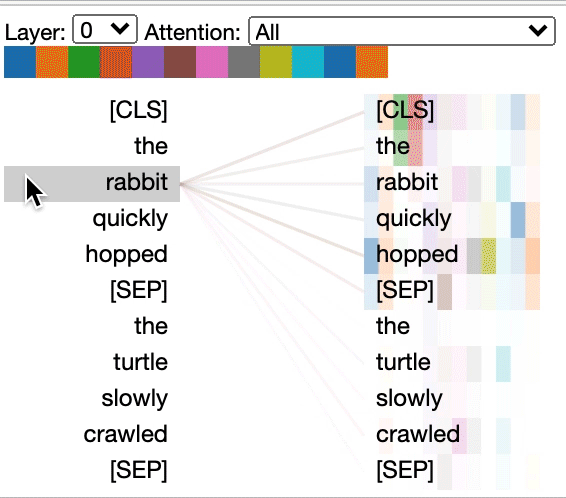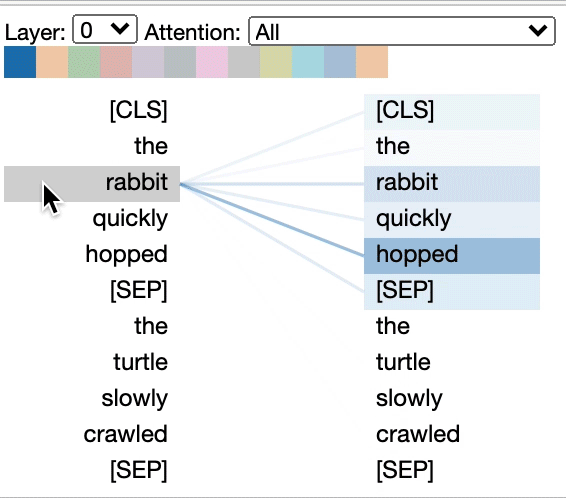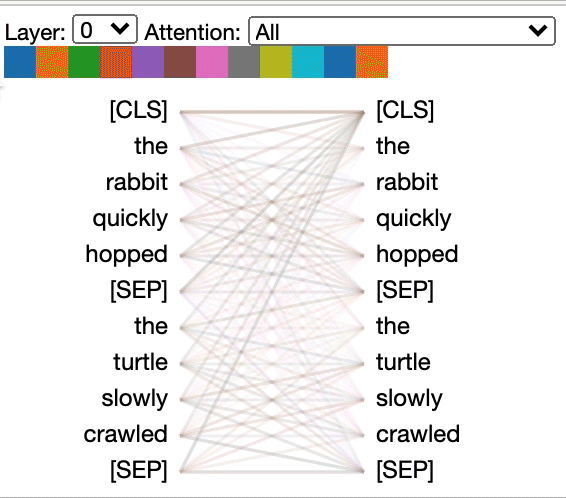
Some models, e.g. BERT, accept a pair of sentences as input. BertViz optionally supports a drop-down menu that allows user to filter attention based on which sentence the tokens are in, e.g. only show attention between tokens in first sentence and tokens in second sentence.
To enable this feature when invoking the head_view or model_view functions, set
the sentence_b_start parameter to the start index of the second sentence. Note that the method for computing this
index will depend on the model.
Example (BERT):
from bertviz import head_view from transformers import AutoTokenizer, AutoModel, utils utils.logging.set_verbosity_error() # Suppress standard warnings# NOTE: This code is model-specific model_version = 'bert-base-uncased' model = AutoModel.from_pretrained(model_version, output_attentions=True) tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_version) sentence_a = "the rabbit quickly hopped" sentence_b = "The turtle slowly crawled" inputs = tokenizer.encode_plus(sentence_a, sentence_b, return_tensors='pt') input_ids = inputs['input_ids'] token_type_ids = inputs['token_type_ids'] # token type id is 0 for Sentence A and 1 for Sentence B attention = model(input_ids, token_type_ids=token_type_ids)[-1] sentence_b_start = token_type_ids[0].tolist().index(1) # Sentence B starts at first index of token type id 1 token_ids = input_ids[0].tolist() # Batch index 0 tokens = tokenizer.convert_ids_to_tokens(token_ids)
head_view(attention, tokens, sentence_b_start)
model_version = 'bert-base-uncased'
model = AutoModel.from_pretrained(model_version, output_attentions=True)
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_version)
sentence_a = "the rabbit quickly hopped"
sentence_b = "The turtle slowly crawled"
inputs = tokenizer.encode_plus(sentence_a, sentence_b, return_tensors='pt')
input_ids = inputs['input_ids']
token_type_ids = inputs['token_type_ids'] # token type id is 0 for Sentence A and 1 for Sentence B
attention = model(input_ids, token_type_ids=token_type_ids)[-1]
sentence_b_start = token_type_ids[0].tolist().index(1) # Sentence B starts at first index of token type id 1
token_ids = input_ids[0].tolist() # Batch index 0
tokens = tokenizer.convert_ids_to_tokens(token_ids)
head_view(attention, tokens, sentence_b_start)" tabindex="0" role="button">
To enable this option in the neuron view, simply set the sentence_a and sentence_b parameters in neuron_view.show().
Support to retrieve the generated HTML representations has been added to head_view, model_view and neuron_view.
Setting the 'html_action' parameter to 'return' will make the function call return a single HTML Python object that can be further processed. Remember you can access the HTML source using the data attribute of a Python HTML object.
The default behavior for 'html_action' is 'view', which will display the visualization but won't return the HTML object.
This functionality is useful if you need to:
- Save the representation as an independent HTML file that can be accessed via web browser
- Use custom display methods as the ones needed in Databricks to visualize HTML objects
Example (head and model views):
from transformers import AutoTokenizer, AutoModel, utils from bertviz import head_viewutils.logging.set_verbosity_error() # Suppress standard warnings tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("bert-base-uncased") model = AutoModel.from_pretrained("bert-base-uncased", output_attentions=True)
inputs = tokenizer.encode("The cat sat on the mat", return_tensors='pt') outputs = model(inputs) attention = outputs[-1] # Output includes attention weights when output_attentions=True tokens = tokenizer.convert_ids_to_tokens(inputs[0])
html_head_view = head_view(attention, tokens, html_action='return')
with open("PATH_TO_YOUR_FILE/head_view.html", 'w') as file: file.write(html_head_view.data)
utils.logging.set_verbosity_error() # Suppress standard warnings tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("bert-base-uncased") model = AutoModel.from_pretrained("bert-base-uncased", output_attentions=True)
inputs = tokenizer.encode("The cat sat on the mat", return_tensors='pt') outputs = model(inputs) attention = outputs[-1] # Output includes attention weights when output_attentions=True tokens = tokenizer.convert_ids_to_tokens(inputs[0])
html_head_view = head_view(attention, tokens, html_action='return')
with open("PATH_TO_YOUR_FILE/head_view.html", 'w') as file: file.write(html_head_view.data) " tabindex="0" role="button">
Example (neuron view):
# Import specialized versions of models (that return query/key vectors) from bertviz.transformers_neuron_view import BertModel, BertTokenizer from bertviz.neuron_view import showmodel_type = 'bert' model_version = 'bert-base-uncased' do_lower_case = True sentence_a = "The cat sat on the mat" sentence_b = "The cat lay on the rug" model = BertModel.from_pretrained(model_version, output_attentions=True) tokenizer = BertTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_version, do_lower_case=do_lower_case) html_neuron_view = show(model, model_type, tokenizer, sentence_a, sentence_b, layer=2, head=0, html_action='return')
with open("PATH_TO_YOUR_FILE/neuron_view.html", 'w') as file: file.write(html_neuron_view.data)
model_type = 'bert' model_version = 'bert-base-uncased' do_lower_case = True sentence_a = "The cat sat on the mat" sentence_b = "The cat lay on the rug" model = BertModel.from_pretrained(model_version, output_attentions=True) tokenizer = BertTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_version, do_lower_case=do_lower_case) html_neuron_view = show(model, model_type, tokenizer, sentence_a, sentence_b, layer=2, head=0, html_action='return')
with open("PATH_TO_YOUR_FILE/neuron_view.html", 'w') as file: file.write(html_neuron_view.data)" tabindex="0" role="button">
The head view and model view may be used to
visualize self-attention for any standard Transformer model,
as long as the attention weights are available and follow the format specified in head_view and
model_view (which is the format
returned from Huggingface models). In some case, Tensorflow checkpoints may be loaded as Huggingface models as described
in the
Huggingface docs.
- 该工具专为较短的输入而设计,如果输入文本很长和/或模型很大,则可能会运行缓慢。为了缓解这种情况,您可能希望通过设置参数来过滤显示的图层
include_layers,如上所述。 - 在 Colab 上运行时,当输入文本较长时,某些可视化将失败(运行时断开连接)。为了缓解这种情况,您可能希望通过设置参数来过滤显示的图层
include_layers,如上所述。 - 神经元视图仅支持该工具附带的自定义 BERT、GPT-2 和 RoBERTa 模型。该视图需要访问查询和键向量,这需要修改模型代码(参见
transformers_neuron_view目录),仅对这三个模型进行了修改。
- 可视化注意力权重阐明了模型内的一种架构,但不一定为预测提供直接解释[ 1,2,3 ]。
- 如果您希望了解输入文本如何更直接地影响输出预测,请考虑Language Interpretability Toolkit或Ecco等工具提供的显着性方法。
Transformer 模型中注意力的多尺度可视化(ACL 系统演示 2019)。
@inproceedings{vig-2019-multiscale, title = "A Multiscale Visualization of Attention in the Transformer Model", author = "Vig, Jesse", booktitle = "Proceedings of the 57th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics: System Demonstrations", month = jul, year = "2019", address = "Florence, Italy", publisher = "Association for Computational Linguistics", url = "https://www.aclweb.org/anthology/P19-3007", doi = "10.18653/v1/P19-3007", pages = "37--42", }
我们感谢以下项目的作者,这些项目已纳入此存储库:
该项目根据 Apache 2.0 许可证获得许可 -有关详细信息,请参阅许可证文件