牛客OJ:用两个栈实现队列
九度OJ:http://ac.jobdu.com/problem.php?pid=1512
GitHub代码: 007-用两个栈实现队列
CSDN题解:剑指Offer--007-用两个栈实现队列
| 牛客OJ | 九度OJ | CSDN题解 | GitHub代码 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 用两个栈实现队列 | 1512-用两个栈实现队列 | 剑指Offer--007-用两个栈实现队列 | 006-重建二叉树 |
**您也可以选择[回到目录-剑指Offer--题集目录索引](http://blog.csdn.net/gatieme/article/details/51916802)**
题目描述
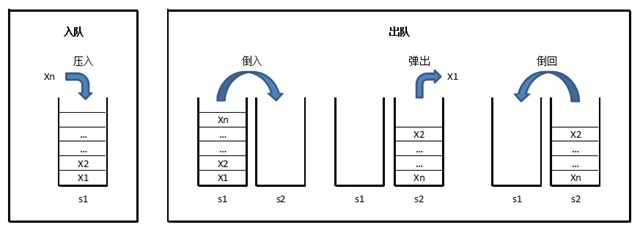
用两个栈来实现一个队列,完成队列的Push和Pop操作。 队列中的元素为int类型。
始终维护s1作为存储空间,以s2作为临时缓冲区。
-
入队时,将元素压入s1。
-
出队时,将s1的元素逐个“倒入”(弹出并压入)s2,将s2的顶元素弹出作为出队元素,之后再将s2剩下的元素逐个“倒回”s1。
见下面示意图:
上述思路,可行性毋庸置疑。但有一个细节是可以优化一下的。即:在出队时,将s1的元素逐个“倒入”s2时,原在s1栈底的元素,不用“倒入”s2(即只“倒”s1.Count()-1个),可直接弹出作为出队元素返回。这样可以减少一次压栈的操作。约有一半人,经提示后能意识到此问题。
上述思路,有些变种,如:
-
入队时,先判断s1是否为空,如不为空,说明所有元素都在s1,此时将入队元素直接压入s1;如为空,要将s2的元素逐个“倒回”s1,再压入入队元素。
-
出队时,先判断s2是否为空,如不为空,直接弹出s2的顶元素并出队;如为空,将s1的元素逐个“倒入”s2,把最后一个元素弹出并出队。 有些人能同时想到大众方法和变种,应该说头脑还是比较灵光的。
相对于第一种方法,变种的s2好像比较“懒”,每次出队后,并不将元素“倒回”s1,如果赶上下次还是出队操作,效率会高一些,但下次如果是入队操作,效率不如第一种方法。我有时会让面试者分析比较不同方法的性能。我感觉(没做深入研究),入队、出队操作随机分布时,上述两种方法总体上时间复杂度和空间复杂度应该相差无几(无非多个少个判断)。
但是每次倒来倒去的还是效率不太好,因此我们思考出了如下的变种
始终维护s1作为输入栈,以s2作为输出栈
-
入队时,将元素压入s1。
-
出队时,判断s2是否为空,如不为空,则直接弹出顶元素;如为空,则将s1的元素逐个“倒入”s2,把最后一个元素弹出并出队。 这个思路,避免了反复“倒”栈,仅在需要时才“倒”一次。但在实际面试中很少有人说出,可能是时间较少的缘故吧。
#include <iostream>
#include <stack>
using namespace std;
// 调试开关
#define __tmain main
#ifdef __tmain
#define debug cout
#else
#define debug 0 && cout
#endif // __tmain
class Solution
{
public:
void push(int node)
{
stackIn.push(node);
}
int pop()
{
int node = -1;
// 两个栈都是NULL的时候,整个队列为空
if(this->empty( ) == true)
{
debug <<"整个队列为NULL" <<endl;
return -1;
}
else
{
// 否则队列中有元素
// 此时分两种情况,
// 当输出栈不为空的时候, 直接将输出栈中元素弹出即可
// 当输出栈为NULL, 但是输入栈不为空的时候,需要将输入栈的元素全部倒入输出栈中
if(stackOut.empty() == true) // 此时输出栈为空, 输入栈必不为空
{
// 此时缓冲栈(输出栈)中没有元素
// 需要将输入栈中的元素倒入输出栈
// 看输入栈中有没有元素
// 否则将元素从输入栈导入输出栈
while(stackIn.empty( ) != true)
{
node = stackIn.top( );
stackIn.pop( );
stackOut.push(node);
debug <<node <<"导入输出栈" <<endl;
}
}
node = stackOut.top( );
stackOut.pop( );
debug <<"队头元素" <<node <<endl;
}
return node;
}
bool empty( )
{
return (stackIn.empty() == true && stackOut.empty() == true);
}
private:
stack<int> stackIn;
stack<int> stackOut;
};
int __tmain( )
{
Solution solu;
solu.push(1);
solu.push(2);
solu.push(3);
solu.push(4);
int node;
while(solu.empty() != true)
{
cout <<solu.pop( );
}
return 0;
}