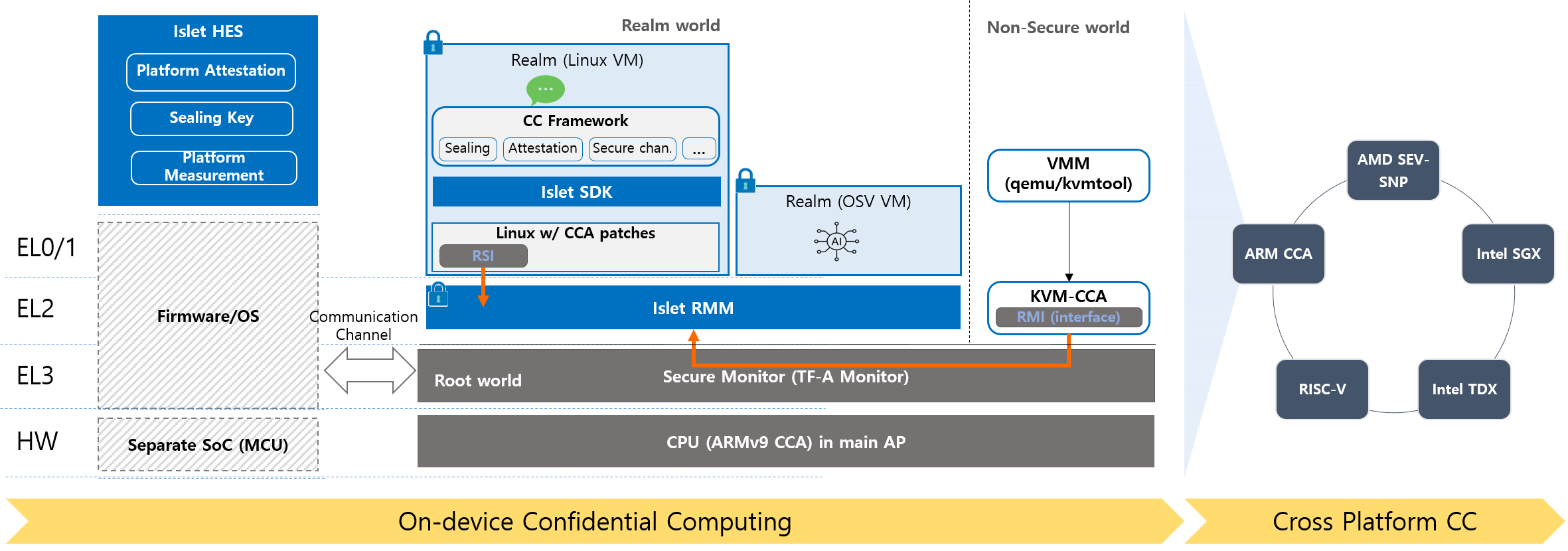
Islet is an open-source software project written in Rust that enables confidential computing on ARM architecture devices using the ARMv9 CCA. The primary objective of Islet is to enable on-device confidential computing and protect user privacy on end user devices.
While current confidential computing solutions mainly focus on server-side protection, it is equally important to safeguard user information at the user device level since that is where private data collection initially occurs. Furthermore, as more and more users rely on privacy apps such as private messengers, secure emails, password managers, and web browsers with privacy settings, there is a growing need to ensure privacy on user devices. Islet, an open-source project, addresses this need by providing a platform for ARM-based confidential computing.
Enabling CC on user devices will not only establish end-to-end CC throughout the entire data processing path, but it will also help create a secure computation model that enables processing of user private data on the user device using the same components that previously were employed at the server side without disclosing business logic. Furthermore, on-device confidential computing will be a key enabler for machine-to-machine computing without the need for server intervention
- Realm Management Monitor
- Hardware Enforced Security
- Confidential Computing API Standardization
- Use case : Confidential Machine Learning
Islet provides a platform for running virtual machines (VMs) confidentially, with standard SDKs for easy integration with other confidential computing frameworks at upper layers. The platform consists of two key components: the Islet Realm Management Monitor (Islet-RMM) and Islet Hardware Enforced Security (Islet-HES).
Islet RMMoperates at EL2 in the Realm world on the application processor cores and manages the confidential VMs, known as realms.- On the other hand,
Islet HESperforms device boot measurement, generates platform attestation reports, and manages sealing key functionality within a secure hardware IP apart from the main application processor.
In designing Islet, we aim to to address the current security challenges in confidential computing technologies right from the very beginning. To ensure that our software is built with safety in mind, we have chosen to use the Rust programming language, known for its unique security model that ensures memory safety and concurrency safety. Moving forward, we also plan to incorporate formal verification techniques to further enhance the security of our design and implementation.
For more information, please visit our developer site.
- This video shows how Islet achieves an end-to-end confidential machine learning with a chat-bot scenario.
- This video flows as follows.
- It starts with a slide that describes all components involved in this demo. All components will run on confidential computing platforms.
- (feed an ML model) The model provider feeds the ML model into the ML server. This is done through a secure channel established with the aid of the certifier framework.
- (run a coding assistant) A mobile device user asks a chat-bot application that runs on Islet for generating a function. And then, that request is passed on to the ML server through a secure channel. Finally, the user can see the result (i.e., function).
- (launch a malicious server) This time, we launch a malicious server to show a failure case. When it attempts to join the certifier service (on the right side of the screen), it will not pass authentication as it results in a different measurement. Therefore, the malicious server cannot interact with the mobile device user in the first place.
- To download this video, click here.