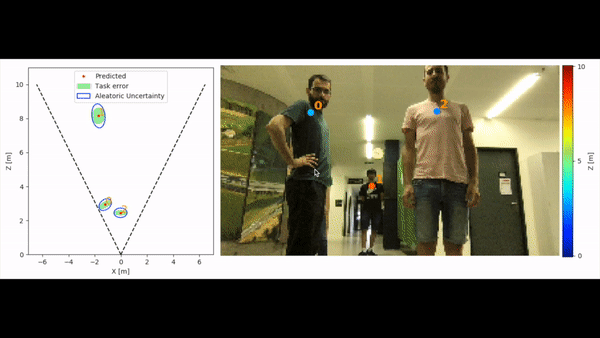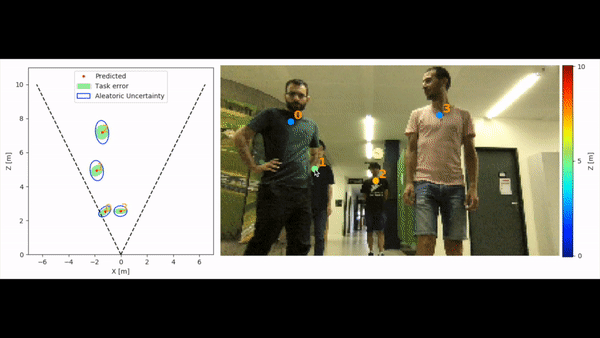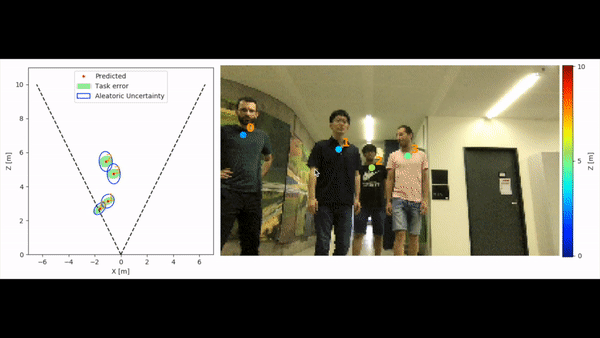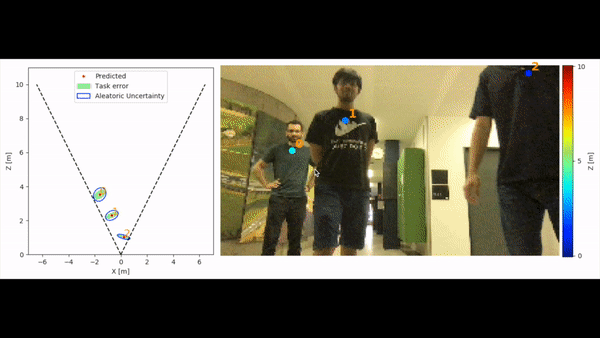
We tackle the fundamentally ill-posed problem of 3D human localization from monocular RGB images. Driven by the limitation of neural networks outputting point estimates, we address the ambiguity in the task by predicting confidence intervals through a loss function based on the Laplace distribution. Our architecture is a light-weight feed-forward neural network that predicts 3D locations and corresponding confidence intervals given 2D human poses. The design is particularly well suited for small training data, cross-dataset generalization, and real-time applications. Our experiments show that we (i) outperform state-of-the-art results on KITTI and nuScenes datasets, (ii) even outperform a stereo-based method for far-away pedestrians, and (iii) estimate meaningful confidence intervals. We further share insights on our model of uncertainty in cases of limited observations and out-of-distribution samples.
@InProceedings{Bertoni_2019_ICCV,
author = {Bertoni, Lorenzo and Kreiss, Sven and Alahi, Alexandre},
title = {MonoLoco: Monocular 3D Pedestrian Localization and Uncertainty Estimation},
booktitle = {The IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV)},
month = {October},
year = {2019}
}
-
Paper on ArXiv
-
Check our video with method description and qualitative results on YouTube
-
Live demo available! (more info in the webcam section)
Python 3 is required. Python 2 is not supported. Do not clone this repository and make sure there is no folder named monoloco in your current directory.
pip3 install monoloco
For development of the monoloco source code itself, you need to clone this repository and then:
pip3 install -e '.[test, prep]'
Python 3.6 or 3.7 is required for nuScenes development kit. All details for Pifpaf pose detector at openpifpaf.
Data
├── arrays
├── models
├── kitti
├── nuscenes
├── logs
Run the following to create the folders:
mkdir data
cd data
mkdir arrays models kitti nuscenes logs
- Download a MonoLoco pre-trained model from
Google Drive and save it in
data/models(default) or in any folder and call it through the command line option--model <model path> - Pifpaf pre-trained model will be automatically downloaded at the first run.
Three standard, pretrained models are available when using the command line option
--checkpoint resnet50,--checkpoint resnet101and--checkpoint resnet152. Alternatively, you can download a Pifpaf pre-trained model from openpifpaf and call it with--checkpoint <pifpaf model path>
All the commands are run through a main file called main.py using subparsers.
To check all the commands for the parser and the subparsers (including openpifpaf ones) run:
python3 -m monoloco.run --helppython3 -m monoloco.run predict --helppython3 -m monoloco.run train --helppython3 -m monoloco.run eval --helppython3 -m monoloco.run prep --help
or check the file monoloco/run.py
The predict script receives an image (or an entire folder using glob expressions),
calls PifPaf for 2d human pose detection over the image
and runs Monoloco for 3d location of the detected poses.
The command --networks defines if saving pifpaf outputs, MonoLoco outputs or both.
You can check all commands for Pifpaf at openpifpaf.
Output options include json files and/or visualization of the predictions on the image in frontal mode,
birds-eye-view mode or combined mode and can be specified with --output_types
-
In case you provide a ground-truth json file to compare the predictions of MonoLoco, the script will match every detection using Intersection over Union metric. The ground truth file can be generated using the subparser
prepand called with the command--path_gt. Check preprocess section for more details or download the file from here. -
In case you don't provide a ground-truth file, the script will look for a predefined path. If it does not find the file, it will generate images with all the predictions without ground-truth matching.
Below an example with and without ground-truth matching. They have been created (adding or removing --path_gt) with:
python3 -m monoloco.run predict --glob docs/002282.png --output_types combined --scale 2 --model data/models/monoloco-190513-1437.pkl --n_dropout 50 --z_max 30
With ground truth matching (only matching people):

Without ground_truth matching (all the detected people):
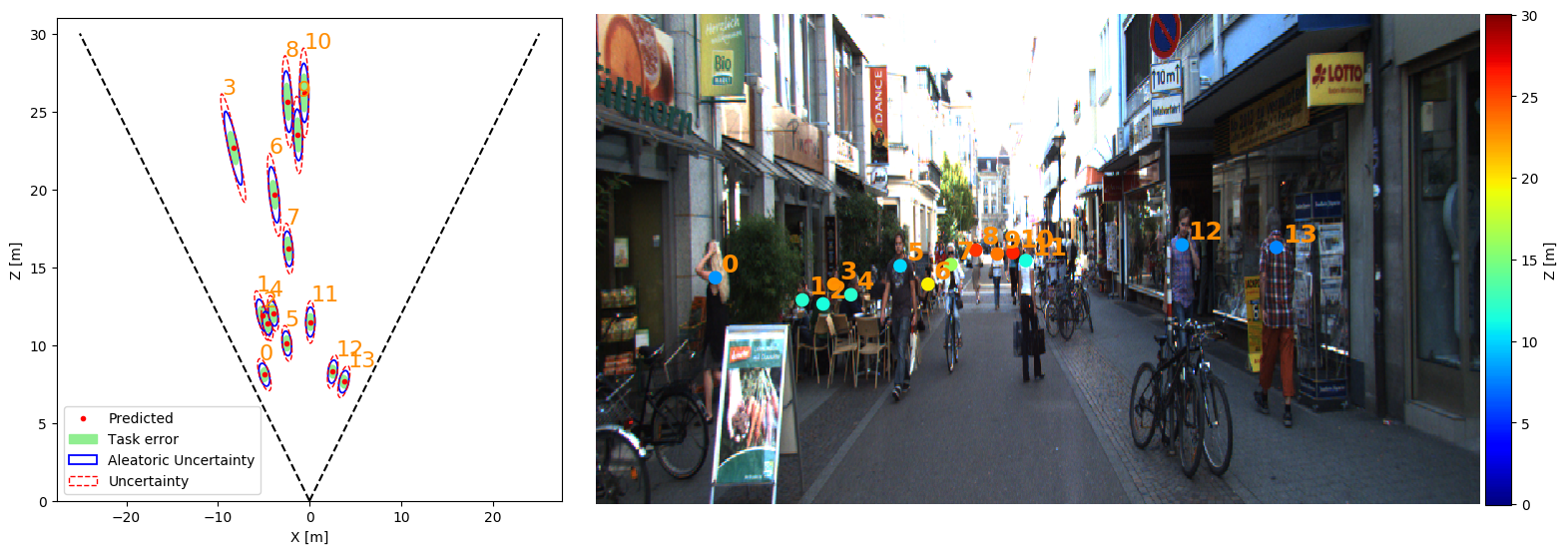

To accurately estimate distance, the focal length is necessary.
However, it is still possible to test Monoloco on images where the calibration matrix is not available.
Absolute distances are not meaningful but relative distance still are.
Below an example on a generic image from the web, created with:
python3 -m monoloco.run predict --glob docs/surf.jpg --output_types combined --model data/models/monoloco-190513-1437.pkl --n_dropout 50 --z_max 25
MonoLoco can run on personal computers with only CPU and low resolution images (e.g. 256x144) at ~2fps.
It support 3 types of visualizations: front, bird and combined.
Multiple visualizations can be combined in different windows.
The above gif has been obtained running on a Macbook the command:
python3 -m monoloco.run predict --webcam --scale 0.2 --output_types combined --z_max 10 --checkpoint resnet50 --model data/models/monoloco-190513-1437.pkl
Download KITTI ground truth files and camera calibration matrices for training
from here and
save them respectively into data/kitti/gt and data/kitti/calib.
To extract pifpaf joints, you also need to download training images soft link the folder in data/kitti/images
Download nuScenes dataset from nuScenes (either Mini or TrainVal),
save it anywhere and soft link it in data/nuscenes
nuScenes preprocessing requires pip3 install nuscenes-devkit
MonoLoco is trained using 2D human pose joints. To create them run pifaf over KITTI or nuScenes training images.
You can create them running the predict script and using --networks pifpaf.
MonoLoco is trained using 2D human pose joints matched with the ground truth location provided by
nuScenes or KITTI Dataset. To create the joints run: python3 -m monoloco.run prep specifying:
-
--dir_annannotation directory containing Pifpaf joints of KITTI or nuScenes. -
--datasetWhich dataset to preprocess. For nuscenes, all three versions of the dataset are supported: nuscenes_mini, nuscenes, nuscenes_teaser.
The preprocessing script also outputs a second json file called names-.json which provide a dictionary indexed by the image name to easily access ground truth files for evaluation and prediction purposes.
Provide the json file containing the preprocess joints as argument.
As simple as python3 -m monoloco.run --train --joints <json file path>
All the hyperparameters options can be checked at python3 -m monoloco.run train --help.
Random search in log space is provided. An example: python3 -m monoloco.run train --hyp --multiplier 10 --r_seed 1.
One iteration of the multiplier includes 6 runs.
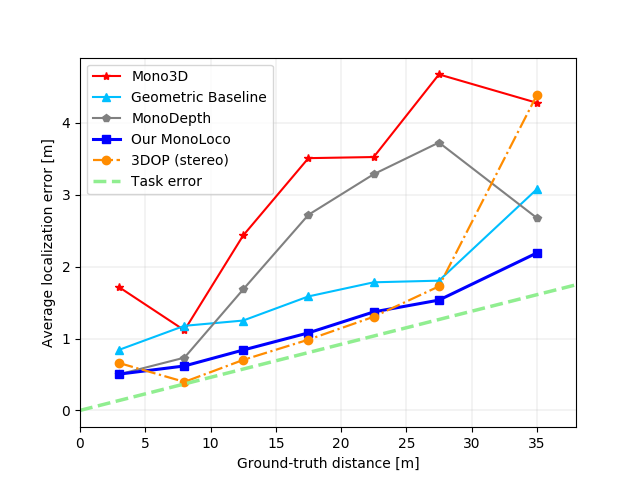
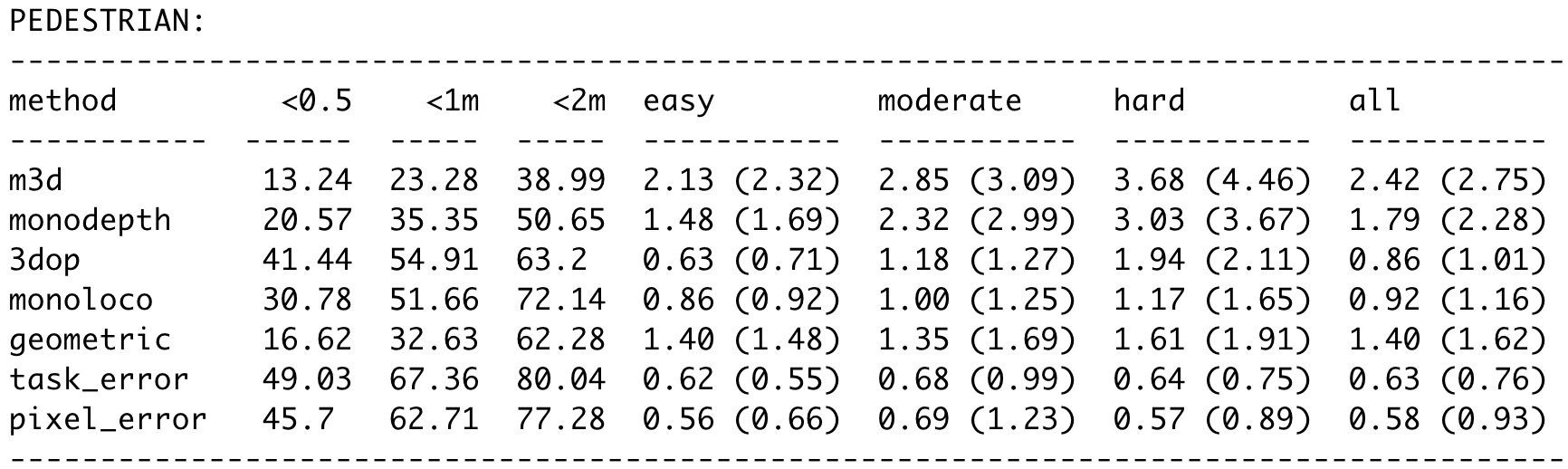
We provide evaluation on KITTI for models trained on nuScenes or KITTI. We compare them with other monocular and stereo Baselines:
Mono3D, 3DOP, MonoDepth and our Geometrical Baseline.
- Mono3D: download validation files from here
and save them into
data/kitti/m3d - 3DOP: download validation files from here
and save them into
data/kitti/3dop - MonoDepth: compute an average depth for every instance using the following script
here
and save them into
data/kitti/monodepth - GeometricalBaseline: A geometrical baseline comparison is provided.
The average geometrical value for comparison can be obtained running:
python3 -m monoloco.run eval --geometric --model data/models/monoloco-190719-0923.pkl --joints data/arrays/joints-nuscenes_teaser-190717-1424.json
The following results are obtained running:
python3 -m monoloco.run eval --model data/models/monoloco-190719-0923.pkl --generate --dir_ann <folder containing pifpaf annotations of KITTI images>