As enterprise adoption of Kubernetes is growing, multiple teams collaborate on a Kubernetes cluster to realize the broader organizational goals. Typically, there is one team that is offering a service that the other team is looking to consume. It can be an ISV offering a service for their data & analytics software that their customer is looking to consume, or it can be a platform team offering a service for an internal application that the product team is planning to use (e.g secret management, data processing, etc.). Such teams can be thought of as providers and consumers in the context of delivering and consuming software on Kubernetes.
KubePlus is a turn-key solution that enables provider teams to deliver any application packaged as a Helm chart as-a-service to its consumers. It does this by abstracting the application Helm chart under provider and consumer APIs.
KubePlus offers following benefits towards deploying a Kubernetes-native application (Helm chart) in SaaS form:
- Application-specific provider and consumer APIs for role based access to the clusters.
- Seamless support for Namespace-based multi-tenancy where each application instance (Helm release) is created in a separate namespace.
- Monitoring and governance of application instances.
- Tracking consumption metrics (cpu, memory, storage and network) at Helm release level. Application providers can use these metrics to define consumption-based chargeback models.
The typical requirements in a service-based delivery model of Kubernetes applications are as follows:
- From cluster admin's perspective it is important to isolate different application instances from one another on the cluster.
- Application consumers need a self-service model to provision application instances.
- Application providers need to be able to troubleshoot and monitor deployed instances of the application.
- Application providers should also be able to track consumption metrics for application instances provisioned on the cluster.
KubePlus achieves these goals as follows. KubePlus defines a provider API to create application-specific consumer APIs.
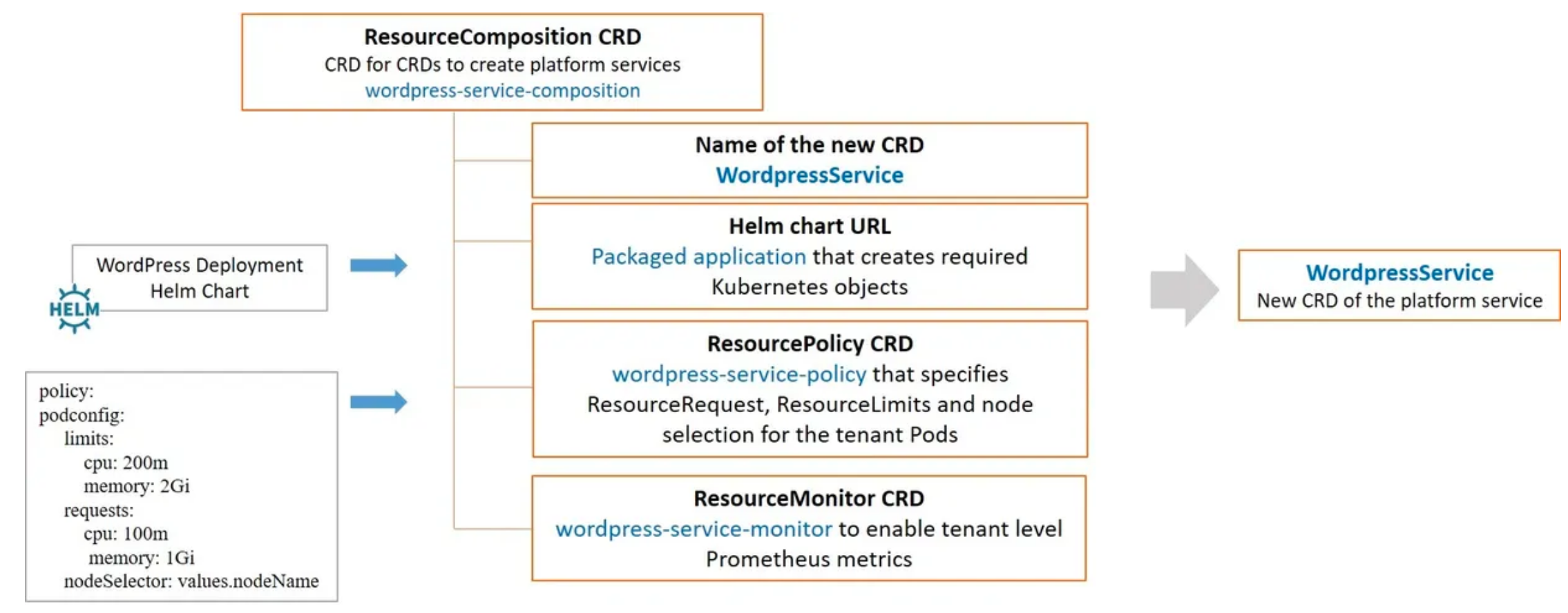
The provider API is a KubePlus CRD (Custom Resource Definition) named ResourceComposition that enables registering an application Helm chart in the cluster by defining a new Kubernetes API (CRD) representing the chart. As part of this, application providers can define application-level policies which KubePlus applies when instantiating the registered chart. The new CRD is essentially the consumer API which the application consumers use to instantiate the registered Helm chart in a self-service manner.
KubePlus offers following functions:
- Create: Create a Kubernetes-native API to represent an application packaged as a Helm chart.
- Govern: Tenant level policies for isolation and resource utilization per application instance.
- Monitor: Tenant level consumption metrics for cpu, memory, storage, network.
- Troubleshoot: Application-level insights through fine-grained Kubernetes resource relationship graphs.
To understand the working of KubePlus, let us see how a Wordpress provider can offer a multi-tenant Wordpress service.
1. Install KubePlus
Cluster administrator installs KubePlus on their cluster.
$ KUBEPLUS_NS=default
$ helm install kubeplus "https://github.com/cloud-ark/operatorcharts/blob/master/kubeplus-chart-2.0.6.tgz?raw=true" -n $KUBEPLUS_NS
2. Retrieve Provider kubeconfig file
Provider registers the application Helm chart in the cluster under a consumer API. For this the provider needs a kubeconfig file. KubePlus creates this kubeconfig file. It has appropriate RBAC policies that enable a provider to register application helm charts under consumer APIs. Cluster admin needs to distribute this kubeconfig file to the provider.
$ kubectl retrieve kubeconfig provider $KUBEPLUS_NS > provider.conf
1. Create consumer API
The provider team defines the consumer API named WordpressService using the ResourceComposition CRD (the provider API). The Wordpress Helm chart that underlies this service is created by the provider team. The spec properties of the WordpressService Custom Resource are the attributes defined in the Wordpress Helm chart's values.yaml.
As part of creating the consumer API, the provider team can define policies such as the cpu and memory that should be allocated to each Wordpress stack or the specific worker node on which to deploy a Wordpress stack, etc. KubePlus will apply these policies to the Helm releases when instantiating the underlying Helm chart.
Here is the ResourceComposition definition for the WordpressService.
2. Grant permission to the consumer to create instances of WordpressService
Before consumers can instantiate WordpressService resources, the provider needs to grant permission to the consumer for that resource. KubePlus comes with a kubectl plugin for this purpose:
kubectl grantpermission consumer wordpressservices provider.conf $KUBEPLUS_NS
The provider's kubeconfig needs to be provided as input to the kubectl grantpermission command.
3. Provider team uses kubeplus kubectl plugins to troubleshoot and monitor WordpressService instances.
Once a consumer has instantiated a WordpressService instance, the provider can monitor and troubleshoot it using the various kubectl plugins that KubePlus provides.
With the kubectl connections plugin provider can check whether all Kubernetes resources have been created as expected. The graphical output makes it easy to check the connectivity between different resources.
kubectl connections WordpressService tenant1 default -k provider.conf -o png -i Namespace:default,ServiceAccount:default -n label,specproperty,envvariable,annotation
Using kubectl metrics plugin provider can check cpu, memory, storage, network ingress/egress for a WordpressService instance. The metrics output is available in pretty, json and prometheus formats.
kubectl metrics WordpressService tenant1 default -o pretty -k provider.conf
The consumer uses WordpressService Custom Resource (the consumer API) to provision an instance of Wordpress stack. The instances can be created using command-line (kubectl) or through a web portal. The portal is one of the KubePlus components running on the cluster and it is accessible through local proxy. Here is consumer portal for WordpressService showing the created tenant1 instance.
Our KubePlus SaaS Manager product offers enterprise-ready control center with embedded Prometheus integration for providers to manage their SaaS across multiple Kubernetes clusters.
KubePlus consists of an Operator and kubectl plugins.
The KubePlus Operator consists of a custom controller, a mutating webhook and the helmer module. Here is a brief summary of these components. Details about them are available here.
The custom controller handles KubePlus CRDs. The primary CRD is ResourceComposition. It is used to:
- Define new CRDs (consumer APIs) wrapping Helm charts.
- Define policies (e.g. cpu/memory limits, node selection, etc.) for service instances.
The mutating webook and helmer modules support the custom controller in delivering the KubePlus experience.
KubePlus kubectl plugins enable providers to discover, monitor and troubleshoot application instances. The primary plugin is: kubectl connections. It tracks resource relationships through owner references, labels, annotations, and spec properties. These relationships enable providers to gain fine grained visibility into running application instances through resource relationship graphs. Additional plugins offer the ability to get aggregated consumption metrics (for cpu, memory, storage, network) and logs at the application instance level.
- Install KubePlus Operator. (Note that you will need Helm v3, and Kubernetes version < 1.20).
$ KUBEPLUS_NS=default (or any namespace in which you want to install KubePlus)
$ helm install kubeplus "https://github.com/cloud-ark/operatorcharts/blob/master/kubeplus-chart-2.0.6.tgz?raw=true" -n $KUBEPLUS_NS
- Install KubePlus kubectl plugins.
$ wget https://github.com/cloud-ark/kubeplus/raw/master/kubeplus-kubectl-plugins.tar.gz
$ gunzip kubeplus-kubectl-plugins.tar.gz
$ tar -xvf kubeplus-kubectl-plugins.tar
$ export KUBEPLUS_HOME=`pwd`
$ export PATH=$KUBEPLUS_HOME/plugins/:$PATH
$ kubectl kubeplus commands
Try the kubectl connections plugin. It can be used with any Kubernetes resource (built-in resources like Pod, Deployment, or custom resources like MysqlCluster).
-
Try following examples:
- Hello World service
- Wordpress service
- Mysql service
- MongoDB service
- Multiple teams with applications deployed later
-
Debug:
- kubectl logs kubeplus $KUBEPLUS_NS -c crd-hook - kubectl logs kubeplus $KUBEPLUS_NS -c helmer - kubectl logs kubeplus $KUBEPLUS_NS -c platform-operator - kubectl logs kubeplus $KUBEPLUS_NS -c webhook-cert-setup - kubectl logs kubeplus $KUBEPLUS_NS -c consumerui -
Cleanup:
- helm delete kubeplus -n $KUBEPLUS_NS - wget https://github.com/cloud-ark/kubeplus/raw/master/deploy/delete-kubeplus-components.sh - ./delete-kubeplus-components.sh
KubePlus is part of CNCF landscape's Application Definition section.
As enterprise teams build their custom platforms using community or in house developed Operators, they need a set of guidelines for Operator readiness in multi-Operator and multi-tenant environments. We have developed the Operator Maturity Model for this purpose. Operator developers are using this model today to ensure that their Operator is a good citizen of the multi-Operator world and ready to serve multi-tenant workloads. It is also being used by Kubernetes cluster administrators for curating community Operators towards building their custom platforms.
-
Being a good citizen of the Multi-Operator world, Kubecon NA 2020
-
KubePlus presentation at community meetings (CNCF sig-app-delivery, Kubernetes sig-apps, Helm)
Submit issues on this repository or reach out to our team on Slack.