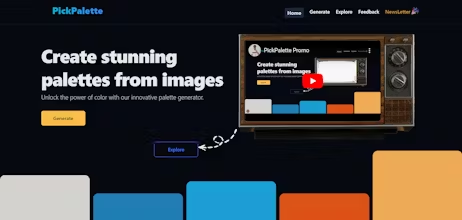
Discover endless color possibilities with PickPalette – effortlessly generate palettes from images, explore diverse schemes, and soon, manage them on a dynamic dashboard. Elevate your design process with our upcoming AI suggestions and visualization tools.
-
Backend Packages -> https://github.com/ArnabChatterjee20k/PickPalette-Backend/blob/main/packages/supabase-edge-functions/Readme.md
-
Live Link -> https://pickpalette.netlify.app/
-
Chrome Extension -> https://github.com/ArnabChatterjee20k/PickPalette-ChromeExtension
-
A palette hub consisting of more than 2500+ proved colors and it is regularly updated
-
Preview mode for testing out the palettes and the algorithm for choosing the correct combination of colors is built from the color theory itself. So choose your colors out of the box and feel free to edit. It is instant as no AI is used and it is developed using general problem solving
-
Generate colors from images instantly using image processing.
-
Lost while choosing colors? A dashboard to cater you. You have your dashboard with seamless optimistic user experience and you just go on editing the colors without any breakdown.
TODO: A NPM package is on the way to connect the dashboard to your tailwind projects so that you can edit colors directly from your dashboard without any prod builds and it will get instantly reflected in your website.
-
From tech point of view,it is corely focused on the user experience as I personally believe every clicks, every touch ,every popup matters. And both the frontend and backend along with data serving layer matters. You can see the learning section to see the algorithms I developed while buiding this. Like the recursive priority algorithm for the scheduler in the dashboard or the color randomiser along with choosing the best color comibination.
For the backend migrations and deployments, you can watch the backend repo
Please review our Code of Conduct before contributing to our project. We want to maintain a welcoming and inclusive community.
- Tech Stack in the frontend -> React js , vite, zustand, supabase, tailwind, radix ui
- Run
npm i - Make a
.envfile and copy all the content from.env.example - Make sure your supabase is setup with the db schema and functions and other stuff. They are mentioned in the backend repo
- For palette hub, the current database data will not be provided. Run the scraper and backend packages to setup all those. Already scripts are written and if any issue occurs , then they are present in the service provider documentation
- Assign yourself to the issue if it's not already assigned.
- Fork the repository to your GitHub account.
- Create a branch with a descriptive name related to the issue (e.g.,
fix-bug-123orfeature-xyz). - Work on the issue, making sure to follow our contributing guidelines.
- Create a Pull Request (PR) when you're ready. Reference the issue number in the PR description.
- Our team will review your PR and provide feedback. Be prepared to make changes if necessary.
- Solve merge conflicts before making pr
Zustand + React Query(Async State Management) for building auto save feature
Encountering race conditions with priority and recursive algo in the color dashboard
The save is autosaving feature. When colors are getting uploaded to the server and suppose at that time some changes happend.
Basically a race condition
Building the manual save in an addition to the autosave and ecountering issues such autosave during manual save or manual save during autosave
Using color theory for choosing the best color from inputs of color. The code is present in utils/categoriseColor.js
-
Define the
categorizedColorsobject: The algorithm starts by defining an objectcategorizedColorswith properties forprimary,secondary,tertiary,background,text, andaccentcolors. Initially, all these properties are set tonull. -
Sort the input colors by perceived brightness: The input array
colorsis sorted in ascending order of perceived brightness using the formula(r * 299 + g * 587 + b * 114) / 1000, wherer,g, andbare the red, green, and blue values of the color, respectively. This formula approximates how humans perceive the brightness of a color. -
Assign the background color: The darkest color from the sorted array (
sortedColors[0]) is assigned tocategorizedColors.background. -
Find the most visually distinct colors: The
findBestCombinationfunction is used to assign theprimary,secondary, andtertiarycolors. It does this by iterating over the remaining colors (excluding the background color) and calculating the color distance between each remaining color and the already assigned colors incategorizedColors. The color with the maximum distance is selected as the best color for the current category (primary,secondary, ortertiary). This ensures that the selected colors are visually distinct from each other. -
Assign the text color: The
findContrastingColorfunction is used to assign thetextcolor. It takes thebackgroundcolor and an array of remaining colors as input. It iterates over the remaining colors and finds the color with the maximum contrast (brightness difference) from thebackgroundcolor, ensuring that it's not equal to any of theprimary,secondary, ortertiarycolors. -
Assign the accent color: The
accentcolor is assigned as the lightest remaining color from the input array. This is done by creating an arrayaccentColorsthat contains all the remaining colors that haven't been assigned to any other category (primary,secondary,tertiary,background, ortext), and then assigning the last color in theaccentColorsarray (which will be the lightest color due to the sorting) tocategorizedColors.accent.
The core functionality of the algorithm is achieved through the following helper functions:
-
calculateColorDistance: This function calculates the maximum color distance between a given color and the already assigned colors incategorizedColors. It does this by iterating over the assigned colors and calculating the Euclidean distance between the given color and each assigned color in the RGB color space. The maximum distance is returned. -
getColorDistance: This function calculates the Euclidean distance between two colors in the RGB color space using the formulasqrt((r1 - r2)^2 + (g1 - g2)^2 + (b1 - b2)^2), wherer1,g1,b1andr2,g2,b2are the red, green, and blue values of the two colors, respectively. -
findContrastingColor: This function takes a base color and an array of sorted colors as input. It iterates over the sorted colors and finds the color with the maximum contrast (brightness difference) from the base color. The contrast is calculated as the absolute difference between the perceived brightness of the base color and the sorted color. The color with the maximum contrast is returned, ensuring that it's not equal to the base color.
By following these steps and using the helper functions, the algorithm assigns visually distinct colors to the primary, secondary, and tertiary properties, finds a contrasting color for the text property, and assigns the lightest remaining color as the accent color. The background color is set to the darkest color from the input array. The algorithm ensures that all assigned colors are present in the input array, and it satisfies the business cases of having the text color distinct from primary, secondary, and tertiary, and the accent color being the lightest remaining color.
- Handle edge cases when user session get expired during fetching , palettes update
- Handle edge cases of authorisation while fetching
- Handle error state of ui in projects page