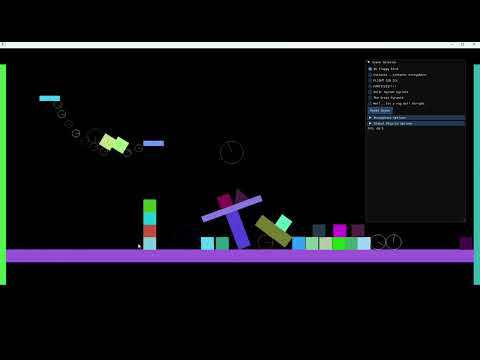
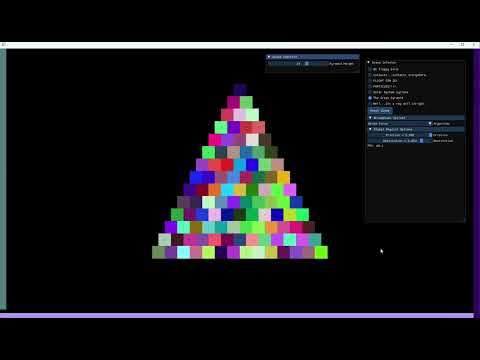
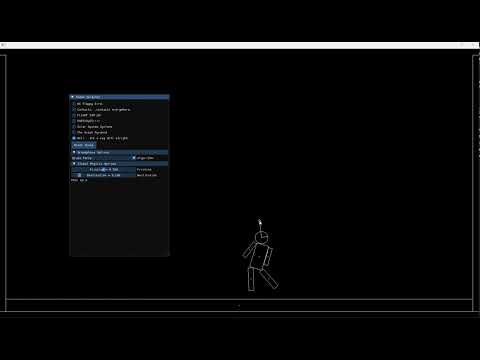
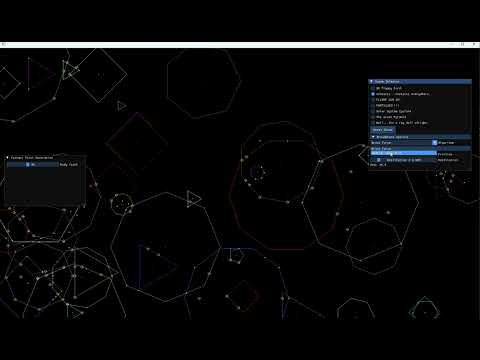
Aerolite Physics Engine is a comprehensive, efficient 2D physics library with planned extensions for 3D simulations. Tailored for game development and graphical simulations, it offers a robust platform for realistic physics behavior in a variety of environments.
- 2D and Planned 3D Support: Robust support for 2D physics and a roadmap for 3D simulation capabilities.
- AeroWorld2D: A dedicated 2D world manager for handling physics simulations.
- Collision Detection and Response: Advanced algorithms for detecting and responding to collisions between various shapes (circles, polygons, boxes) using methods like AABB and SAT (Separating Axis Theorem).
- Rigid Body Dynamics: Simulates realistic rigid body dynamics, including rotation and translation.
- Impulse Resolution: Implements impulse resolution for accurate collision responses.
- Force Generators: Flexible force generators to simulate gravity, drag, springs, and more.
- Constraint Systems: Implements constraints for realistic joint and articulated structure simulation.
- Particle Systems: Efficient particle system for simulating large numbers of interacting objects.
- Material Properties: Customize friction and restitution for different materials for varied interaction effects.
- Numerical Integration: Utilizes Euler and Runge-Kutta integration methods for precise motion calculation.
- Broad and Narrow Phase Collision Detection: Efficiently detects collisions using AABB for broad phase and SAT for narrow phase.
- Impulse-Based Dynamics: Applies realistic impulses to bodies for authentic movement.
- Constraint Solving: Simulates complex joint behavior with constraints.
- Particle Dynamics: Manages large numbers of particles effectively for simulations like smoke or liquid.
- Creating and Configuring a 2D Body
// Creating a box body
auto box = std::make_unique<Aerolite::Body2D>(new BoxShape(50, 50), 100, 100, 10.0);
box->restitution = 0.8;
- Creating and Adding bodies to the world
auto box = std::make_unique<Aerolite::Body2D>(new BoxShape(50, 50), 100, 100, 10.0);
world->AddBody2D(std::move(box));
-
Running the simulation
world->Update(deltaTime); -
Applying force
// Applying a force to a body
Vec2 force(10.0, 0.0);
box->ApplyForce(force);
- Collision Detection & Response
// Assuming bodyA and bodyB are already created and initialized
Aerolite::Contact2D contact;
if (CollisionDetection2D::IsColliding(*bodyA, *bodyB, contact)) {
contact.ResolveCollision();
}
To install Aerolite Physics Engine, clone the repository and include it in your project:
git clone https://github.com/your-repository/aerolite.gitCopyright (c) [year] [fullname]
Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all copies or substantial portions of the Software.
THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM, OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE SOFTWARE.