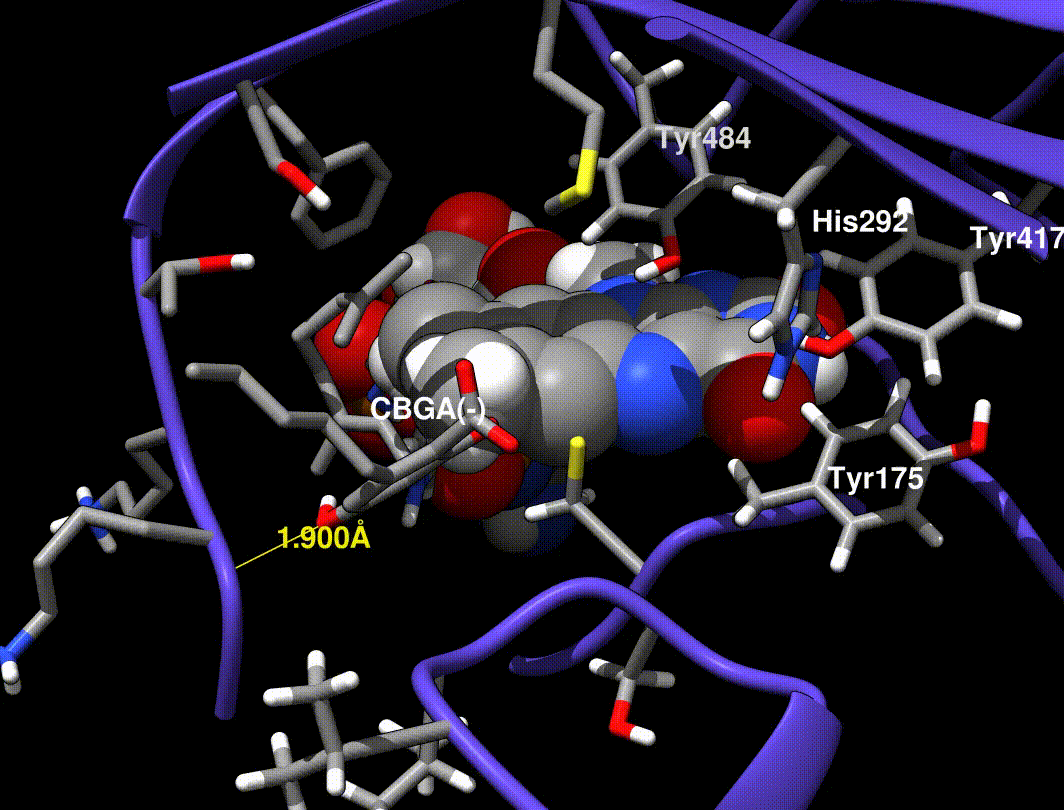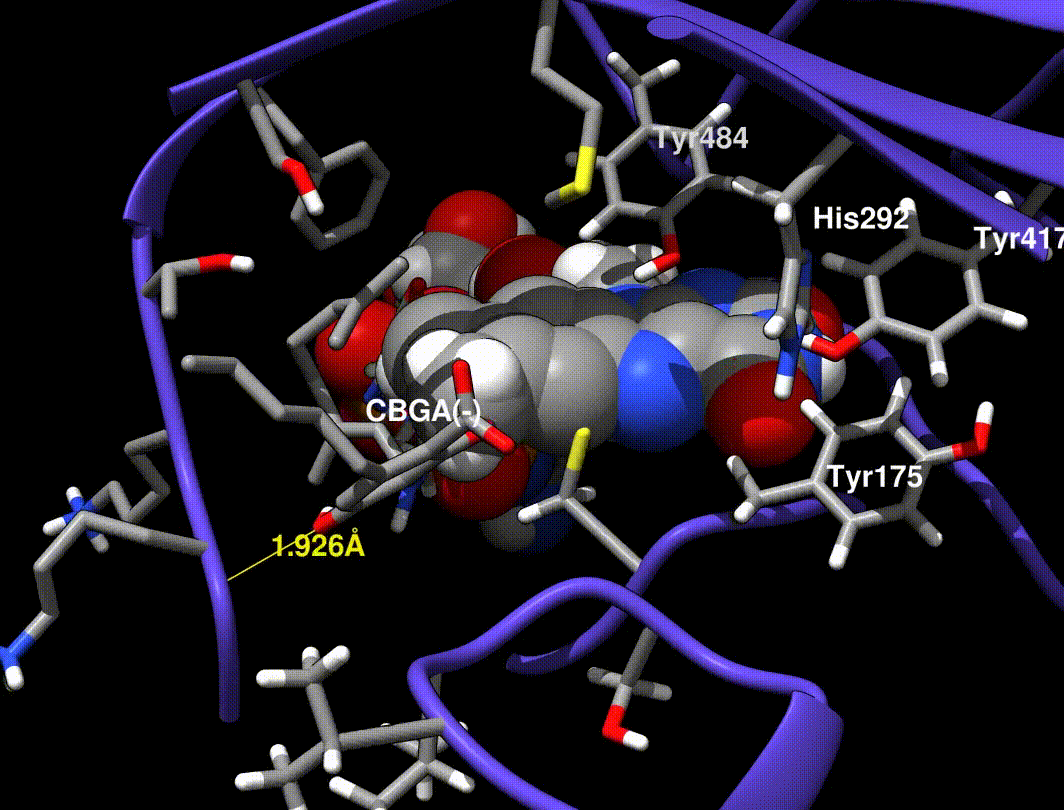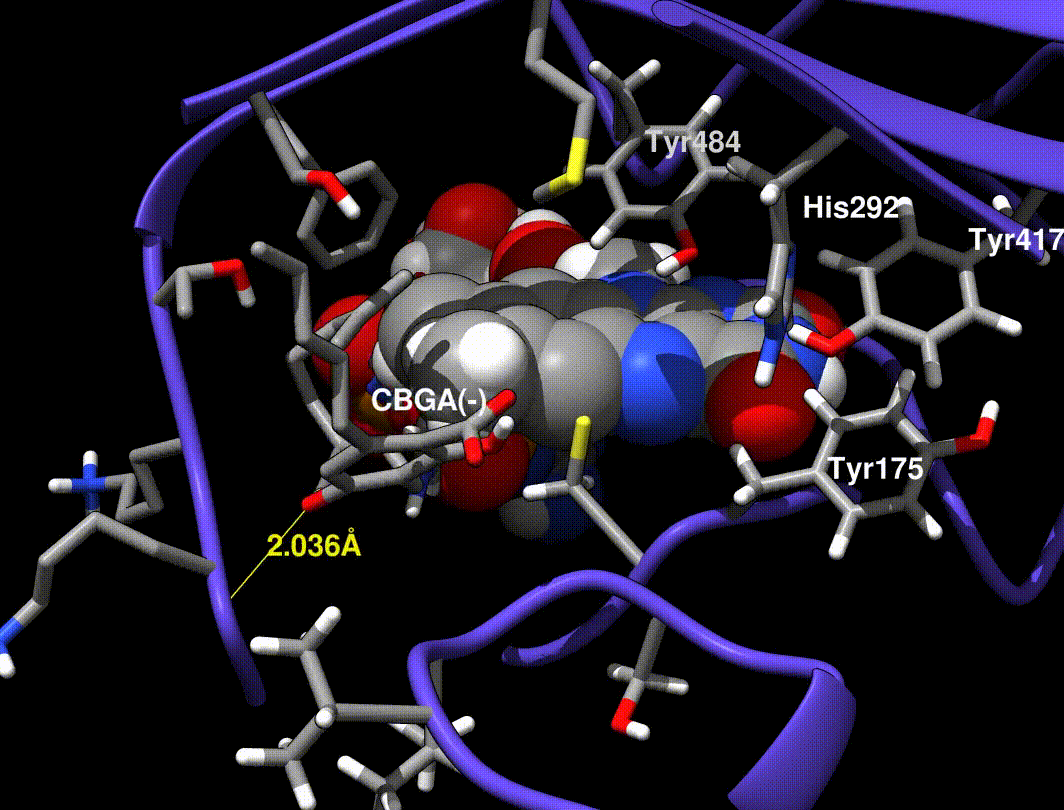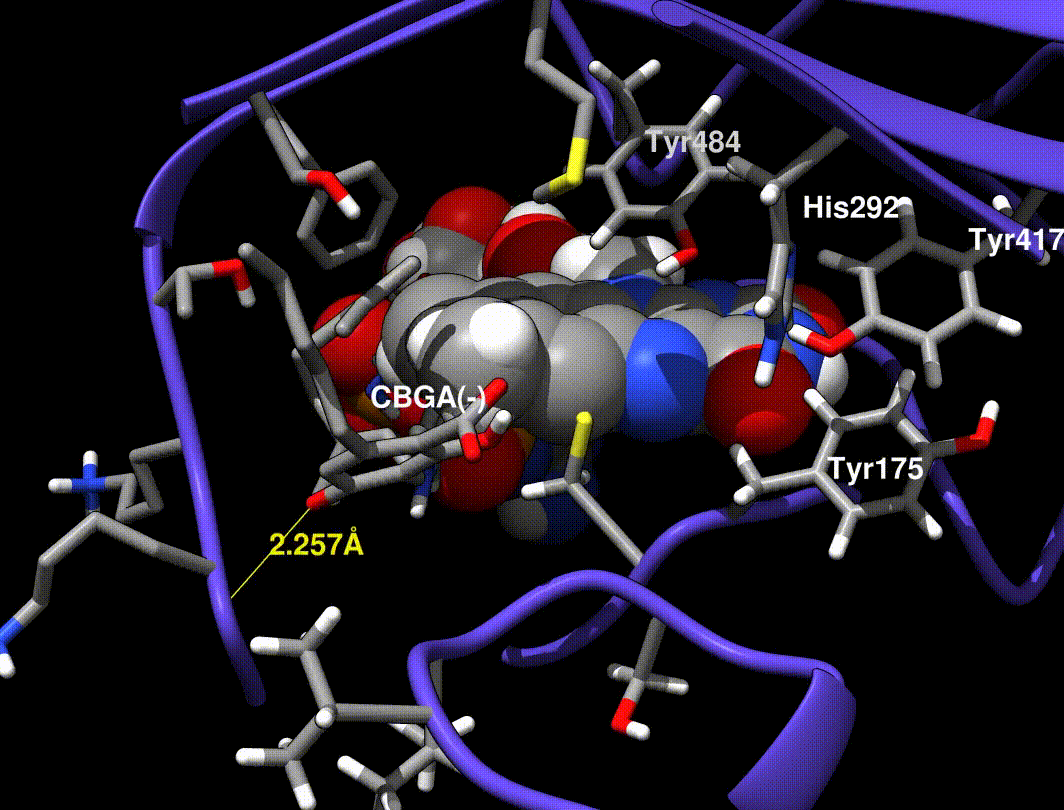
- Hydride transfer to FAD forms a tertiary carbocation that arranges the ring closure
- Tyr484 abstracts a proton from CBGA to form an alkoxide nucleophile
- Mutations at Tyr484 abolish catalysis (catalytic base)
- Mutations at His114 and Cys176 abolish catalysis (covalent FAD bound residues)
- Mutations at Tyr417 and His292 greatly reduce Kcat (non-covalent FAD bound residues)
BRENDA: EC 1.21.3.7
DOI: 10.1007/978-3-319-54564-6_8
Active-site + FAD + substrate
In [exp.01], a minimized CBGA(-) conformer was placed by hand in the active site and run through the same minimization steps in [exp.00]. More importantly, Tyr484 was replaced with a tyrosine phenolate (charge -1.0) in the QC runs only (the phenol was used in minimization runs).
A Tyr484 phenolate is proposed to be the catalytic base, but phenolate is very unstable, so I find it implausible that this species exists without interaction from neighboring side chains.
- O2
- NAG
- HOOH
- I'm unsure if the temp of the system in the amber sims
- Curently all His residues are HIE (except FAD-bound His)
- Bound His114 is cuently parameterized as HID
- Might actually be an OK approximation
- Adding some params from 4-HNE might be best
- Haven't checked for differences compared to HID
- http://research.bmh.manchester.ac.uk/bryce/amber
- I dont think Cys176 needs to be CYX
- I think CYX just tells Amber to delete the proton
- No noticeable problems with CYS so far
- I think CYX just tells Amber to delete the proton
- Unsure of His114 protonation state
- It curently exists as HID (neutral)
- Protonate His292
- Replace with HIP
- Protonations should reflect:
- pH 5.0
- Expected H-bonds