This Python-based project is part of an experiment to evaluate the parallel performance between Java and Python programming languages, using an algorithm that aims to solve the Traveling Salesman Problem (TSP) using a parallelized approach with the Partially Mapped Crossover (PMX) technique. The TSP is a classic optimization problem where the goal is to find the most efficient route that visits a set of cities exactly once and returns to the starting city. This project can be executed using multithreading or multiprocessing to explore different paths concurrently.
This project was based of TSP-Java from Miguel Rôlo. The main goal is to adapt the original project to be able to generate reports for a performance analysis between parallel capabilities in different programming languages. Comparing the performance of the Java version with the Python version.
To run the project, you need to have Python SDK installed on your machine. You can download it here.
After that, you can run the main class main.py from multithreading or multiprocessing packages.
The program supports multiprocessing to leverage the computational resources of multiple cores or processors. By distributing the workload across multiple processes, the algorithm can explore different paths parallelly, leading to faster convergence towards the optimal solution. This feature enhances the scalability and performance of the algorithm on multi-core systems.
The program supports multithreading to utilize the concurrent execution capabilities of modern processors. By running multiple threads simultaneously, the algorithm can explore different paths concurrently, speeding up the search for the optimal solution. This feature improves the efficiency of the algorithm by taking advantage of the parallel processing capabilities of the system.
The genetic algorithm incorporates the PMX crossover technique to create diverse offspring. PMX ensures that the child solutions inherit parts of their parents' paths, preserving the integrity of the route while introducing variability. This enhances the algorithm's ability to explore and converge towards optimal solutions.
The genetic algorithm incorporates a mutation mechanism with adjustable probability. Mutation introduces diversity in the population by randomly altering some solutions, preventing premature convergence to suboptimal solutions. Users can fine-tune the mutation probability to strike a balance between exploration and exploitation.
The genetic algorithm maintains a population of potential solutions, evolving them over generations. A diverse population helps the algorithm explore a broader solution space. Users can configure the size of the population based on the characteristics of the TSP instance, allowing for flexibility in handling different problem complexities.
The program performs multiple runs to evaluate the convergence behavior of the algorithm. By executing the algorithm multiple times, users can observe the consistency of the results and analyze the convergence trends. This feature provides insights into the algorithm's performance and robustness across different runs.
The program generates detailed reports summarizing the results of the TSP solver. These reports include information about the best solution found, the convergence behavior, and the execution time. Users can analyze these reports to assess the algorithm's performance and compare different configurations or problem instances.
 |
 |
 |
 |
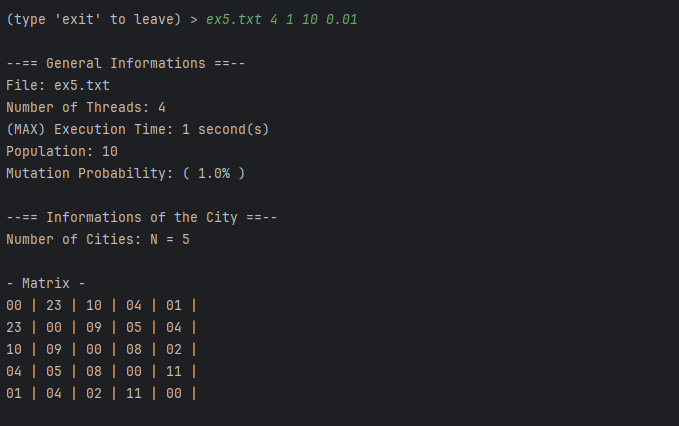
To execute the TSP solver you need to fill the following parameters:
| Param | Example | Description |
|---|---|---|
fileName |
ex13.txt | Already gets from "files" folder, just put the file name |
threadsNumber |
4 | Number of Threads to execute the program |
numberOfExecutions |
30 | Number of convergences |
populationNumber |
100 | Population size |
mutationProbability |
0.01 | from 0.01 to 1 |
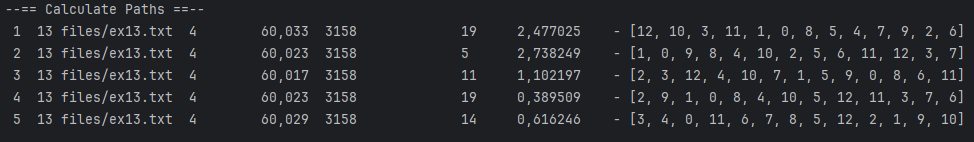
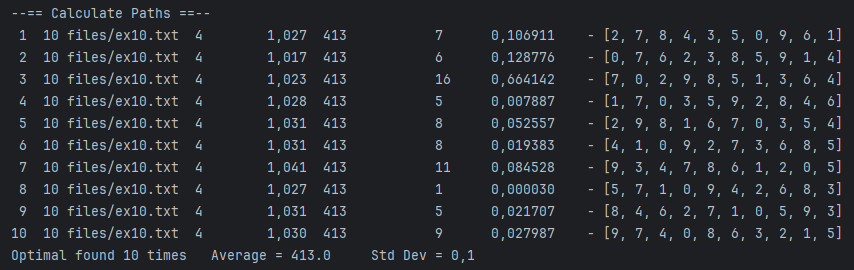
Final Result:
> <fileName> <threadsNumber> <numberOfExecutions> <populationNumber> <mutationProbability>Example
> ex13.txt 4 30 100 0.01 | File | Best distance |
|---|---|
| ex5 | 21 |
| ex6 | 23 |
| ex7 | 105 |
| ex8 | 244 |
| ex9 | 1472 |
| ex10 | 413 |
| sp11 | 133 |
| uk12 | 1733 |
| ex13 | 3158 |
| burma14 | 3323 |
| lau15 | 291 |
| ulysses16 | 6859 |
| gr17 | 2085 |
| ulysses22 | 7013 |
| gr24 | 1272 |
| fri26 | 937 |
| dantzig42 | 699 |
| att48 | 33523 |
The reports are generated in the reports folder, as a .txt and .json files.
(Apache License, Version 2.0) You're free to use this content and codes in any project, personal or commercial.
There's no need to ask permission before using theses. Giving attribution is not required, but appreciated.