The latest version is 3.3.4. You find it on Bintray.
EasyDao has tested on Oracle 10, 11, 12 and PostgreSQL 9. Maybe it works with other Oracle and PostgreSQL versions.
For generating dao and model you need using the easydao-maven-plugin. You can see how to use it: sample applications
- no JPA
- no Hibernate
- no heavyweight tools
- no special knowledge
- no cost
- instant support Spring-based projects
- generates Dao for Spring Framework JdbcTemplate
- supports new and old projects from Java5
- supports big and small projects
- generates model as POJO
- CRUD Dao methods
- ultra lightweight dependency
- you get meta information about database (metadata.txt)
- based on maven
- configuration is very simple
- configuration in pom.xml
- open source and free with MIT licence
- ultra fast code generation
- you can use it from Jenkins
- handling composite primary keys
- handling SQL arrays
- handling primary key sequences
- database design is convention over configuration
- flexible: replace the table and field names without changing database
- open source and free demo application
- learning time is about 5 minutes
easydao-maven-plugin is running on Java 8, but generated source compatible with Java 5.
EasyDao is on Bintray, see the pom.xml of the sample applications.
- Create a projectname-db-model maven project. Follow easydao-generating-dao example. Do not forget settings of easydao-maven-plugin configuration. It will creating your database dao and model classes with mvn clean install. Please, use maven release plugin if you go in staging or production.
- In the application project set pom.xml dependency to generated projectname-db-model.
- Build your application project.
Add to settings.xml:
<?xml version='1.0' encoding='UTF-8'?>
<settings xsi:schemaLocation='http://maven.apache.org/SETTINGS/1.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/settings-1.0.0.xsd' xmlns='http://maven.apache.org/SETTINGS/1.0.0' xmlns:xsi='http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance'>
<profiles>
...
<profile>
<id>vanio-bintray-releases</id>
<repositories>
<repository>
<snapshots>
<enabled>false</enabled>
</snapshots>
<id>bintraycentral</id>
<name>bintray</name>
<url>http://dl.bintray.com/vanioinformatika/releases/</url>
</repository>
</repositories>
<pluginRepositories>
<pluginRepository>
<snapshots>
<enabled>false</enabled>
</snapshots>
<id>bintraycentral</id>
<name>bintray-plugins</name>
<url>http://dl.bintray.com/vanioinformatika/releases/</url>
</pluginRepository>
</pluginRepositories>
</profile>
<activeProfiles>
...
<activeProfile>vanio-bintray-releases</activeProfile>
</activeProfiles>
</settings><plugin>
<groupId>hu.vanio.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>easydao-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>VERSION_NUMBER</version>
<configuration>
<dbName>sampledb</dbName>
<dbType>POSTGRESQL9</dbType>
<dbUrl>jdbc:postgresql://localhost:5432/sampledb</dbUrl>
<dbUsername>postgres</dbUsername>
<dbPassword>sample</dbPassword>
<packageOfJavaModel>hu.vanio.easydao.sample.model</packageOfJavaModel>
<packageOfJavaDao>hu.vanio.easydao.sample.dao</packageOfJavaDao>
</configuration>
<executions>
<execution>
<goals>
<goal>generate</goal>
</goals>
</execution>
</executions>
</plugin>For Oracle 12c users: use Java 8 and ojdbc8 in your pom.xml, otherwise you get an error: ORA-28040: No matching authentication protocol
Changing JDBC driver: vanioinformatika#15 (comment)
Please check the Oracle documentation: 9.2 Support for Login Authentication http://docs.oracle.com/database/122/JJDBC/JJDBC.pdf
If you are using Java 8, then set the javadoc plugin with -Xdoclint:none:
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-javadoc-plugin</artifactId>
<version>2.10.3</version>
<configuration>
<additionalparam>-Xdoclint:none</additionalparam>
</configuration>
</plugin>'-Xdoclint:none' is not working with Java 7_60 or newer Java 7!
Using the java source (screenshots)
You can find the results of the code generation in <generatedSourcePath>/metadata.txt. It contains several useful information about your database, and you can easily define replacement files based on its content.
Configuration parameters are required or optional. All optional parameters have default value, these default values are recommended.
Required parameters are project dependent.
Configuration example:
<plugin>
<groupId>hu.vanio.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>easydao-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>VERSION_NUMBER</version>
<configuration>
<!-- required -->
<dbName>sampledb</dbName>
<dbType>POSTGRESQL9</dbType>
<!-- docker inspect sampledb | grep IPAddress -->
<dbUrl>jdbc:postgresql://172.17.0.2/sampledb</dbUrl>
<dbUsername>postgres</dbUsername>
<dbPassword>sample</dbPassword>
<packageOfJavaModel>hu.vanio.easydao.sample.model</packageOfJavaModel>
<packageOfJavaDao>hu.vanio.easydao.sample.dao</packageOfJavaDao>
<!-- optionals -->
<tablePrefix>true</tablePrefix>
<tableSuffix>false</tableSuffix>
<fieldPrefix>true</fieldPrefix>
<fieldSuffix>false</fieldSuffix>
<!-- please do not change: generatedSourcePath>/tmp/easydaodemo-database_model</generatedSourcePath-->
<daoSuffix>Dao</daoSuffix>
<replacementTableFilename>replacement-table</replacementTableFilename>
<replacementFieldFilename>replacement-field</replacementFieldFilename>
<enumFieldFilename>enum-field</enumFieldFilename>
<replacementTypeMapFilename>replacement-type</replacementTypeMapFilename>
<sequenceNameConvention>PREFIXED_TABLE_NAME</sequenceNameConvention>
<generateModelToString>false</generateModelToString>
<licenseFilename>${basedir}/src/myLicense.txt</licenseFilename>
<language>hu</language>
<tableNameIncludes>
<tableNameInclude></tableNameInclude>
</tableNameIncludes>
<encoding>utf-8</encoding>
<silent>true</silent>
<addDbNameToPackageNames>true</addDbNameToPackageNames>
</configuration>
<executions>
<execution>
<goals>
<goal>generate</goal>
</goals>
</execution>
</executions>
</plugin>Required parameters has * sign.
Database name, required. If you are using more than one database in your code, then you need namespaces. The value of the dbName parameter will act as a namespace, it will be the last element of the package name of the generated classes. If you set to e.g: callisto, the package name of the generated model and dao classes will be: <packageOfJavaModel>.callisto and <packageOfJavaDao>.callisto respectively.
Generated dao classes are based on Spring Framework! If you are using more than one database, then the generated models will use different DataSources. The callisto will be set in the dao classes as data source name with a @Qualifier annotation.
Database type, required. You must set to ORACLE10, ORACLE11 or POSTGRESQL9
Database connection parameters, required.
Package name of the generated Java model classes, required. Java model codes will contain this package name, e.g: hu.vanio.easydao.sample.model.sampledb
Package name of the generated Java dao classes, required. Java dao codes will contain this package name, e.g: hu.vanio.easydao.sample.dao.sampledb
Database table prefix: true or false, optional. Default is true. If true, then the first part of the table names will be removed before generating Java names. Parts are separated by underscore characters. e.g: SHP_CUSTOMER_ORDER -> CustormerOrder.java and CustomerOrderDao.java
Database table suffix: true or false, optional. Default is false. If true, then the last part of the table names will be removed before generating Java names. Parts are separated by underscore characters. e.g: CUSTOMER_ORDER_SHP -> CustomerOrder.java and CustomerOrderDao.java
Database field prefix: true or false, optional. Default is true. If true, then the first part of the field names will be removed before generating Java names. Parts are separated by underscore characters. e.g: CUS_CUSTOMER table field is CUS_PK -> pk
If true, then the last part of the field names will be removed before generating Java names. Parts are separated by underscore characters. e.g: CUSTOMER_CUS table field is PK_CUS -> pk
Optional, changing its value is not recommended! Generate source codes to this directory. Default value is target/generated-source/easydao-classes/
Generated Java dao class name suffix, optional. Default value is Dao.
If true, a toString method that outputs data in JSON format will be generated for all model classes.
Replacement file name for tables, optional, default value is replacement-table. The name of the properties file in src/main/resources without the properties extension, e.g: replacement-table
If you want to ignore a table from the Java code generation, put it into the file, e.g:
CUS_CUSTOMER =
If you want to generate Java code with a special name (e.g: Order.java), then:
CUS_CUSTOMER = User
You can find the results of the code generation in <generatedSourcePath>/metadata.txt. It contains several useful information about your database, and you can easily define replacement files based on its content.
Replacement file name for fields, optional, default value is replacement-field. Resource bundle file in src/main/resources without file extension, e.g: replacement-field
If you want to ignore a field from java code generation, then put it into the file as TABLENAME.FIELDNAME, e.g:
CUS_CUSTOMER.SECRET_CODE =
If you want to generate with a special name (e.g: orderType), then:
CUS_CUSTOMER.ORDER_MODE = orderType
You can find the results of the code generation in <generatedSourcePath>/metadata.txt. It contains several useful information about your database, and you can easily define replacement files based on its content.
Map file name for fields with enumerated values. Resource bundle file in src/main/resources without file extension, e.g: enum-field
If you want to use Java enum for a database field, put it into the file as TABLENAME.FIELDNAME = , e.g:
CUS_CUSTOMER_ORDER.ORDER_MODE = hu.vanio.myapp.model.OrderMode
Map file name for database types that should not be mapped by the default type map. Resource bundle file in src/main/resources without file extension, e.g: replacement-type
If you want to use a custom type instead of the built in one for one or a set of database types, put it into the file as = , , e.g:
date.* = hu.vanio.myapp.model.MyCustomDateType, hu.vanio.myapp.converter.MyCustomDateTypeConverter
Defines database sequence naming convention with SEQ string, optional, default value is SUFFIXED_TABLE_NAME.
-
recommended Generate sequence names by table name's suffix with _SEQ (e.g.: MY_TABLE_NAME -> MY_TABLE_NAME_SEQ) SUFFIXED_TABLE_NAME
-
Generate sequence names by table name's prefix with SEQ_ (e.g.: MY_TABLE_NAME -> SEQ_MY_TABLE_NAME): PREFIXED_TABLE_NAME
-
Generate sequence names by field's prefix with SEQ_ (e.g.: MY_FIELD_NAME -> SEQ_MY_FIELD_NAME) PREFIXED_FIELD_NAME
-
Generate sequence names by field's names suffix with _SEQ (e.g.: MY_FIELD_NAME -> MY_FIELD_NAME_SEQ) SUFFIXED_FIELD_NAME
-
Generate sequence names by table name's prefix with SEQ_ and with field name (e.g.: MY_TABLE_NAME.MY_FIELD_NAME -> SEQ_MY_TABLE_NAME_MY_FIELD_NAME) PREFIXED_TABLE_NAME_WITH_FIELD_NAME
-
Generate sequence names by table name's suffix with field name and _SEQ (e.g.: MY_TABLE_NAME.MY_FIELD_NAME -> MY_TABLE_NAME_MY_FIELD_NAME_SEQ) SUFFIXED_TABLE_NAME_WITH_FIELD_NAME;
Defines your license file, default: null -> no license. It will be inserted in your generated sources. Text must be in java comment format.
Defines the language of the comments in the generated Java sources. Possible values: 'hu' or 'en' ('en' is the defult)
Defines a list of regex patterns to specify the table names to be included in Java code generation.
Defines the encoding of the generated Java sources. Default: ${project.build.sourceEncoding}
Indicates whether normal output should be suppressed during code generation. If set, only warnings will be printed.). Default: true
If true, database name will be added at the end of the java package names. If you have only one database schema, set it to false.
Example:
Let's assume you have a base package of hu.vanio.easydao.sample and your database name is sampledb
-
If you set addDbNameToPackageNames to false, your model and dao packages will be
hu.vanio.easydao.sample.modelandhu.vanio.easydao.sample.dao -
If you set addDbNameToPackageNames to true (the default), your model and dao packages will be
hu.vanio.easydao.sample.model.sampledbandhu.vanio.easydao.sample.dao.sampledb
The latter is useful when you have more than one databases, so your model and dao class names won't clash.
As of 1.0.9, you can use Java enums for fields with enumerated values. You have two choices: regular and irregular enumerations. If you use fields with enumerated values, values stored in the database need to be mapped to the corresponding enum value and vica versa. EasyDao generates the necessary code for you, however if you use irregular enums you have to comply with a few rules. For the details, see the Irregular enumerations section.
An enumeration is regular if all values can be used as a Java identifier (i.e. it starts with a letter, doesn't contain dots and dashes...) Regular enumerations will be converted to String via the Java enum's name() method. Strings will be converted to Java enum instances by calling the enum's valueOf() method.
Let's assume you have a field MY_TABLE.MY_FIELD that can only contain 'A', 'B' and 'C'
- Create a java enum that contains A, B and C values (e.g. MyFieldEnum)
- Specify the field name and the corresponding enum's fully qualified class name in the enum-field.properties file:
MY_TABLE.MY_FIELD = com.mycompany.myapp.model.MyFieldEnum - Specify the location of the enum-field.properties file in the EngineConfiguration (enumFieldFileName property)
- Start generation
public enum MyFieldEnum {
A, B, C
}An enumeration is irregular if at least one of the values cannot be used as a Java identifier. Irregular enumerations have to comply with two rules. They have to implement getEnumName() and static getEnumInstance() methods. Irregular enumerations will be converted to String via the Java enum's getEnumName() method. Strings will be converted to Java enum instances by calling the enum's getEnumInstance() method.
Let's assume you have a field MY_TABLE.MY_FIELD that can only contain 'NORMAL', '2WAY' and '3WAY' 2WAY and 3WAY ar not legal Java identifiers, so a regular Java enum cannot be used here. All values that cannot be used as a Java identifier, need to be changed, (e.g. 2WAY -> _2WAY, 3WAY -> _3WAY) Of course storing the original value is important as it needs to be used when writing the field to the database and reading it back. You can see an example implementation below.
- Create a java enum that contains NORMAL, _2WAY and _3WAY values (e.g. MyFieldIrregularEnum)
The underscore at the beginning of the names are there to tackle the Java identifier name problem.
- Implement getEnumName() method (it will be used to create the String representation of the enum value)
- Implement static getEnumInstance(String) method (it will be used to find the enum value that corresponds to the specified String)
- Specify the field name and the corresponding enum's fully qualified class name in the enum-field.properties file and indicate that it is an irregular enum:
MY_TABLE.MY_FIELD = com.mycompany.myapp.model.MyFieldIrregularEnum, IRREGULAR - Specify the location of the enum-field.properties file in the EngineConfiguration (enumFieldFileName property)
- Start generation
public enum MyFieldIrregularEnum {
NORMAL("NORMAL"),
_2WAY("2WAY"),
_3WAY("3WAY");
private final String enumName;
MyFieldIrregularEnum(String enumName) {
this.enumName = enumName;
}
public String getEnumName() {
return enumName;
}
public static MyFieldIrregularEnum getEnumInstance(String value) {
for (MyFieldIrregularEnum v : values()) {
if (v.getEnumName().equalsIgnoreCase(value)) {
return v;
}
}
throw new IllegalArgumentException("No enum constant " + MyFieldIrregularEnum.class.getName() + "." + value);
}
}EasyDAO maps database types to the most sensible Java types, but sometimes it's not appropriate. In these cases you can override the default type mapping via a properties file. Overriding it consists of the following:
- implementation of the custom type class, see the example below.
- implementation of a type converter class that converts the custom type to a type that is recognized by the database driver and/or spring JDBC, see the example below
- registering the custom type in the replacement-type.properties and specifying the file name in the maven plugin configuration
Let's assume we have an Oracle database and the default DATE -> java.sql.Timestamp mapping is not appropriate for some reason. In this case we need to implement the MyCustomDateType class and the corresponding MyCustomDateTypeConverter as seen below. In addition you have to register the new custom type in the replacement type map file (replacement-type.properties):
date.* = hu.vanio.myapp.model.MyCustomDateType, hu.vanio.myapp.converter.MyCustomDateTypeConverter
Note the
date.*expression on the left hand side. It means that any field with a type that starts with the stringdatewill be mapped to the given custom type.
package hu.vanio.myapp.model;
public class MyCustomDateType {
// properties...
// methods...
/** Constructor */
public MyCustomDateType(String) {
// ...
}
public java.sql.Date toSqlDate() {
java.sql.Date dateValue = ....
return dateValue;
}
}Type converters are convention based so it's not necessary to extend any base class or implement any interface. The only requirement is to implement two public static methods: extractValue and convertValue.
WARNING: This class must be thread safe, so don't use any instance fields!
package hu.vanio.myapp.converter;
import hu.vanio.myapp.model.MyCustomDateType;
/** Converter class. */
public class MyCustomDateTypeConverter {
/**
* Extracts the value of the field with the specified name as a custom type from the specified resultset.
*/
static public MyCustomDateType extractValue(ResultSet rs, String fieldName) throws SQLException {
String strValue = rs.getString(fieldName);
return new MyCustomDateType(strValue);
}
/**
* Maps the custom Java type to a Java type that can be written to the database field. i.e. if the database field
* is of type DATE you have to return either java.util.Date, java.sql.Date or java.sql.Timestamp.
*/
static public Date convertValue(MyCustomDateType value) {
// Additional processing may come here
return value.toSqlDate();
}
}If you just want to use this easy model and dao generator, then use the maven plugin at https://github.com/vanioinformatika/easydao-maven-plugin and a small dependeny in your project: https://github.com/vanioinformatika/easydao-core
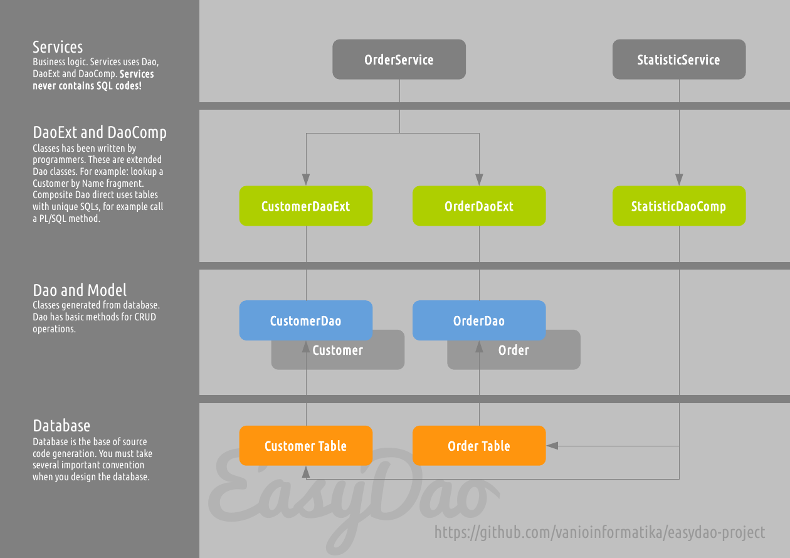
This section describes EasyDao logic. This means how to create your projects and database, and what conventions are.
There are four logic layer:
This is your real database. It is important that table and field names are following naming conventions, e.g: if you prefixes tables (CUS_CUSTOMER), than all table must have prefix. EasyDao has a feature for replacing wrong table and/or field names. See: https://github.com/vanioinformatika/easydao-maven-plugin#replacementtablefilename
Tables must have at least one primary key. I advice that, do not use composite primary keys, but always use at least one primary key. See: http://stackoverflow.com/questions/1383062/composite-primary-key
These classes generated from the database, and you never modify it manually. Dao classes directly reaches tables of database. The dao classes based on Spring Framework JdbcTemplate.
They provides the necessary business logic on database. Not autogenerated classes. EasyDao gives interfaces for it.
DaoExt classes extends Dao classes, and contains several unique methods for exactly one table. DaoComp classes not related to one table. They are using several tables with one complex query.
DaoExt classes must implements hu.vanio.easydao.core.DaoExt interface. DaoComp classes must implements hu.vanio.easydao.core.DaoComp interface.
Service classes contains Spring @Transactional annotation, and they are using Dao, DaoExt and DaoComp classes. Services implements business logic, collaboration between database, queue, filesystem, algorithm, etc. Not autogenerated classes. Service layer never contains SQL codes! It is using Dao classes: Dao, DaoExt and DaoComp.
DaoExt, DaoComp and Service classes are depends on business logic and created by developers.
You can see this one on the next image and PDF.
Download as PDF:
EasyDao logic
Download as PDF:
EasyDao logic

