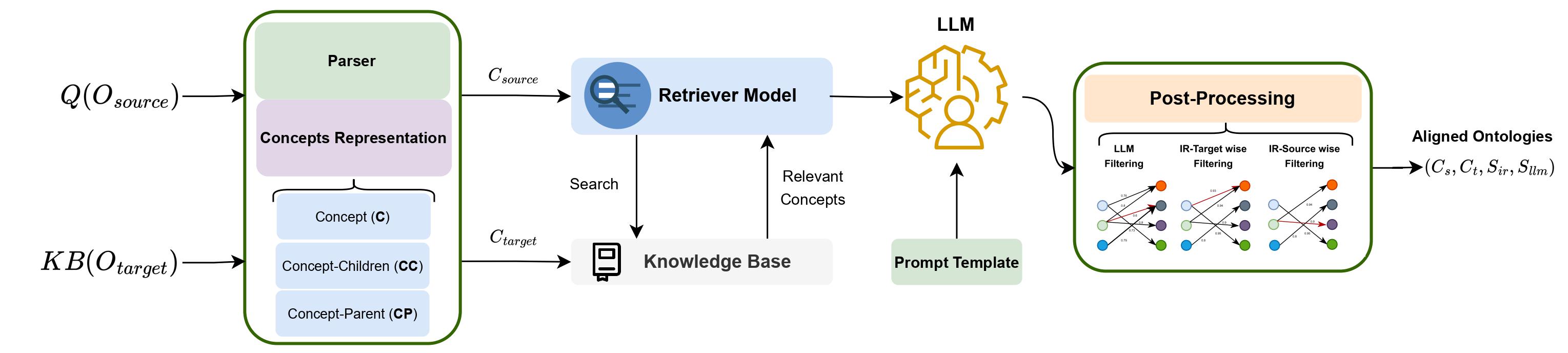
The LLMs4OM framework is a novel approach for effective Ontology Matching (OM) using LLMs. This framework utilizes two modules for retrieval and matching, respectively, enhanced by zero-shot prompting across three ontology representations: concept, concept-parent, and concept-children. It is capable of comprehensive evaluations using 20 OM datasets (but not limited to) from various domains. The LLMs4OM framework, can match and even surpass the performance of traditional OM systems, particularly in complex matching scenarios.
The following diagram represent the LLMs4OM framework.
The LLMs4OM framework offers a retrieval augmented generation (RAG) approach within LLMs for OM. LLMs4OM uses
You can also install and use the LLMs4OM using the following commands.
git clone https://github.com/HamedBabaei/LLMs4OM.git
cd LLMs4OM
pip install -r requirements.txt
mv .env-example .env
Next, update your tokens in .env or if you don't want to use LLaMA-2 or GPT-3.5 LLMs just put dummy tokens there.
Once you installed the requirements and prepared the .env file, you can move forward with experimentation.
A RAG specific quick tour with Mistral-7B and BERTRetriever using C representation.
from ontomap.ontology import MouseHumanOMDataset
from ontomap.base import BaseConfig
from ontomap.evaluation.evaluator import evaluator
from ontomap.encoder import IRILabelInRAGEncoder
from ontomap.ontology_matchers import MistralLLMBertRAG
from ontomap.postprocess import process
# Setting configurations for experimenting 'rag' on GPU with batch size of 16
config = BaseConfig(approach='rag').get_args(device='cuda', batch_size=16)
# set dataset directory
config.root_dir = "datasets"
# parse task source, target, and reference ontology
ontology = MouseHumanOMDataset().collect(root_dir=config.root_dir)
# init encoder (concept-representation)
encoded_inputs = IRILabelInRAGEncoder()(ontology)
# init Mistral-7B + BERT
model = MistralLLMBertRAG(config.MistralBertRAG)
# generate results
predicts = model.generate(input_data=encoded_inputs)
# post-processing
predicts, _ = process.postprocess_hybrid(predicts=predicts,
llm_confidence_th=0.7,
ir_score_threshold=0.9)
# evaluation
results = evaluator(track='anatomy',
predicts=predicts,
references=ontology["reference"])
print(results)A Retrieval specific quick tour with BERTRetriever using C representation.
from ontomap.ontology import MouseHumanOMDataset
from ontomap.base import BaseConfig
from ontomap.evaluation.evaluator import evaluator
from ontomap.encoder.lightweight import IRILabelInLightweightEncoder
from ontomap.ontology_matchers.retrieval.models import BERTRetrieval
from ontomap.postprocess import process
# Setting configurations for experimenting 'retrieval' on CPU
config = BaseConfig(approach='retrieval').get_args(device='cpu')
# set dataset directory
config.root_dir = "datasets"
# parse task source, target, and reference ontology
ontology = MouseHumanOMDataset().collect(root_dir=config.root_dir)
# init encoder (concept-representation)
encoded_inputs = IRILabelInLightweightEncoder()(ontology)
# init BERTRetrieval
model = BERTRetrieval(config.BERTRetrieval)
# generate results
predicts = model.generate(input_data=encoded_inputs)
# post-processing
predicts = process.eval_preprocess_ir_outputs(predicts=predicts)
# evaluation
results = evaluator(track='anatomy',
predicts=predicts,
references=ontology["reference"])
print(results)from ontomap.ontology_matchers.rag.models import ChatGPTOpenAIAdaRAG
from ontomap.ontology_matchers.rag.models import FalconLLMAdaRAG, FalconLLMBertRAG
from ontomap.ontology_matchers.rag.models import LLaMA7BLLMAdaRAG, LLaMA7BLLMBertRAG
from ontomap.ontology_matchers.rag.models import MistralLLMAdaRAG, MistralLLMBertRAG
from ontomap.ontology_matchers.rag.models import MPTLLMAdaRAG, MPTLLMBertRAG
from ontomap.ontology_matchers.rag.models import VicunaLLMAdaRAG, VicunaLLMBertRAG
from ontomap.ontology_matchers.rag.models import MambaLLMAdaRAG, MambaLLMBertRAGfrom ontomap.ontology_matchers.retrieval.models import AdaRetrieval
from ontomap.ontology_matchers.retrieval.models import BERTRetrieval
from ontomap.ontology_matchers.retrieval.models import SpecterBERTRetrieval
from ontomap.ontology_matchers.retrieval.models import TFIDFRetrieval# CommonKG track
from ontomap.ontology.commonkg import NellDbpediaOMDataset, YagoWikidataOMDataset
# MSE track
from ontomap.ontology.mse import MaterialInformationEMMOOMDataset, MaterialInformationMatOntoMDataset
# Phenotype track
from ontomap.ontology.phenotype import DoidOrdoOMDataset, HpMpOMDataset
# Anatomy
from ontomap.ontology.anatomy import MouseHumanOMDataset
# Biodiv
from ontomap.ontology.biodiv import EnvoSweetOMDataset, FishZooplanktonOMDataset,\
MacroalgaeMacrozoobenthosOMDataset, TaxrefldBacteriaNcbitaxonBacteriaOMDataset, \
TaxrefldChromistaNcbitaxonChromistaOMDataset, TaxrefldFungiNcbitaxonFungiOMDataset,\
TaxrefldPlantaeNcbitaxonPlantaeOMDataset, TaxrefldProtozoaNcbitaxonProtozoaOMDataset
# Bio-ML
from ontomap.ontology.bioml import NCITDOIDDiseaseOMDataset, OMIMORDODiseaseOMDataset, \
SNOMEDFMABodyOMDataset, SNOMEDNCITNeoplasOMDataset, SNOMEDNCITPharmOMDataset# Retriever models concept representations
from ontomap.encoder.lightweight import IRILabelInLightweightEncoder # C
from ontomap.encoder.lightweight import IRILabelChildrensInLightweightEncoder # CC
from ontomap.encoder.lightweight import IRILabelParentsInLightweightEncoder # CP
# RAG models concept representations
from ontomap.encoder.rag import IRILabelInRAGEncoder # C
from ontomap.encoder.rag import IRILabelChildrensInRAGEncoder # CC
from ontomap.encoder.rag import IRILabelParentsInRAGEncoder # CPTo use LLMs4OM pipleine follow the followings. It will run one model at a time over 20 OM tasks.
from ontomap import OMPipelines
# setting hyperparameters
approach="rag"
encoder="rag"
use_all_encoders=False
approach_encoders_to_consider=['label'] # C representation
use_all_models=False
load_from_json=False
device="cuda"
do_evaluation=False
batch_size=16
llm_confidence_th=0.7
ir_score_threshold=0.9
model="['MistralBertRAG']"
outputs='output-rag-mistral'
# arguments
args = {
'approach': '$approach',
'encoder': '$encoder',
'use-all-encoders': use_all_encoders,
'approach-encoders-to-consider': approach_encoders_to_consider,
'use-all-models': use_all_models,
'models-to-consider': model,
'load-from-json': load_from_json,
'device': device,
'do-evaluation': do_evaluation,
'outputs-dir': outputs,
'batch-size': batch_size,
'llm_confidence_th': llm_confidence_th,
'ir_score_threshold': ir_score_threshold
}
# Running OMPipelines
runner = OMPipelines(**args)
runner()If you found this project useful in your work or research please cite it by using this BibTeX entry:
Pre-print:
@misc{giglou2024llms4om,
title={LLMs4OM: Matching Ontologies with Large Language Models},
author={Hamed Babaei Giglou and Jennifer D'Souza and Felix Engel and Sören Auer},
year={2024},
eprint={2404.10317},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={cs.AI}
}