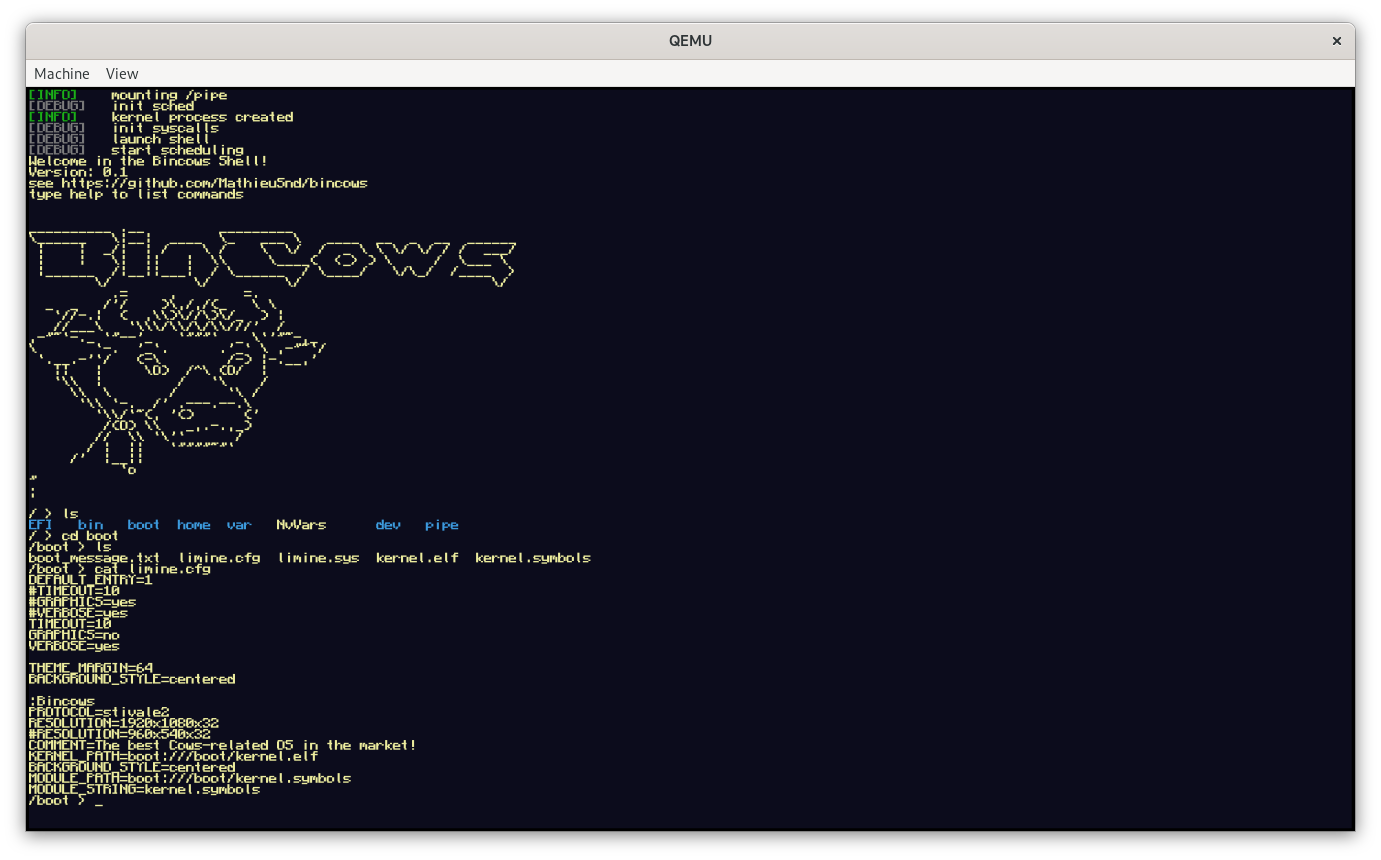
Bincows aims to be an UNIX operating written in C system targeting x86_64 architecture. It is a side projet of mine to learn more about operating systems and practical development on modern systems such as desktop computers. It is very unstable, so booting it on your own machine is possible though discouraged.
Do not hesitate to leave an issue if you find a bug or cannot build and emulate the system.
For now, Bincows support driver for:
- PCIe
- PS/2 Keyboard
- NVMe drives
Bincows embeds a TTY shell with a set of programs:
- ls
- cat
- txe (TeXt Editor)
- clear
It only uses one processor and Round Robin scheduling.
Bincows only supports the Limine bootloader.
In order to build Bincows, you will need x86_64-elf-gcc cross compiler along with x86_64_64-elf binutil.
By default, Bincows uses the Lightweight AML Interpreter to exploit ACPI power
managment. You can define the USE_LAI as 0 to avoid using it.
To emulate Bincows, you will need QEMU and an UEFI BIOS for qemu (for example OVMF, of which a copy is available in this repository). See the Emulation using QEMU section.
This section describes how to build the Bincows ecosystem (kernel, libc and programs)
To build the bincows ecosystem, you will need a cross compiler (GCC and the GNU binutils suite) targeting x86_64 ELF. Consider visiting this page to build one yourself or downloading a build. You have to define the GNU_PREFIX environment variable as the path to GCC and binutils bin directory.
If you don't disable the use of LAI by setting USE_LAI environment variable to 0, you must recursively clone the repository to get the submodules.
Then, from the root of this repository, you can build the kernel, libc and programs by typing:
$ make all
The default kernel target is debug, since the system is still unstable. If you want to play with fire, you can change the target using an environment variable:
KERNEL_TARGET=release
Once the build succeed, you can run the following command to launch a qemu emulation:
$ make qemu_run
This will first create a binary image file containing a bincows partition, using a loopback device. You will need superuser privileges to do so. Then, it will lauch qemu with numberous arguments.
Note that you can parametrize the emulation using environment variables:
-
QEMU_RAM_MB- number of megabytes of RAM. Defaults to 128. -
QEMU_GRAPHICS_OPTIONS- qemu graphical options. Defaults to-vga virtio. See QEMU documentation. -
USED_LOOPBACK: loopback device path. Defaults to/dev/loop2. -
QEMU_BIOS_FILE: path to the qemu bios. Defaults to/usr/share/ovmf/OVMF.fd -
QEMU_LOG_FILE: path to the the QEMU log file. Defaults toqemu.log -
QEMU_EXTRA_OPTIONS: additional options (e.g.: tracing events options). Defaults to an empty string -
IMAGE_FILE: path to the image file to build. Defaults todisk.bin
This project is distributed under MIT Licence.
I currently work on multithreading, the support of inter-thread communication concepts of UNIX concepts.
Later on, I might work for the support to AHCI, a graphical desktop environment, SMP, etc.