CosmoScout VR is a modular virtual universe developed at the German Aerospace Center (DLR). It lets you explore, analyze and present huge planetary data sets and large simulation data in real-time.
The software can be build on Linux (gcc or clang) and Windows (msvc). Nearly all dependencies are included as git submodules, please refer to the documentation in order to get started.
Below is a rough sketch of the possibilities you have with CosmoScout VR. While this list is far from complete it provides a good overview of the current feature set. You can also read the changelog to learn what's new in the current version. There is also an interesting article in the DLR magazine, and several papers which provide some insight into the ideas behind CosmoScout VR.
- Solar System Simulation
- Positioning of celestial bodies and space crafts based on SPICE
- Rendering of highly detailed level-of-detail planets based on WebMapServices (with csp-lod-bodies)
- Rendering of configurable atmospheres (Mie- and Rayleigh-scattering) around planets (with csp-atmospheres)
- Physically based rendering of 3D satellites (with csp-satellites)
- Rendering of Tycho, Tycho2 and Hipparcos star catalogues (with csp-stars)
- Rendering of orbits and trajectories based on SPICE (with csp-trajectories)
- Rendering of shadows
- HDR-Rendering
- Flexible User Interface
- Completely written in JavaScript with help of the Chromium Embedded Framework
- Main UI can be drawn in the screen- or world-space
- Web pages can be placed on planetary surfaces
- Interaction works both in VR and on the Desktop
- Clear API between C++ and JavaScript
- Cross-Platform
- Runs on Linux
- Runs on Windows
- Runs on MacOS
- System Architecture
- Plugin-based - most functionality is loaded at run-time
- Network synchronization of multiple instances
- Hardware device support - CosmoScout VR basically supports everything which is supported by ViSTA and VRPN. The devices below are actively supported (or planned to be supported).
- Mouse
- Keyboard
- HTC-Vive
- ART-Tracking systems
- 3D-Connexion Space Navigator
- Multi-screen systems like tiled displays or CAVE's
- Multi-screen systems on distributed rendering clusters
- Side-by-side stereo systems
- Quad-buffer stereo systems
- Anaglyph stereo systems
- Game Pads like the X-Box controller
For each release, binary packages are automatically created via Github Actions.
When started for the very first time, some example datasets will be downloaded from the internet. This will take some time! The progress of this operation is shown on the loading screen.
If the binary releases do not work for you or you want to test the latest features, you have to compile CosmoScout VR yourself.
This is actually quite easy as there are several guides in the docs directory to get you started!
CosmoScout VR can be extended via plugins. In fact, without any plugins, CosmoScout VR is just a black and empty universe. Here is a list of available plugins.
| Official Plugins | Description | Screenshot |
|---|---|---|
| csp-anchor-labels | Draws a click-able label at each celestial anchor. When activated, the user automatically travels to the selected body. The size and overlapping-behavior of the labels can be adjusted. | 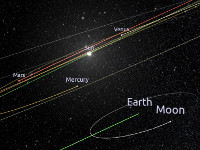 |
| csp-atmospheres | Draws atmospheres around celestial bodies. It calculates single Mie- and Rayleigh scattering via raycasting in real-time. |  |
| csp-custom-web-ui | Allows adding custom HTML-based user interface elements as sidebar-tabs, as floating windows or into free space. | 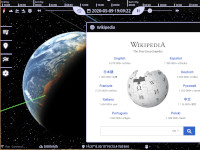 |
| csp-demo-node-editor | An example on how to use the csl-node-editor plugin library for creating data flow graphs within CosmoScout VR. |
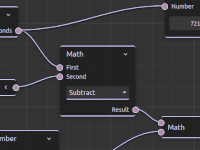 |
| csp-fly-to-locations | Adds several quick travel targets to the sidebar. It supports shortcuts to celestial bodies and to specific geographic locations on those bodies. |  |
| csp-lod-bodies | Draws level-of-detail planets and moons. This plugin supports the visualization of entire planets in a 1:1 scale. The data is streamed via Web-Map-Services (WMS) over the internet. A dedicated MapServer is required to use this plugin. | 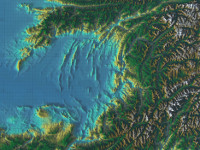 |
| csp-measurement-tools | Provides several tools for terrain measurements. Like measurement of distances, height profiles, volumes or areas. | 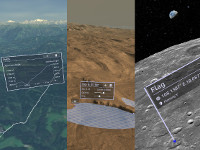 |
| csp-minimap | Displays a configurable 2D-Minimap in the user interface. | 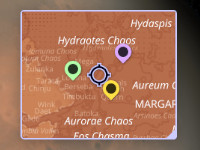 |
| csp-recorder | A CosmoScout VR plugin which allows basic capturing of high-quality videos. Requires that csp-web-api is enabled. |
 |
| csp-rings | Draws simple rings around celestial bodies. The rings can be configured with an inner and an outer radius and a texture. |  |
| csp-satellites | Draws GTLF models at positions based on SPICE data. It uses physically based rendering for surface shading. |  |
| csp-sharad | Renders radar datasets acquired by the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter. The SHARAD profiles are rendered inside of Mars, the Martian surface is made translucent in front of the profiles. |  |
| csp-simple-bodies | Renders simple spherical celestial bodies. The bodies are drawn as an ellipsoid with an equirectangular texture. |  |
| csp-stars | Draws 3D-stars loaded from catalogues. For now Tycho, Tycho2 and the Hipparcos catalogue are supported. |  |
| csp-timings | Uses the built-in timer queries of CosmoScout VR to draw on-screen live frame timing statistics. This plugin can also be used to export recorded time series to a CSV file. | 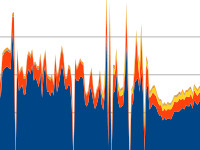 |
| csp-trajectories | Draws trajectories of celestial bodies and spacecrafts based on SPICE. The color, length, number of samples and the reference frame can be configured. | 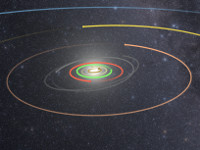 |
| csp-web-api | Allows to control CosmoScout VR via an HTTP protocol. It also allows capturing screenshots over HTTP. |  |
| csp-wms-overlays | Overlays time dependent map data from Web-Map-Services (WMS) over bodies rendered by other plugins. | 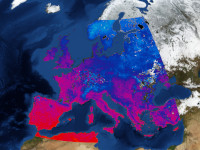 |
Some badges in this README.md are from shields.io. The documentation of CosmoScout VR also uses icons from simpleicons.org.







