ArangoDB is a multi-model, open-source database with flexible data models for documents, graphs, and key-values. Build high performance applications using a convenient SQL-like query language or JavaScript extensions. Use ACID transactions if you require them. Scale horizontally with a few mouse clicks.
The supported data models can be mixed in queries and allow ArangoDB to be the aggregation point for your data.
To get started, try one of our 10 minutes tutorials in your favorite programming language or try one of our ArangoDB Cookbook recipes.
For the impatient: download and install ArangoDB. Start the server arangod and point your browser to http://127.0.0.1:8529/.
- Multi-Model: Documents, graphs and key-value pairs — model your data as you see fit for your application.
- Joins: Conveniently join what belongs together for flexible ad-hoc querying, less data redundancy.
- Transactions: Easy application development keeping your data consistent and safe. No hassle in your client.
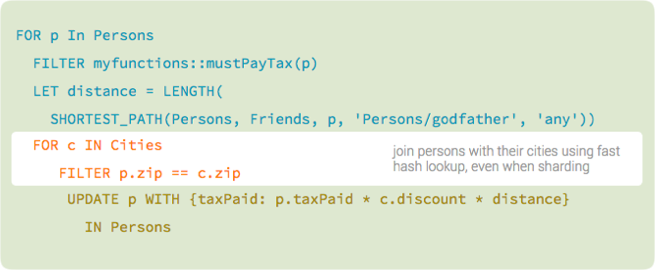
Here is an AQL query that makes use of all those features:
Joins and transactions are key features for flexible, secure data designs, widely used in relational databases but lacking in many NoSQL products. However, there is no need to forego them in ArangoDB. You decide how and when to use joins and strong consistency guarantees, without sacrificing performance and scalability.
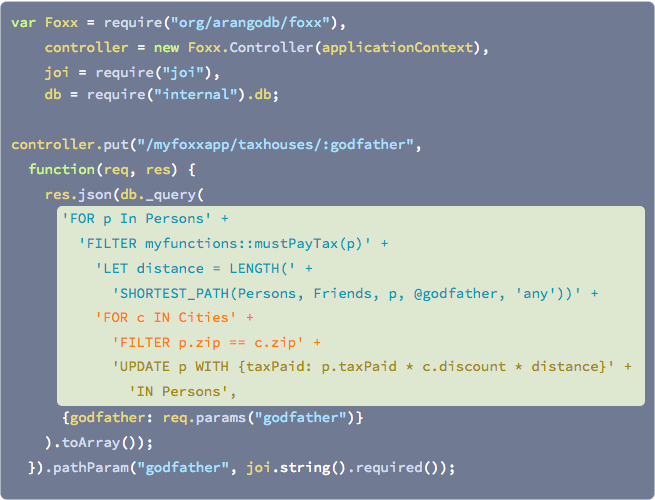
Furthermore, ArangoDB offers a JavaScript framework called Foxx that is executed in the database server with direct access to the data. Build your own data-centric microservices with a few lines of code:
Microservice Example
By extending the HTTP API with user code written in JavaScript, ArangoDB can be turned into a strict schema-enforcing persistence engine.
Next step, bundle your Foxx application as a docker container and get it running in the cloud.
Other features of ArangoDB include:
- Schema-free schemata let you combine the space efficiency of MySQL with the performance power of NoSQL
- Use a data-centric microservices approach with ArangoDB Foxx and fuse your application-logic and database together for maximal throughput
- JavaScript for all: no language zoo, you can use one language from your browser to your back-end
- ArangoDB is multi-threaded - exploit the power of all your cores
- Flexible data modeling: model your data as combination of key-value pairs, documents or graphs - perfect for social relations
- Free index choice: use the correct index for your problem, be it a skip list or a fulltext search
- Configurable durability: let the application decide if it needs more durability or more performance
- Powerful query language (AQL) to retrieve and modify data
- Transactions: run queries on multiple documents or collections with optional transactional consistency and isolation
- Replication and Sharding: set up the database in a master-slave configuration or spread bigger datasets across multiple servers
- It is open source (Apache License 2.0)
For more in-depth information read the design goals of ArangoDB
The What's new in ArangoDB 2.8 can be found in the documentation.
AQL Graph Traversals / Pattern Matching: AQL offers a new feature to traverse over a graph without writing JavaScript functions but with all the other features you know from AQL. For this purpose, a special version of FOR variable-name IN expression has been introduced.
The added Array Indexes are a major improvement to ArangoDB that you will love and never want to miss again. Hash indexes and skiplist indexes can now be defined for array values as well, so it’s freaking fast to access documents by individual array values.
Additional, there is a cool new aggregation feature that was added after the beta releases. AQL introduces the keyword AGGREGATE for use in AQL COLLECT statements. Using AGGREGATE allows more efficient aggregation (incrementally while building the groups) than previous versions of AQL, which built group aggregates afterwards from the total of all group values
Optimizer improvements: The AQL query optimizer can now use indexes if multiple filter conditions on attributes of the same collection are combined with logical ORs, and if the usage of indexes would completely cover these conditions.
ArangoDB 2.8 now has an automatic deadlock detection for transactions. A deadlock is a situation in which two or more concurrent operations (user transactions or AQL queries) try to access the same resources (collections, documents) and need to wait for the others to finish, but none of them can make any progress.
Foxx Improvements
The module resolution used by require now behaves more like in node.js. The org/arangodb/request module now returns response bodies for error responses by default. The old behavior of not returning bodies for error responses can be re-enabled by explicitly setting the option returnBodyOnError to false.
Please check the Installation Manual for installation and compilation instructions.
The User Manual has an introductory chapter showing the basic operations of ArangoDB.
We really appreciate feature requests and bug reports. Please use our Github issue tracker for reporting them:
https://github.com/arangodb/arangodb/issues
You can use the Google group for improvements, feature requests, comments