| page_type | languages | products | extensions | name | description | urlFragment | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
sample |
|
|
|
Load Testing Pipeline with JMeter, ACI and Terraform |
Azure Pipeline that provisions JMeter on Azure Container Instance using Terraform for load testing scenarios |
jmeter-aci-terraform |
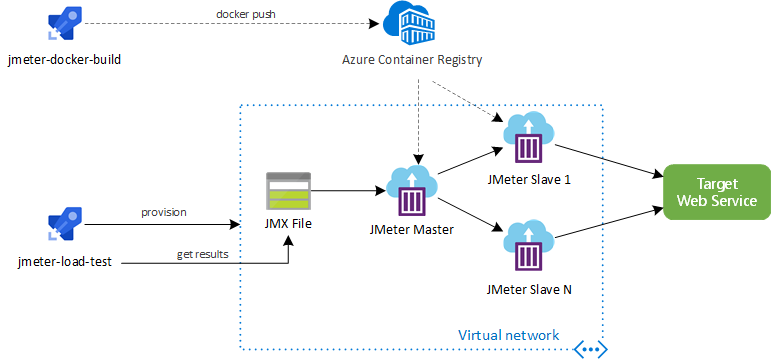
This project is a load testing pipeline that leverages Apache JMeter as an open source load and performance testing tool and Terraform to dynamically provision and destroy the required infrastructure on Azure.
The flow is triggered and controlled by an Azure Pipeline on Azure DevOps. The pipeline contains a set of tasks that are organized logically in SETUP, TEST, RESULTS and TEARDOWN groups.
| Task group | Tasks |
|---|---|
| SETUP | |
| TEST | |
| RESULTS | |
| TEARDOWN |
On the SETUP phase, JMeter agents are provisioned as Azure Container Instance (ACI) using a custom Docker image on Terraform. Through a master/slave approach, JMeter master is responsible to configure all slaves using its own protocol, consolidating all results and generating the resulting artifacts (dashboard, logs, etc).
The infrastructure provisioned by Terraform includes:
- Resource Group
- Virtual Network (VNet)
- Storage Account File Share
- 1 JMeter master on ACI
- N JMeter slaves on ACI
On the RESULTS phase, a JMeter Report Dashboard and Tests Results are published in the end of each load testing execution.
| Folder | Description |
|---|---|
| docker | JMeter custom image |
| docs | Documentation and images |
| jmeter | Contains JMX files used by JMeter agents |
| pipelines | Docker and JMeter pipeline definitions |
| scripts | Scripts that support pipeline execution |
| terraform | Terraform template for infrastructure creation |
First, you need to login on Azure CLI and configure Azure DevOps CLI with your organization/project settings:
az login
az devops configure --defaults organization=https://dev.azure.com/your-organization project=YourProjectThen, you can create/import this repository on Azure DevOps:
REPOSITORY_NAME=jmeter-load-test
REPOSITORY_URL=https://github.com/Azure-Samples/jmeter-aci-terraform
az repos create --name $REPOSITORY_NAME
az repos import create --git-source-url $REPOSITORY_URL --repository $REPOSITORY_NAMEYou can also use the UI to import it on Azure DevOps - As long as you don't forget to fill
$REPOSITORY_NAMEvariable with the actual repository name.
Get you service principal, your ACR credentials, and fill the following empty variables. Then, run this block on Bash:
CLIENT_ID=
CLIENT_SECRET=
TENANT_ID=
SUBSCRIPTION_ID=
ACR_NAME=
ACR_PASSWORD=Then run the following commands to create the variable groups JMETER_AZURE_PRINCIPAL and JMETER_TERRAFORM_SETTINGS:
PRIN_GROUP_ID=$(az pipelines variable-group create --name JMETER_AZURE_PRINCIPAL --authorize \
--variables ARM_CLIENT_ID=$ARM_CLIENT_ID \
ARM_TENANT_ID=$ARM_TENANT_ID \
ARM_SUBSCRIPTION_ID=$ARM_SUBSCRIPTION_ID \
| jq .id)
az pipelines variable-group variable create --group-id $PRIN_GROUP_ID --secret true \
--name ARM_CLIENT_SECRET \
--value $ARM_CLIENT_SECRET
SETT_GROUP_ID=$(az pipelines variable-group create --name JMETER_TERRAFORM_SETTINGS --authorize \
--variables TF_VAR_JMETER_IMAGE_REGISTRY_NAME=$ACR_NAME \
TF_VAR_JMETER_IMAGE_REGISTRY_USERNAME=$ACR_NAME \
TF_VAR_JMETER_IMAGE_REGISTRY_SERVER=$ACR_NAME.azurecr.io \
TF_VAR_JMETER_DOCKER_IMAGE=$ACR_NAME.azurecr.io/jmeter \
| jq .id)
az pipelines variable-group variable create --group-id $SETT_GROUP_ID --secret true \
--name TF_VAR_JMETER_IMAGE_REGISTRY_PASSWORD \
--value $ACR_PASSWORDPIPELINE_NAME_DOCKER=jmeter-docker-build
az pipelines create --name $PIPELINE_NAME_DOCKER --repository $REPOSITORY_NAME \
--repository-type tfsgit --branch master \
--yml-path pipelines/azure-pipelines.docker.ymlPIPELINE_NAME_JMETER=jmeter-load-test
az pipelines create --name $PIPELINE_NAME_JMETER --repository $REPOSITORY_NAME \
--repository-type tfsgit --branch master --skip-first-run \
--yml-path pipelines/azure-pipelines.load-test.yml
az pipelines variable create --pipeline-name $PIPELINE_NAME_JMETER --name TF_VAR_JMETER_JMX_FILE --allow-override
az pipelines variable create --pipeline-name $PIPELINE_NAME_JMETER --name TF_VAR_JMETER_SLAVES_COUNT --allow-overrideBy default, this repository uses a sample.jmx file under the jmeter folder. This JMX file contains a test definition for performing HTTP requests on azure.microsoft.com endpoint through the 443 port. You can simply update the it with the test definition of your preference.
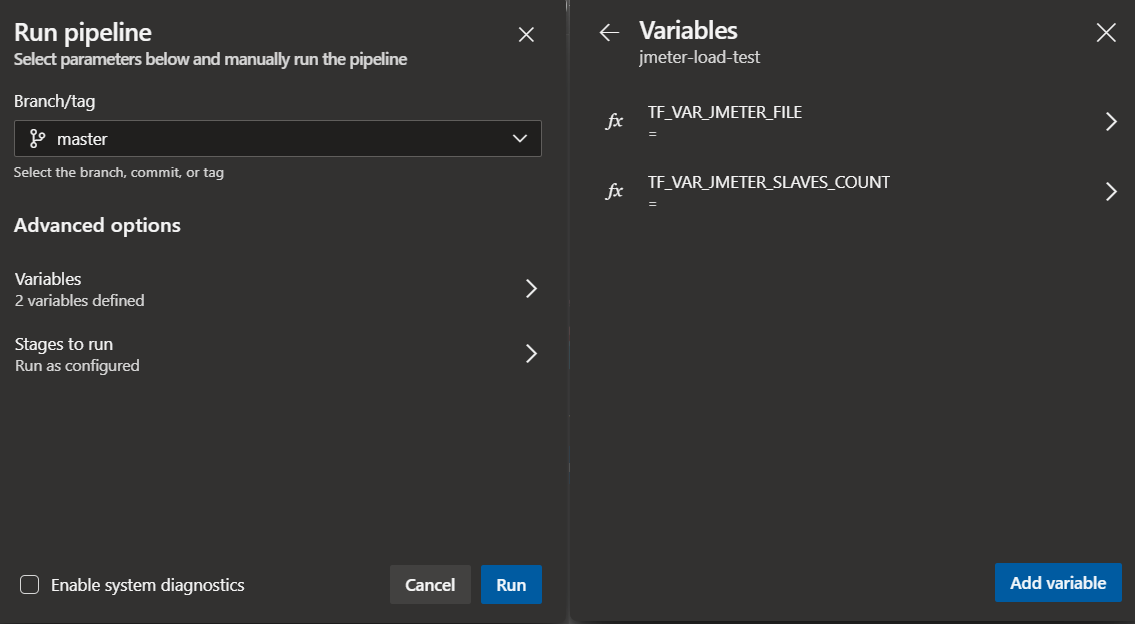
You can choose the JMeter file you want to run (e.g. jmeter/sample.jmx) and how many JMeter slaves you will need for your test. Then you can run the JMeter pipeline using the CLI:
JMETER_JMX_FILE=sample.jmx
JMETER_SLAVES_COUNT=1
az pipelines run --name $PIPELINE_NAME_JMETER \
--variables TF_VAR_JMETER_JMX_FILE=$JMETER_JMX_FILE TF_VAR_JMETER_SLAVES_COUNT=$JMETER_SLAVES_COUNTOr even use the UI to define variables and Run the pipeline:
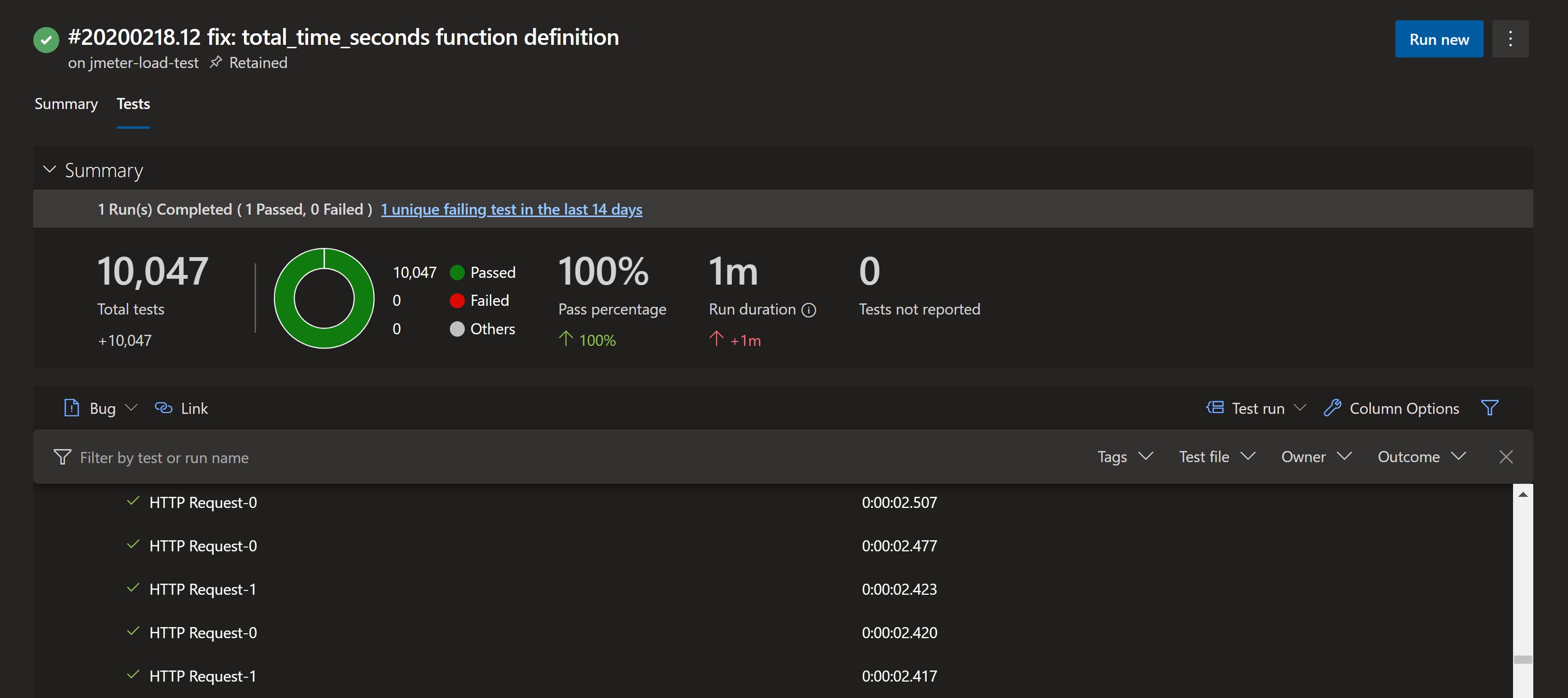
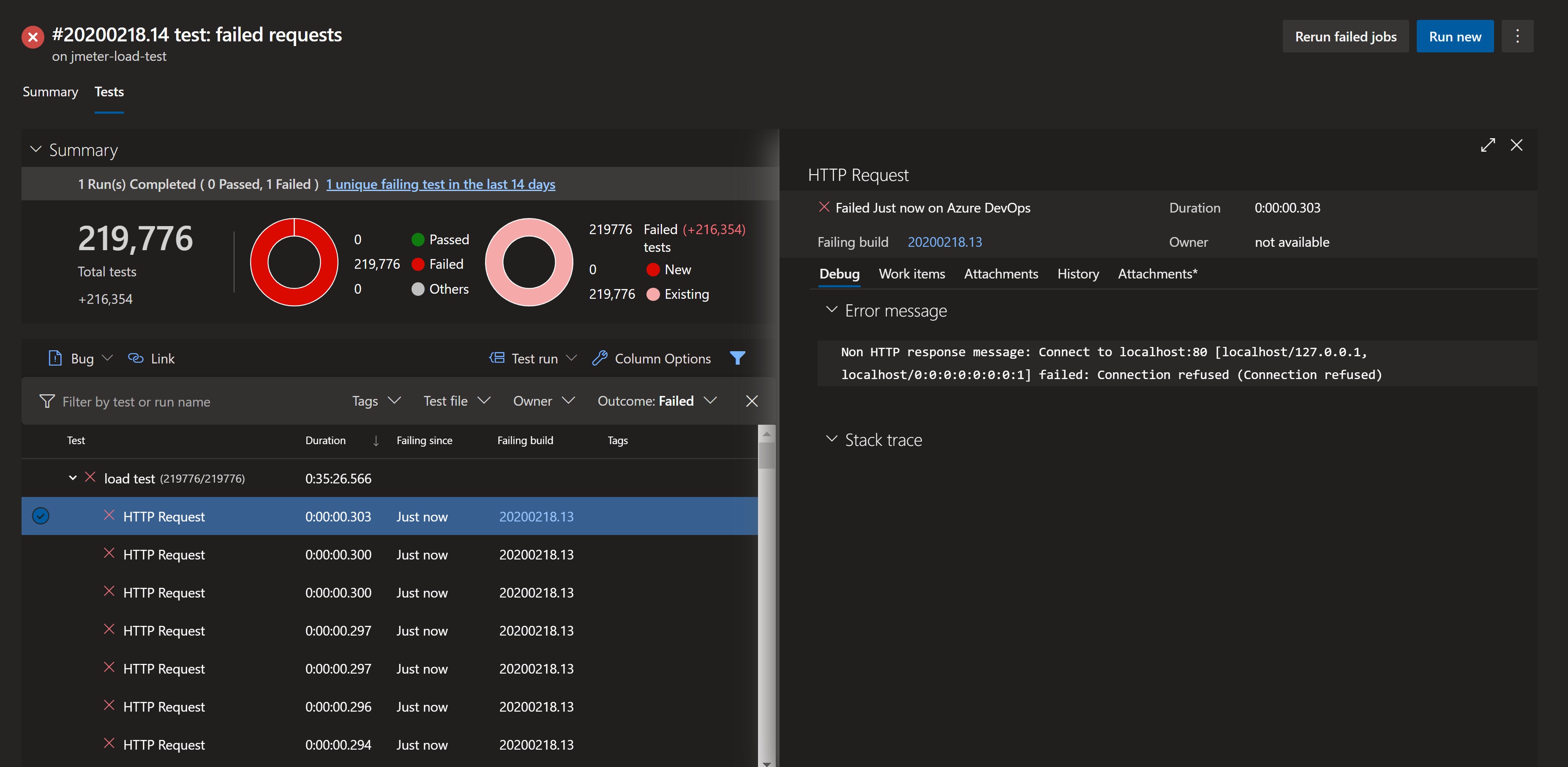
JMeter test results are created in a JTL file (results.jtl) with CSV formatting. A Python script was created to convert JTL to JUnit format and used during the pipeline to have full integration with Azure DevOps test visualization.
Error messages generated by JMeter for failed HTTP requests can also be seen on Azure DevOps.
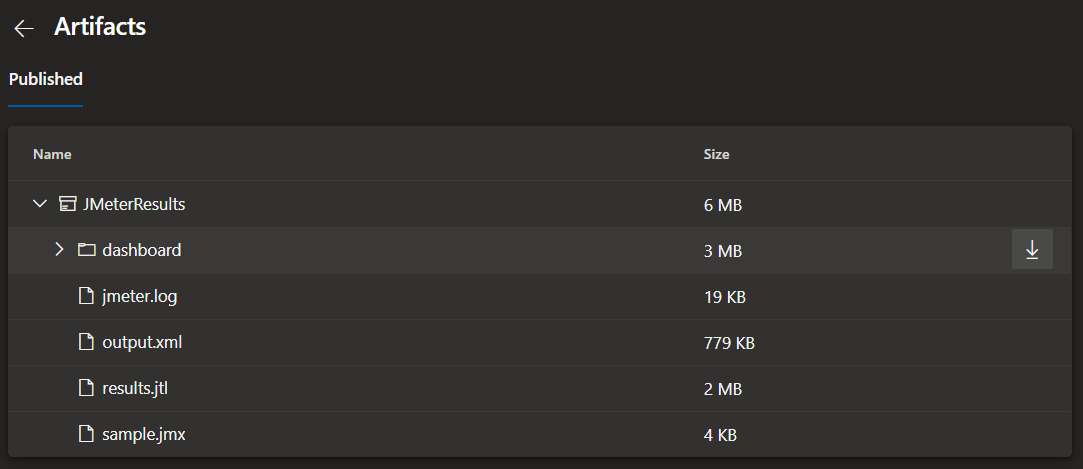
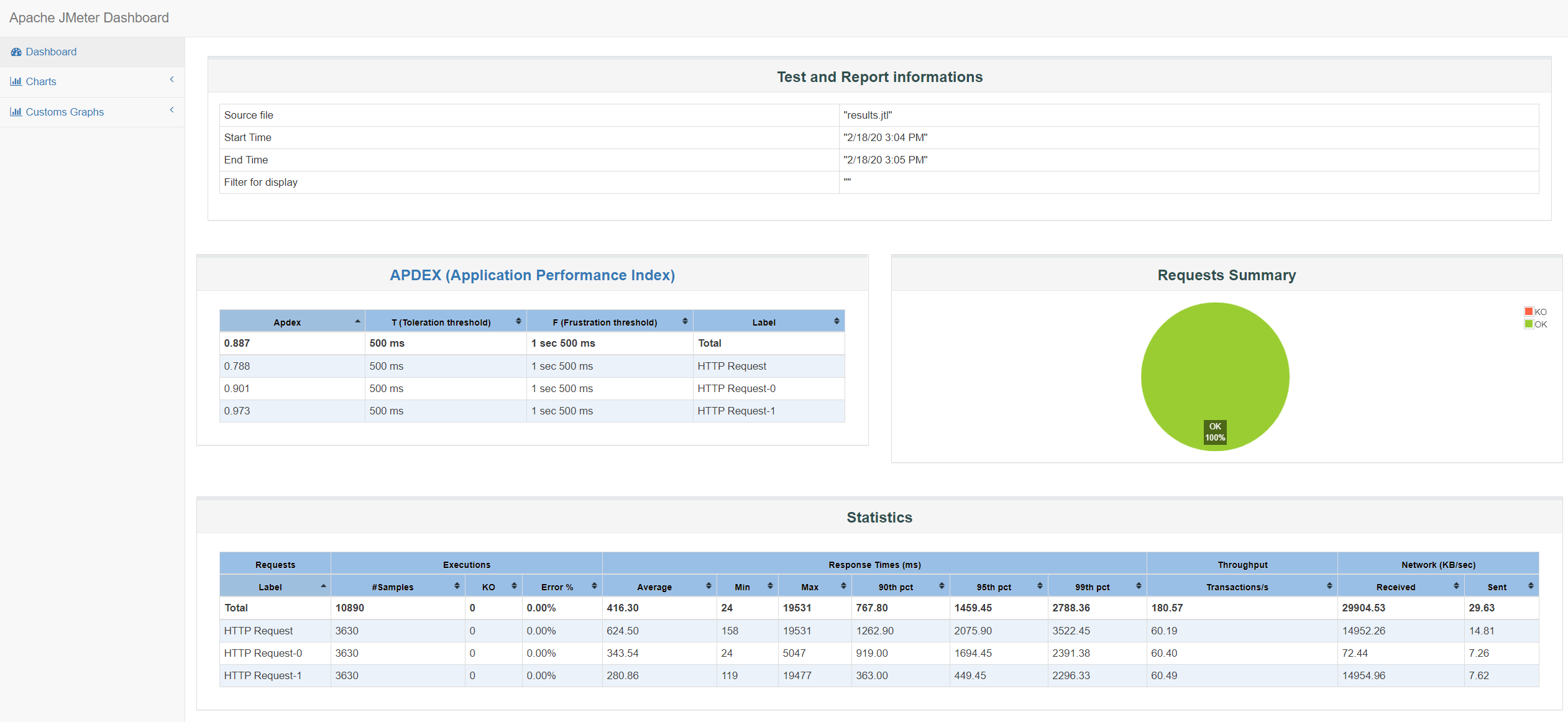
Some artifacts are published after the test ends. Some of them are a static JMeter Dashboard, logs and others.
You can also download these build artifacts using
az pipelines runs artifact download.
After downloading the dashboard and unzipping it, open dashboard/index.html on your browser:
All Terraform parameters can be configured using the Variable Group JMETER_TERRAFORM_SETTINGS. Please read JMeter Pipeline Settings to know more details about it.
This sample only shows how to manually trigger a JMeter Pipeline. You can easily adapt its content and incorporate it on other pipelines, apply continuous integration or other improvements.
This sample uses static JMX files on jmeter directory. You can use many techniques to parameterize JMX files. Some of them are:
Also, you can dynamically generate JMX files from Swagger/Open API using swagger-codegen or other similar projects.
Current Terraform template creates a new VNET to host JMeter installation. Instead you can modify the template to deploy agents in an existing VNET or your can apply VNET peering to connect them into an existing infrastructure.
-
Load Test duration Please note that for Microsoft hosted agents, you can have pipelines that runs up to 1 hour (private project) or 6 hours (public project). You can have your own agents to bypass this limitation.
-
ACI on VNET regions Please note that not all regions currently support ACI and VNET integration. If you need private JMeter agents, you can deploy it in a different region and use VNET peering between them.
- User Manual: Remote Testing
- User Manual: Apache JMeter Distributed Testing Step-by-step
- Azure DevOps CLI reference
This project welcomes contributions and suggestions. Most contributions require you to agree to a Contributor License Agreement (CLA) declaring that you have the right to, and actually do, grant us the rights to use your contribution. For details, visit https://cla.opensource.microsoft.com.
When you submit a pull request, a CLA bot will automatically determine whether you need to provide a CLA and decorate the PR appropriately (e.g., status check, comment). Simply follow the instructions provided by the bot. You will only need to do this once across all repos using our CLA.
This project has adopted the Microsoft Open Source Code of Conduct. For more information see the Code of Conduct FAQ or contact [email protected] with any additional questions or comments.