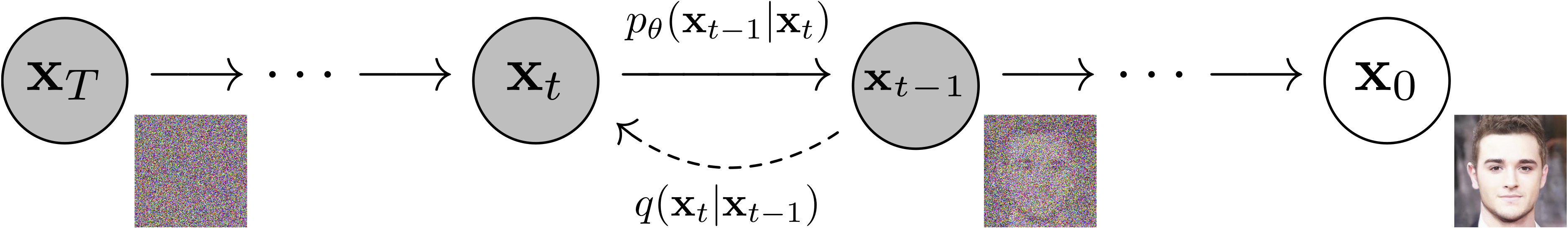
Pytorch implementation of "Improved Denoising Diffusion Probabilistic Models", "Denoising Diffusion Probabilistic Models" and "Classifier-free Diffusion Guidance"
-
Install pip package containing the pytorch lightning model, which includes also the training step
pip install ddpm -
Clone the repository
git clone [email protected]:Michedev/VAE_anomaly_detection.git
-
Install anaconda or miniconda, but install anaconda-project
conda install anaconda-project -
Train the model
anaconda-project run trainBy default, the version of trained DDPM is from "Improved Denoising Diffusion Probabilistic Models" paper on MNIST dataset. You can switch to the original DDPM by disabling the variational lower bound with the following command:
anaconda-project run train model.vlb=FalseYou can also train the DDPM with the Classifier-free Diffusion Guidance by changing the model:
anaconda-project run train model=unet_class_conditionedor via the shortcut
anaconda-project run train-class-conditionedFinally, under saved_models/{train-datetime} you can find the trained model, the tensorboard logs, the training config
-
Train a model (See previous section)
-
Generate a new batch of images
anaconda-project run generate -r RUNThe other options are:
[--seed SEED] [--device DEVICE] [--batch-size BATCH_SIZE] [-w W] [--scheduler {linear,cosine,tan}] [-T T]
Under config there are several yaml files containing the training parameters such as model class and paramters, noise steps, scheduler and so on. Note that the hyperparameters in such files are taken from the papers "Improved Denoising Diffusion Probabilistic Models" and "Denoising Diffusion Probabilistic Models". Down below the explaination of the config file for train the model:
defaults:
- model: unet_paper # take the model config from model/unet_paper.yaml
- scheduler: cosine # use the cosine scheduler from scheduler/cosine.yaml
- dataset: mnist
- optional model_dataset: ${model}-${dataset} # set particular hyper parameters for specific couples (model, dataset)
- optional model_scheduler: ${model}-${scheduler} # set particular hyper parameters for specific couples (model, scheduler)
batch_size: 128 # train batch size
noise_steps: 4_000 # noising steps; the T in "Improved Denoising Diffusion Probabilistic Models" and "Denoising Diffusion Probabilistic Models"
accelerator: null # training hardware; for more details see pytorch lightning
devices: null # training devices to use; for more details see pytorch lightning
gradient_clip_val: 0.0 # 0.0 means gradient clip disabled
gradient_clip_algorithm: norm # gradient clip has two values: 'norm' or 'value
ema: true # use Exponential Moving Average implemented in ema.py
ema_decay: 0.99 # decay factor of EMA
hydra:
run:
dir: saved_models/${now:%Y_%m_%d_%H_%M_%S}
.
├── anaconda-project-lock.yml # lock file for anaconda-project
├── anaconda-project.yml # project specs
├── callbacks # Pytorch Lightning callbacks for training
│ ├── ema.py # exponential moving average callback
├── config # config files for training for hydra
│ ├── dataset # dataset config files
│ ├── model # model config files
│ ├── model_dataset # specific (model, dataset) config
│ ├── model_scheduler # specific (model, scheduler) config
│ ├── scheduler # scheduler config files
│ └── train.yaml # training config file
├── generate.py # script for generating images
├── model # model files
│ ├── classifier_free_ddpm.py # Classifier-free Diffusion Guidance
│ ├── ddpm.py # Denoising Diffusion Probabilistic Models
│ ├── distributions.py # distributions functions for diffusion
│ ├── unet_class.py # UNet model for Classifier-free Diffusion Guidance
│ └── unet.py # UNet model for Denoising Diffusion Probabilistic Models
├── pyproject.toml # setuptool file to publish model/ to pypi
├── readme.md # this file
├── readme_pip.md # readme for pypi
├── train.py # script for training
├── utils # utility functions
└── variance_scheduler # variance scheduler files
├── cosine.py # cosine variance scheduler
└── linear.py # linear variance scheduler
To add a custom dataset, you need to create a new class that inherits from torch.utils.data.Dataset and implement the len and getitem methods. Then, you need to add the config file to the config/dataset folder with a similar structure of mnist.yaml
width: 28 # meta info about the dataset
height: 28
channels: 1 # number of image channels
num_classes: 10 # number of classes
files_location: ~/.cache/torchvision_dataset # location where to store the dataset, in case to be downloaded
train: #dataset.train is instantiated with this config
_target_: torchvision.datasets.MNIST # Dataset class. Following arguments are passed to the dataset class constructor
root: ${dataset.files_location}
train: true
download: true
transform:
_target_: torchvision.transforms.ToTensor
val: #dataset.val is instantiated with this config
_target_: torchvision.datasets.MNIST # Same dataset of train, but the validation split
root: ${dataset.files_location}
train: false
download: true
transform:
_target_: torchvision.transforms.ToTensor
anaconda-project run train scheduler=linear accelerator='gpu' model.vlb=False noise_steps=1000
Use the labels for Diffusion Guidance, as in "Classifier-free Diffusion Guidance" with the following command
anaconda-project run train model=unet_class_conditioned noise_steps=1000
- Add a new class (preferabily under
variance_scheduler/) which subclassesSchedulerclass or just copy the same methods syntax ofScheduler - Define a new config under
config/schedulerwith the name my-scheduler.yaml containing the following fields
_target_: {your scheduler import path} (e.g. variance_scheduler.Linear)
... // your scheduler additional parameters
Finally train with the following command
anaconda-project run train scheduler=my-scheduler
-
Add a new class which subclasses
torch.utils.data.Dataset -
Define a new config under
config/datasetwith the name my-dataset.yaml containing the following fields
width: ???
height: ???
channels: ???
train:
_target_: {your dataset import path} (e.g. torchvision.datasets.MNIST)
// your dataset additional parameters
val:
_target_: {your dataset import path} (e.g. torchvision.datasets.MNIST)
// your dataset additional parameters
Finally train with the following command
anaconda-project run train dataset=my-dataset
- Remove cudatoolkit from anaconda-project.yml file at the bottom of the file,
under
env_specs -> default -> packages - De-comment
- osx-64underenv_specs -> default -> platforms - Delete anaconda-project-lock.yml file
- Run
anaconda-project prepareto generate the new lock file
To have an alternative a PyTorch CPU-only environment,
de-comment the following lines at the bottom of anaconda-project.yml
under env_specs
# pytorch-cpu:
# packages:
# - cpuonly
# channels:
# - pytorch
# platforms:
# - linux-64
# - win-64