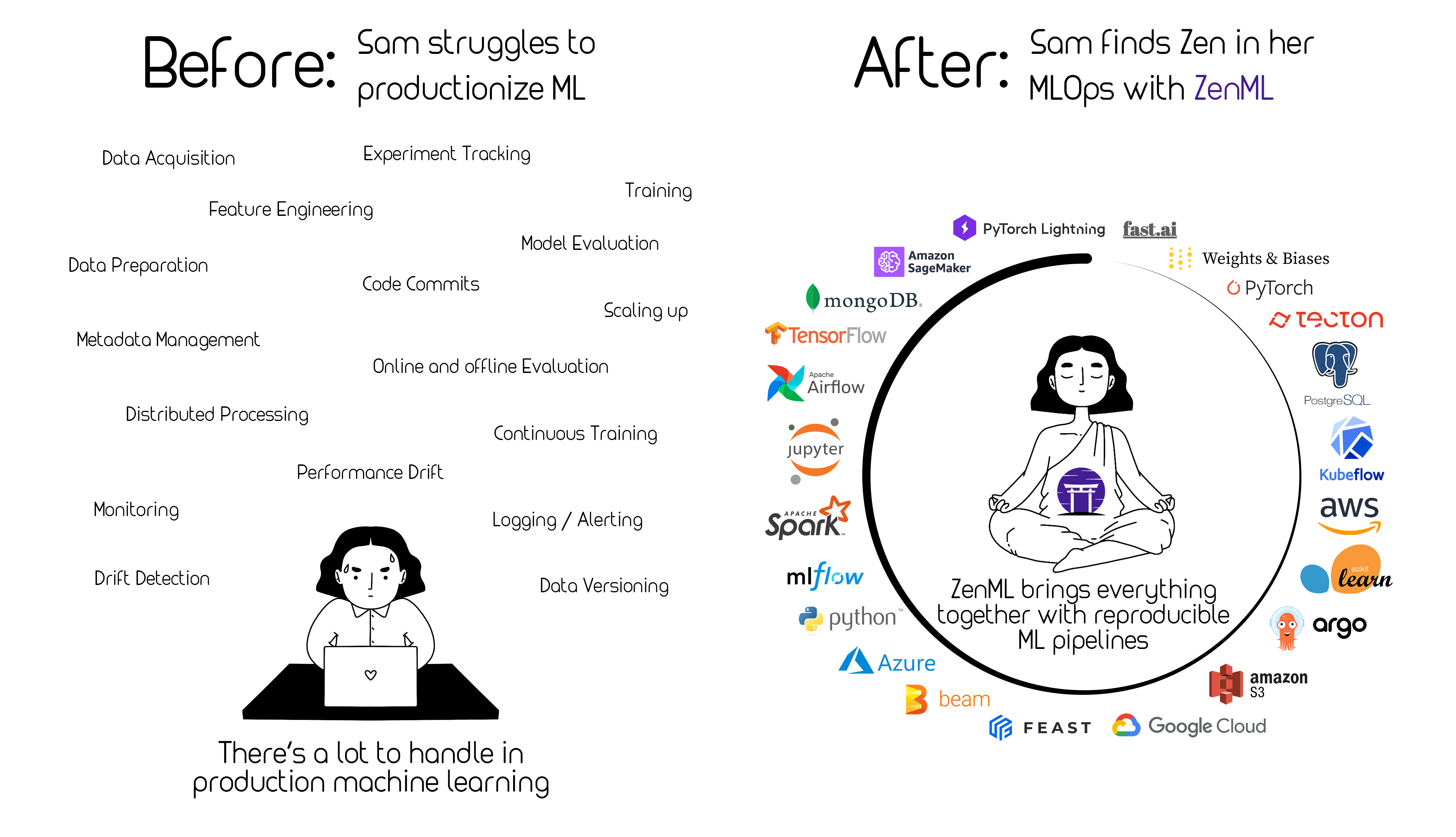
ZenML is an extensible, open-source MLOps framework to create production-ready machine learning pipelines. Built for data scientists, it has a simple, flexible syntax, is cloud- and tool-agnostic, and has interfaces/abstractions that are catered towards ML workflows.
At its core, ZenML pipelines execute ML-specific workflows from sourcing data to splitting, preprocessing, training, all the way to the evaluation of results and even serving. There are many built-in batteries to support common ML development tasks. ZenML is not here to replace the great tools that solve these individual problems. Rather, it integrates natively with popular ML tooling and gives standard abstraction to write your workflows.
🎉 Version 0.6.2 out now! Check out the release notes here.
ZenML pipelines are designed to be written early on the development lifecycle. Data scientists can explore their pipelines as they develop towards production, switching stacks from local to cloud deployments with ease. You can read more about why we started building ZenML on our blog. By using ZenML in the early stages of your project, you get the following benefits:
- Reproducibility of training and inference workflows
- A simple and clear way to represent the steps of your pipeline in code
- Plug-and-play integrations: bring all your favorite tools together
- Easy switching between local and cloud stacks
- Painless deployment and configuration of infrastructure
- Scale up your stack transparently and logically to suit your training and deployment needs
| ZenML Resources | Description |
|---|---|
| 🧘♀️ ZenML 101 | New to ZenML? Here's everything you need to know! |
| ⚛️ Core Concepts | Some key terms and concepts we use. |
| 🗃 Functional API Guide | Build production ML pipelines with simple functions. |
| 🚀 New in v0.6.2 | New features, bug fixes. |
| 🗳 Vote for Features | Pick what we work on next! |
| 📓 Docs | Full documentation for creating your own ZenML pipelines. |
| 📒 API Reference | The detailed reference for ZenML's API. |
| ⚽️ Examples | Learn best through examples where ZenML is used? We've got you covered. |
| 📬 Blog | Use cases of ZenML and technical deep dives on how we built it. |
| 🔈 Podcast | Conversations with leaders in ML, released every 2 weeks. |
| 📣 Newsletter | We build ZenML in public. Subscribe to learn how we work. |
| 💬 Join Slack | Need help with your specific use case? Say hi on Slack! |
| 🗺 Roadmap | See where ZenML is working to build new features. |
| 🙋♀️ Contribute | How to contribute to the ZenML project and code base. |
ZenML makes sure for every pipeline you can trust that:
- Code is versioned
- Data is versioned
- Models are versioned
- Configurations are versioned
You can utilize caching to help iterate quickly through ML experiments. (Read our blogpost to learn more!)
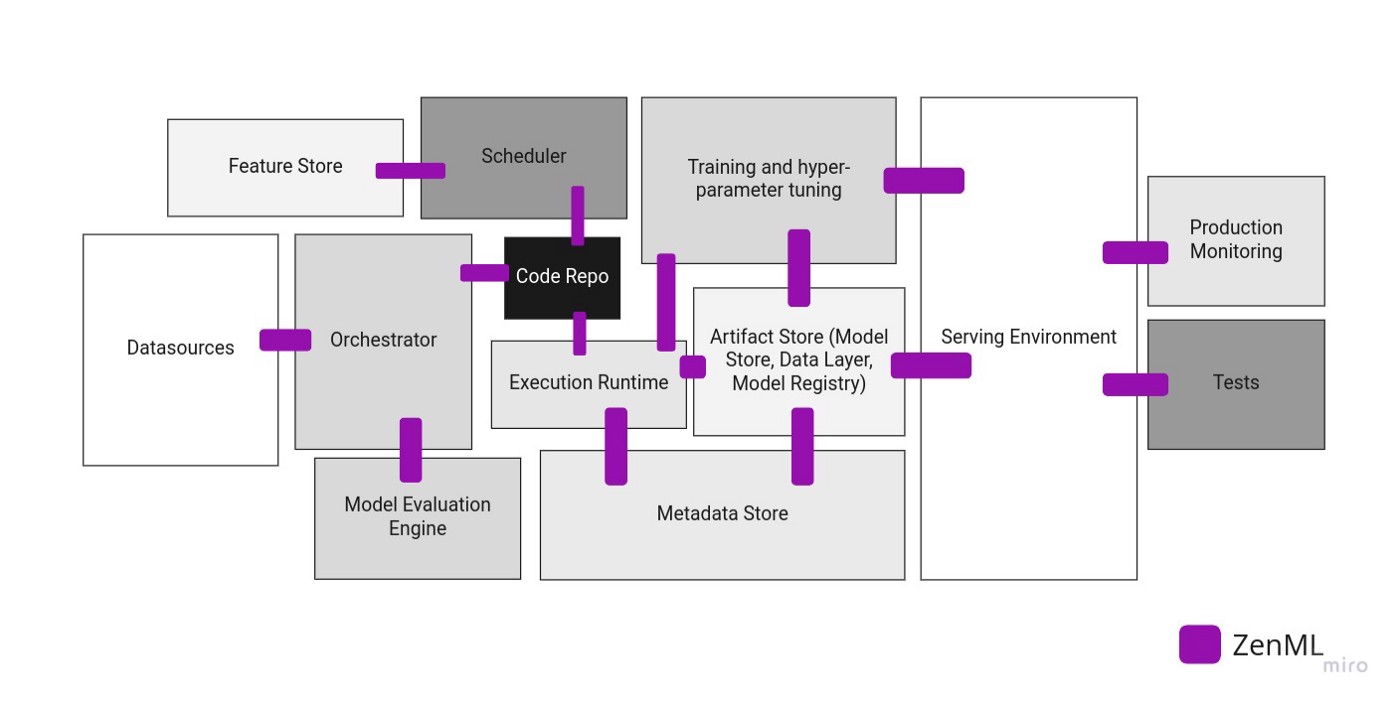
Once code is organized into a ZenML pipeline, you can supercharge your ML development with powerful integrations on multiple MLOps stacks. There are lots of moving parts for all the MLOps tooling and infrastructure you require for ML in production and ZenML aims to bring it all together under one roof.
We currently support Airflow and Kubeflow as third-party orchestrators for your ML pipeline code. ZenML steps can be built from any of the other tools you usually use in your ML workflows, from scikit-learn to PyTorch or TensorFlow.
Switching from local experiments to cloud-based pipelines doesn't need to be complicated. ZenML supports running pipelines on Kubernetes clusters in the cloud through our Kubeflow integration. Switching from your local stack to a cloud stack is easy to do with our CLI tool.
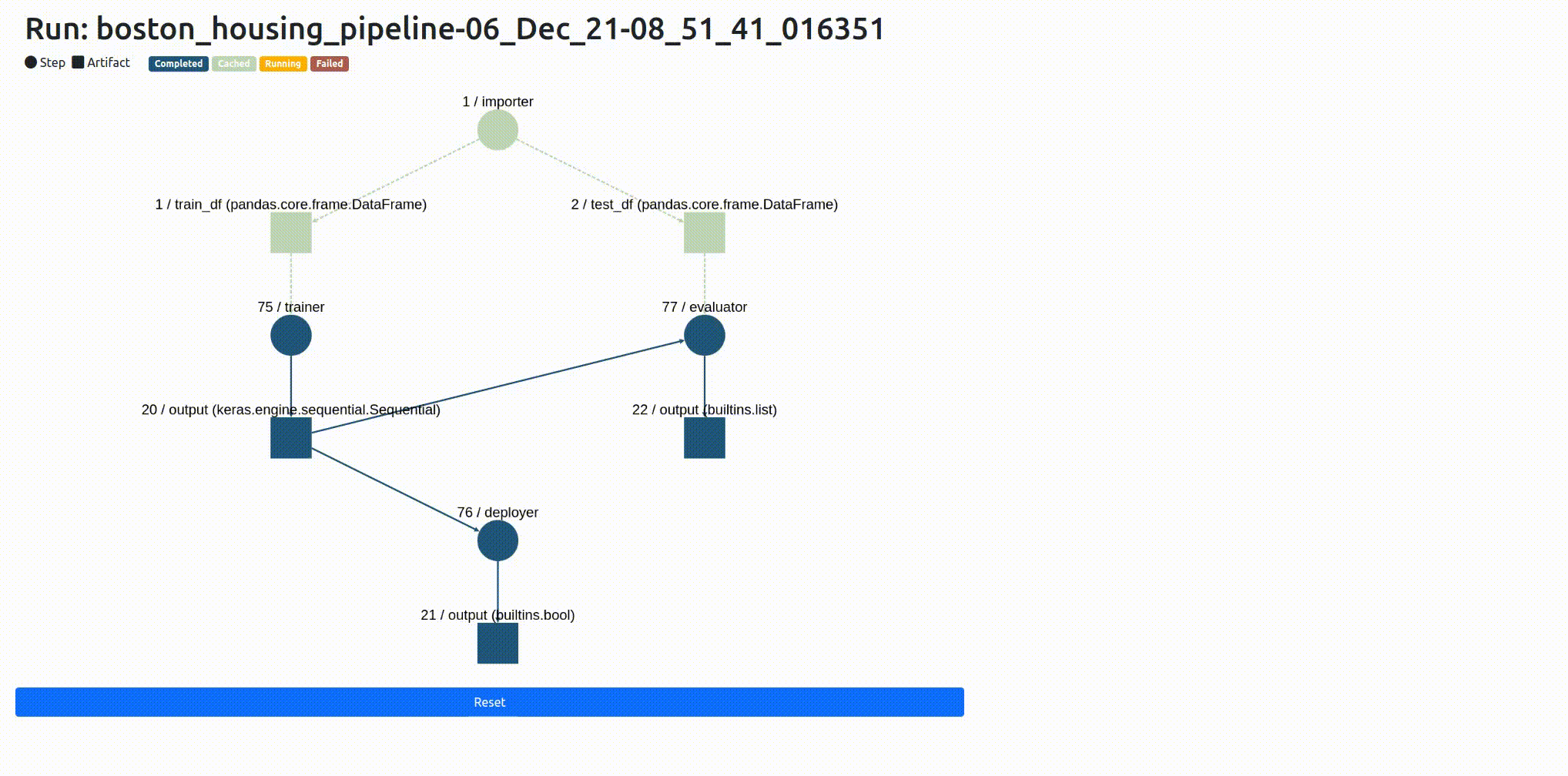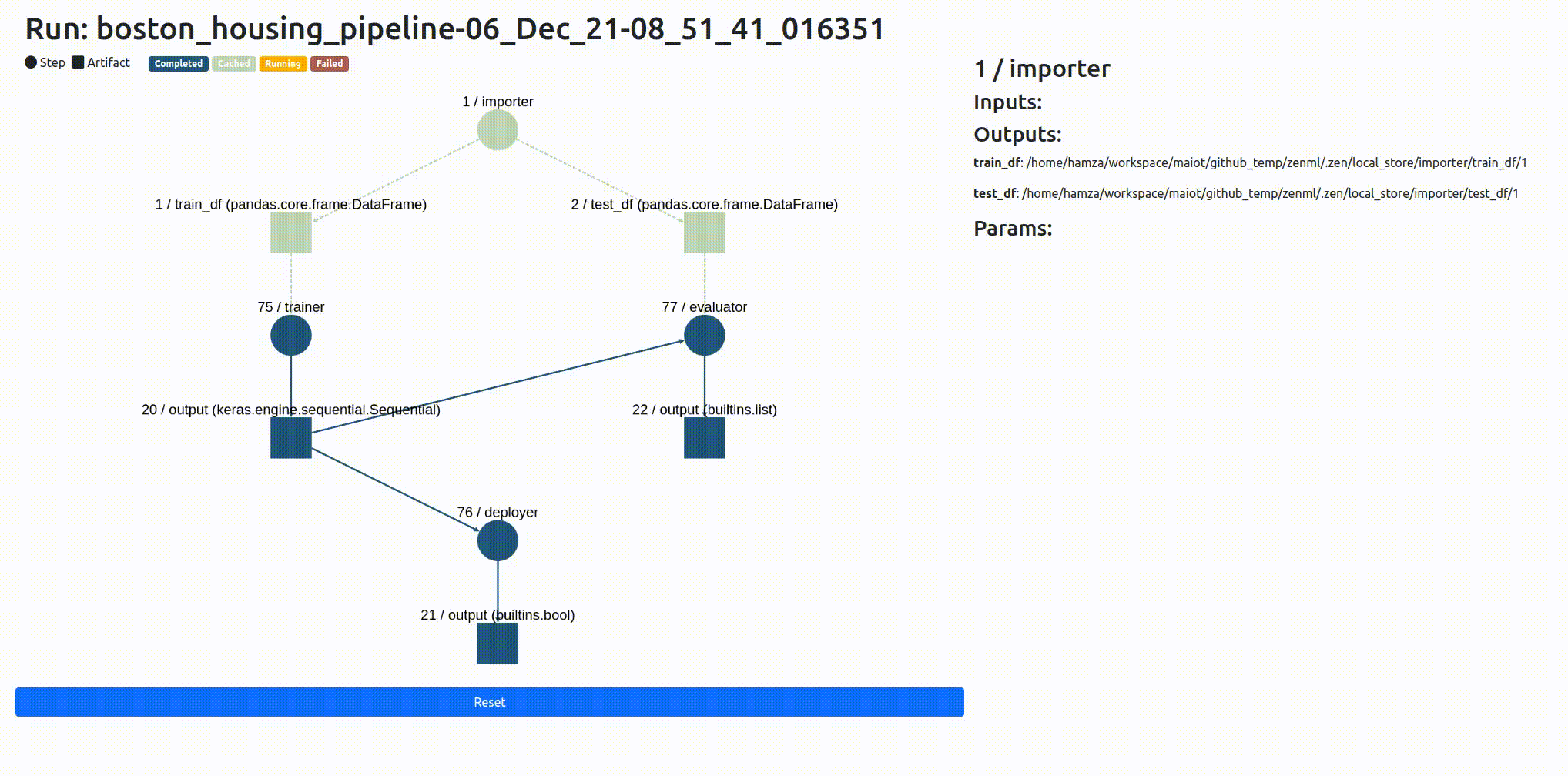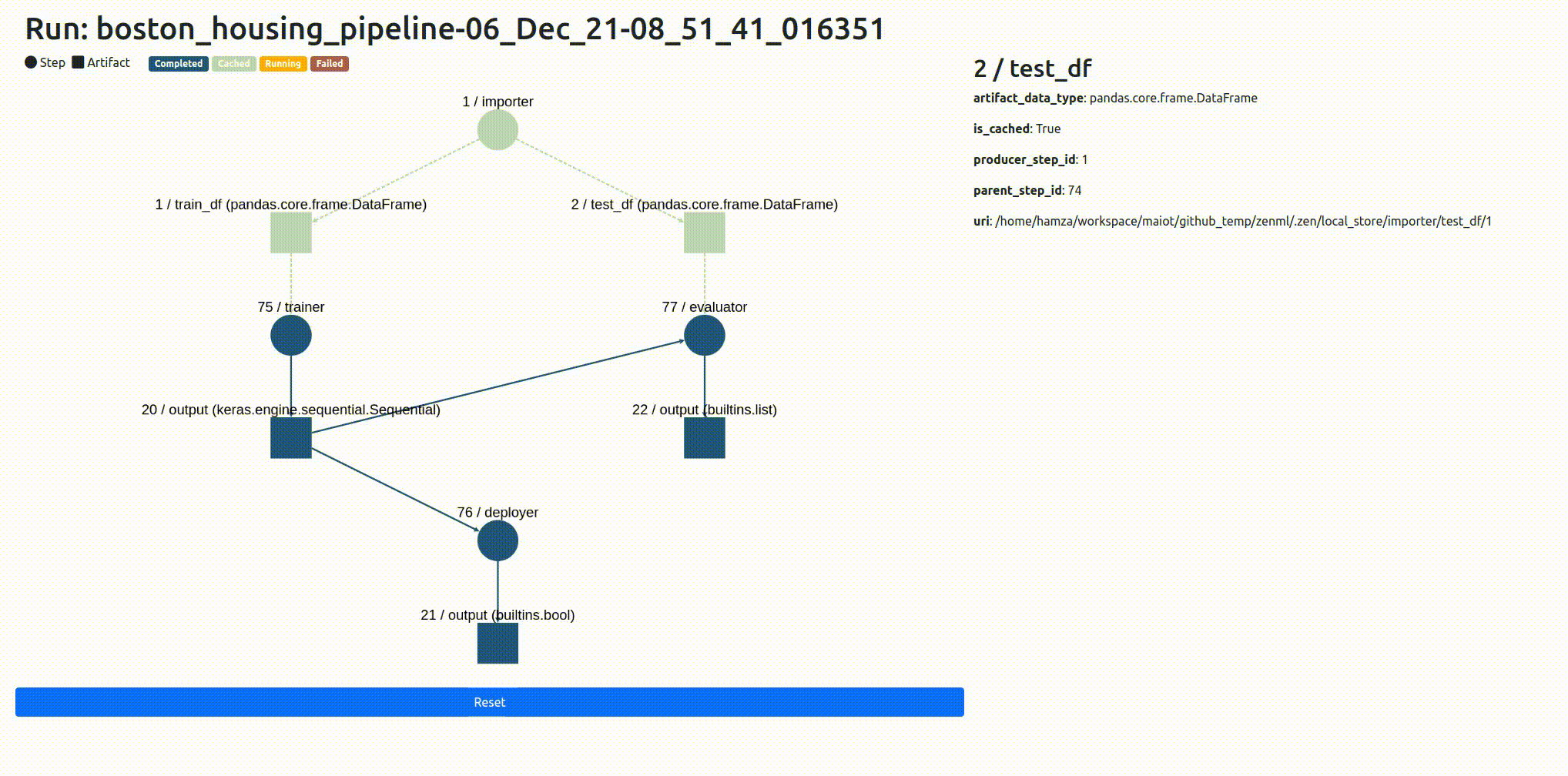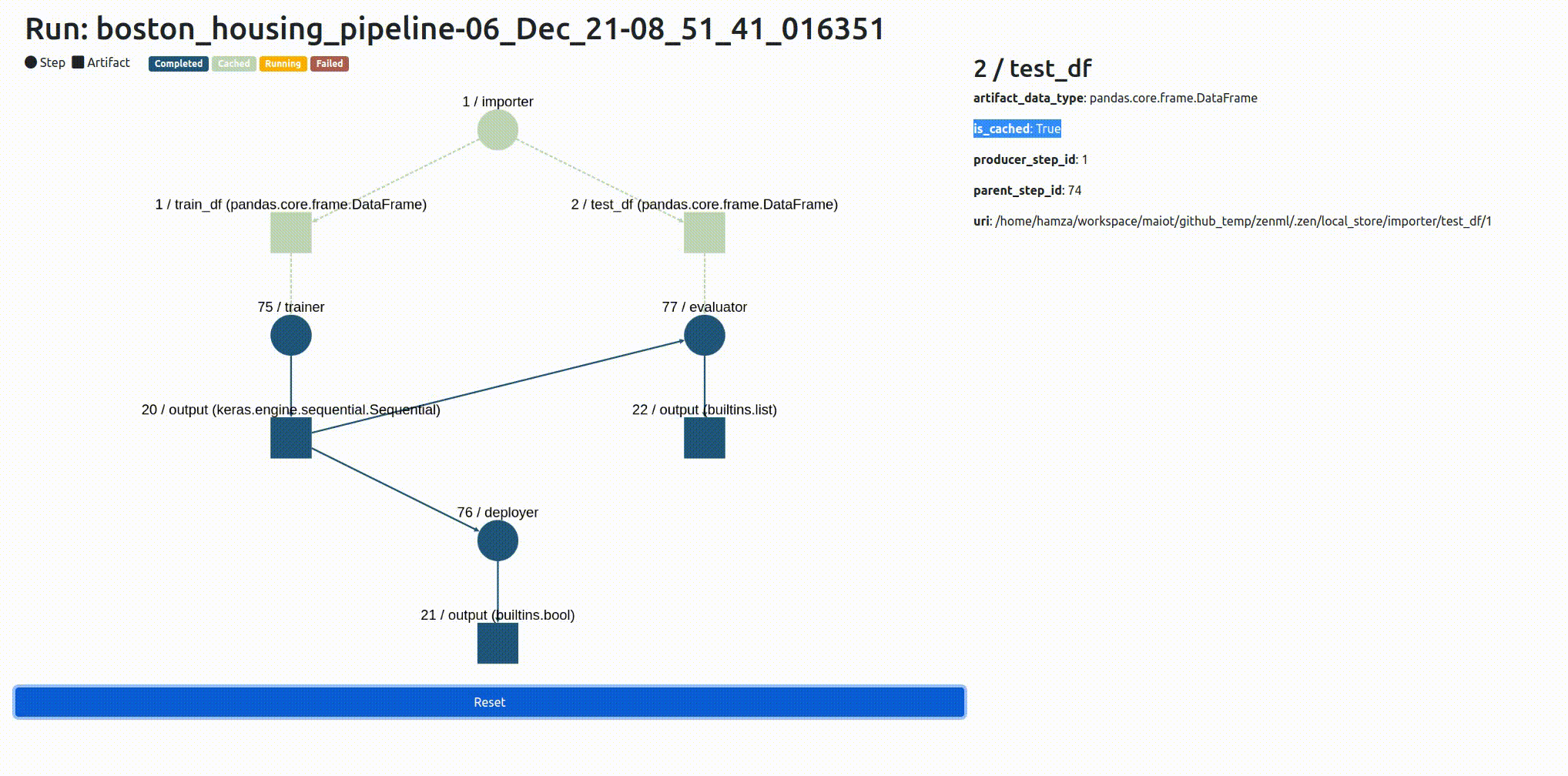
It’s not uncommon for pipelines to be made up of many steps, and those steps can interact and intersect with one another in often complex patterns. We’ve built a way for you to inspect what’s going on with your ZenML pipeline:
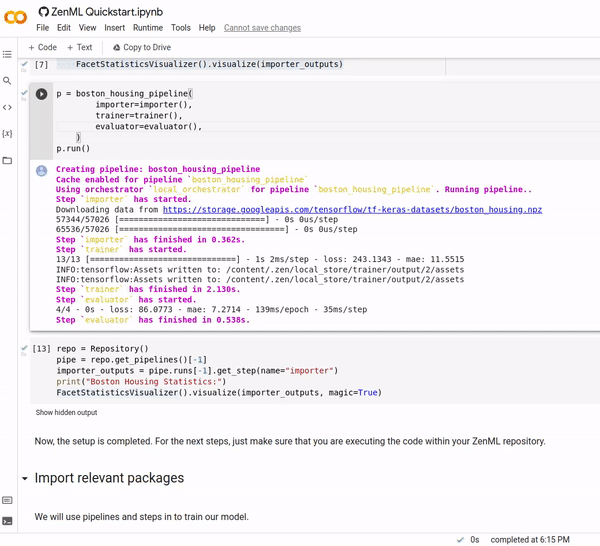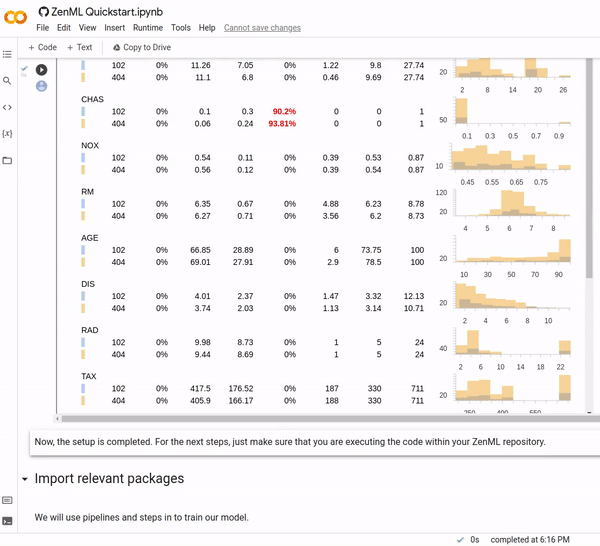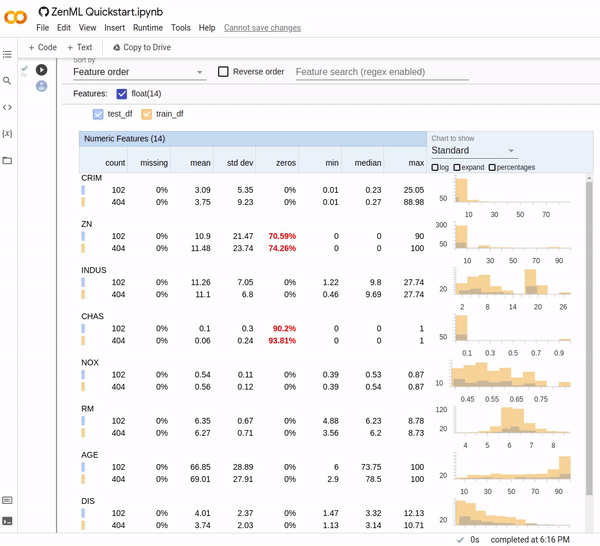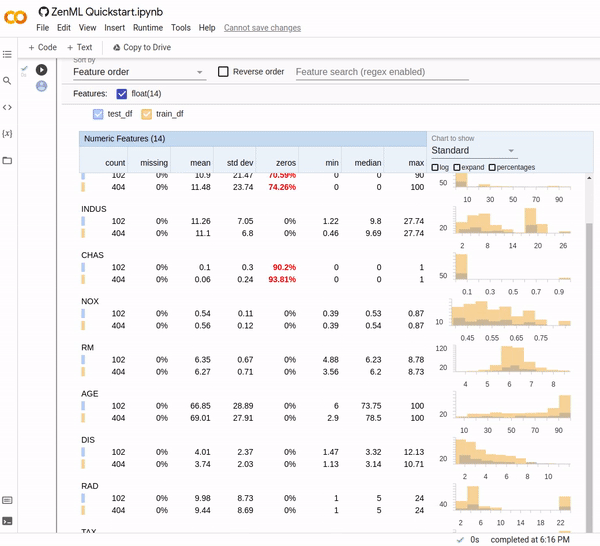
Now you can use awesome third-party libraries to visualize ZenML steps and artifacts. We support the facets visualization for statistics out of the box, to find data drift between your training and test sets.
We use the built-in FacetStatisticsVisualizer using the Facets Overview integration.
Once you've run your experiment, you need a way of seeing what was produced and how it was produced. We offer a flexible interface to support post-execution workflows. This allows you to access any of the artifacts produced by pipeline steps as well as any associated metadata.
pipeline = repo.get_pipeline(pipeline_name=..., stack_key=...) # access a pipeline by name and/or stack key
runs = pipeline.runs # all runs of a pipeline chronologically ordered
run = runs[-1] # latest run
steps = run.steps # all steps of a pipeline
step = steps[0]
output = step.output
df = output.read(materializer_class=PandasMaterializer)
df.head()Not everyone wants to keep their configuration of pipeline runs in the same place as the active code defining steps. You can define the particular customization of runs with YAML code if that's your jam!
steps:
step_name:
parameters:
parameter_name: parameter_value
some_other_parameter_name: 2
some_other_step_name:
...Requirements: ZenML supports Python 3.6, 3.7 and 3.8.
ZenML is available for easy installation into your environment via PyPI:
pip install zenmlAlternatively, if you’re feeling brave, feel free to install the bleeding edge: NOTE: Do so on your own risk, no guarantees given!
pip install git+https://github.com/zenml-io/zenml.git@main --upgradeZenML is also available as a Docker image hosted publicly on DockerHub. Use the following command to get started in a bash environment:
docker run -it zenmldocker/zenml /bin/bashThe quickest way to get started is to create a simple pipeline.
zenml init
zenml integration install sklearn # we use scikit-learn for this exampleimport numpy as np
from sklearn.base import ClassifierMixin
from zenml.integrations.sklearn.helpers.digits import get_digits, get_digits_model
from zenml.pipelines import pipeline
from zenml.steps import step, Output
@step
def importer() -> Output(
X_train=np.ndarray, X_test=np.ndarray, y_train=np.ndarray, y_test=np.ndarray
):
"""Loads the digits array as normal numpy arrays."""
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = get_digits()
return X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test
@step
def trainer(
X_train: np.ndarray,
y_train: np.ndarray,
) -> ClassifierMixin:
"""Train a simple sklearn classifier for the digits dataset."""
model = get_digits_model()
model.fit(X_train, y_train)
return model
@step
def evaluator(
X_test: np.ndarray,
y_test: np.ndarray,
model: ClassifierMixin,
) -> float:
"""Calculate the accuracy on the test set"""
test_acc = model.score(X_test, y_test)
print(f"Test accuracy: {test_acc}")
return test_acc
@pipeline
def mnist_pipeline(
importer,
trainer,
evaluator,
):
"""Links all the steps together in a pipeline"""
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = importer()
model = trainer(X_train=X_train, y_train=y_train)
evaluator(X_test=X_test, y_test=y_test, model=model)
pipeline = mnist_pipeline(
importer=importer(),
trainer=trainer(),
evaluator=evaluator(),
)
pipeline.run()ZenML is being built in public. The roadmap is a regularly updated source of truth for the ZenML community to understand where the product is going in the short, medium, and long term.
ZenML is managed by a core team of developers that are responsible for making key decisions and incorporating feedback from the community. The team oversees feedback via various channels, and you can directly influence the roadmap as follows:
- Vote on your most wanted feature on our Discussion board.
- Create a Feature Request in the GitHub board.
- Start a thread in our Slack channel.
We would love to develop ZenML together with our community! Best way to get started is to select any issue from the good-first-issue label. If you would like to contribute, please review our Contributing Guide for all relevant details.
First point of call should be our Slack group. Ask your questions about bugs or specific use cases and someone from the core team will respond.
ZenML is distributed under the terms of the Apache License Version 2.0. A complete version of the license is available in the LICENSE.md in this repository. Any contribution made to this project will be licensed under the Apache License Version 2.0.