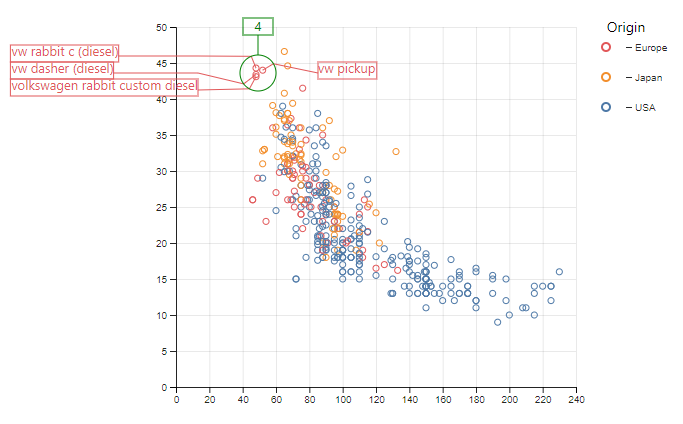
Excentric Labeling is a labeling technique, which is presented by Jean-Daniel Fekete and Catherine Plaisant in this paper. In this repository, we implement the layout algorithm about it.
- live demo
- source code
- out-of-box interaction helper function, which combines excentric-labeling algrithom, rendering and event handler.
<script src="https://unpkg.com/[email protected]/dist/index.js"></script>Then anywhere in your JavaScript code.
js const excentricLabeling = window.excentricLabeling
npm i excentric-labeling
Then anywhere in your code.
import excentricLabeling from "excentricLabeling"OR
const excentricLabeling = require("excentric-labeling");import excentricLabeling from "excent";
declare const rawData: RawInfo[];
declare const x: number;
declare const y: number;
const computor: Computor = excentricLabeling();
computor.defaultLabelWidth(20)
.defaultLabelHeight(5)
.radius(10)
const result= computor(rawData, x, y)RawInfo[], the position of points. User can specify the width and/or height for the point. Otherwise, the algorithm will use the width and height from settings: computor.defaultLabelWidth(20), computor.defaultLabelHeight(10).
type RawInfo = {
x: number,
y: number,
labelWidth?: number,
labelHeight?: number,
[redundantProp: string]: any,
};The function will return LayoutInfo[]. For one LayoutInfo, it includes the necessaray infomation about one point in the visualization. Furthermore, it is sorted in ascending order by the distance from itself to the query point.
type LayoutInfo = {
x: number, // x coordinate of the point
y: number, // y coordinate of the point
left: boolean, // If true, the label of this point should be on the left of this point.
controlPoints: {x: number, y: number}[], // Control points of the line which connect point and label
labelBBox: { // The Bounding Box of label
x: number,
y: number,
width: number,
height: number
},
rawInfo: RawInfo // The original input infomation of this point.
};After the computor is created, users can configure it or get configuration information through the following API. If you provide no paramter, it will return the corresponding setting's value. Otherwise, it will set the corresponding setting's value with the given parameter, and return the computor itself to facilitate method chaining.
interface Computer {
// if `isInfosFiltered` equals `false`, then computer will filter out the elements outside the lens
(rawInfos: RawInfo[], cx: number, cy: number, isInfosFiltered?: boolean): LayoutInfo[];
elementsInLens: (() => RawInfo[]);
elementsNumInLens: (() => number);
defaultLabelWidth: (() => number)
& ((size: number) => Computer);
defaultLabelHeight: (() => number)
& ((size: number) => Computer);
radius: (() => number)
& ((radius: number) => Computer);
maxLabelsNum: (() => number)
& ((maxLabelsNum: number) => Computer);
verticallyCoherent: (() => boolean)
& ((verticallyCoherent: boolean) => Computer);
horizontallyCoherent: (() => boolean)
& ((horizontallyCoherent: boolean) => Computer);
spaceBetweenLabels: (() => number)
& ((spaceBetweenLabels: number) => Computer);
leftSpace: (() => number)
& ((space: number) => Computer);
rightSpace: (() => number)
& ((space: number) => Computer);
leftAndRightSpace: (() => [number, number])
& ((space: number) => Computer)
& ((space: [number, number]) => Computer);
}Be aware that the order will be changed