深蓝学院课程作业: 移动机器人的运动规划
主要是环境配置
source devel/setup.bash
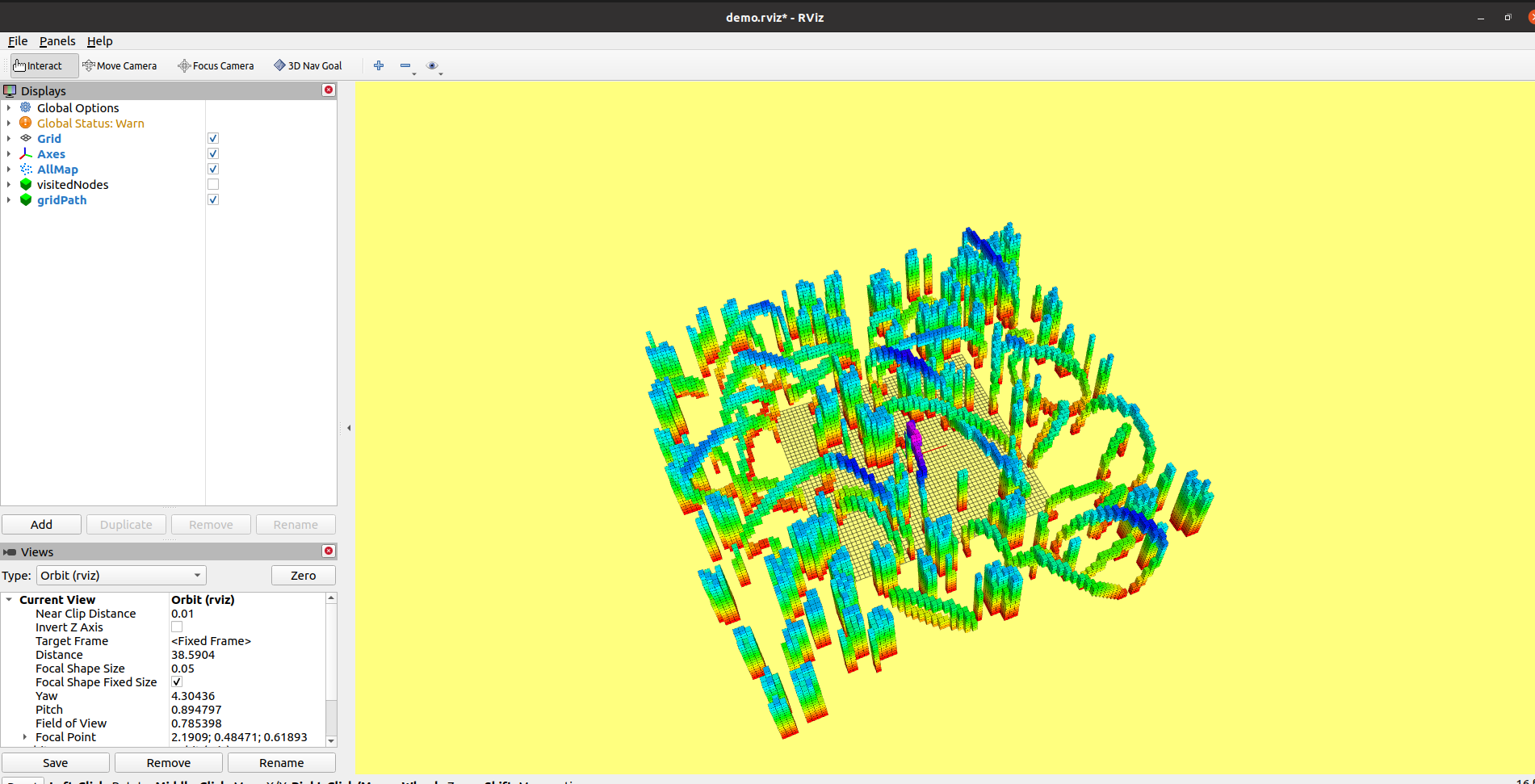
roslaunch grid_path_searcher demo.launch实现A*和JPS算法
source devel/setup.bash
roslaunch grid_path_searcher demo.launch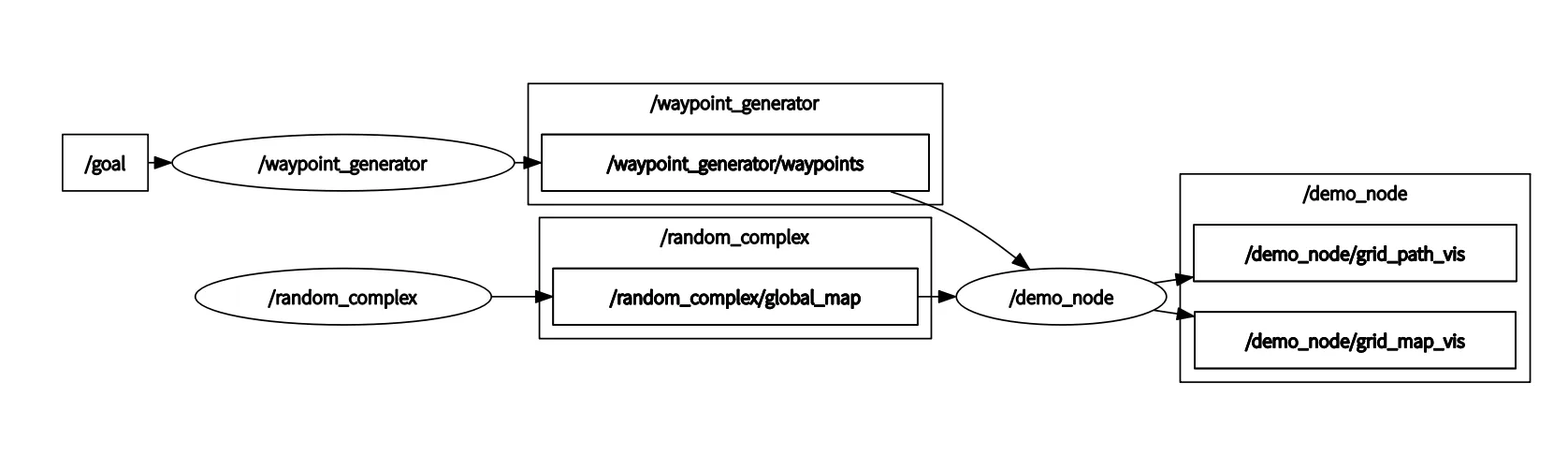 实现A*算法,其中启发函数是Euclidean
实现JPS算法
实现A*算法,其中启发函数是Euclidean
实现JPS算法
主函数在demo_node.cpp 具体使用哪个算法,需要在demo_node.cpp里选择
//_use_jps = 0 -> Do not use JPS
//_use_jps = 1 -> Use JPS
//you just need to change the #define value of _use_jps
#define _use_jps 1
#if _use_jpsrostopic list
/demo_node/grid_map_vis
/demo_node/grid_path_vis
/demo_node/grid_path_vis_array
/demo_node/visited_nodes_vis
/goal
/random_complex/global_map
/rosout
/rosout_agg
/tf
/tf_static
/waypoint_generator/odom
/waypoint_generator/traj_start_trigger
/waypoint_generator/waypoints
/waypoint_generator/waypoints_visdemo_node接收/goal和/map(障碍物),输出path
pkg waypoint_generator用来接收/goal生成3d pose发布在/waypoint_generator/waypoints
node random_complex用来生成地图发布在/random_complex/global_map
demo_node内部调用Astar_searcher找到/goal并发布/demo_node/grid_map_vis和/demo_node/grid_path_vis\
_grid_map_vis_pub = nh.advertise<sensor_msgs::PointCloud2>("grid_map_vis", 1);
_grid_path_vis_pub = nh.advertise<visualization_msgs::Marker>("grid_path_vis", 1);地图由_grid_map_vis_pub发布,读取map里的障碍物信息pcl::toROSMsg,生成满足分辨率要求的地图,publish sensor_msgs::PointCloud2类型的消息;
路径由_grid_path_vis_pub发布,类型为visualization_msgs::Marker
A*流程和JPS流程相似:
核心代码的实现在
void AstarPathFinder::AstarGraphSearch(Vector3d start_pt, Vector3d end_pt)rrt*算法 使用OMPL库的RRTSTAR
void pathFinding(const Vector3d start_pt, const Vector3d target_pt)
{
// Construct the robot state space in which we're planning.
ob::StateSpacePtr space(new ob::RealVectorStateSpace(3));
// Set the bounds of space to be in [0,1].
ob::RealVectorBounds bounds(3);
bounds.setLow(0, - _x_size * 0.5);
bounds.setLow(1, - _y_size * 0.5);
bounds.setLow(2, 0.0);
bounds.setHigh(0, + _x_size * 0.5);
bounds.setHigh(1, + _y_size * 0.5);
bounds.setHigh(2, _z_size);
space->as<ob::RealVectorStateSpace>()->setBounds(bounds);
// Construct a space information instance for this state space
ob::SpaceInformationPtr si(new ob::SpaceInformation(space));
// Set the object used to check which states in the space are valid
si->setStateValidityChecker(ob::StateValidityCheckerPtr(new ValidityChecker(si)));
si->setup();
// Set our robot's starting state
ob::ScopedState<> start(space);
/**
*
*
STEP 2: Finish the initialization of start state
*
*
*/ // todo can I simply it?
start[0] = (&start_pt)->operator[](0) ;
start[1] = (&start_pt)->operator[](1) ;
start[2] = (&start_pt)->operator[](2) ;
// Set our robot's goal state
ob::ScopedState<> goal(space);
/**
*
*
STEP 3: Finish the initialization of goal state
*
*
*/
goal[0] = (&target_pt)->operator[](0) ;
goal[1] = (&target_pt)->operator[](1) ;
goal[2] = (&target_pt)->operator[](2) ;
// Create a problem instance
/**
*
*
STEP 4: Create a problem instance,
please define variable as pdef
*
*
*/
auto pdef(std::make_shared<ob::ProblemDefinition>(si));
// Set the start and goal states
pdef->setStartAndGoalStates(start, goal);
// Set the optimization objective
/**
*
*
STEP 5: Set the optimization objective, the options you can choose are defined earlier:
getPathLengthObjective() and getThresholdPathLengthObj()
*
*
*/
pdef->setOptimizationObjective(getPathLengthObjective(si));
// Construct our optimizing planner using the RRTstar algorithm.
/**
*
*
STEP 6: Construct our optimizing planner using the RRTstar algorithm,
please define varible as optimizingPlanner
*
*
*/
ob::PlannerPtr optimizingPlanner(new og::RRTstar(si));
// Set the problem instance for our planner to solve
optimizingPlanner->setProblemDefinition(pdef);
optimizingPlanner->setup();
// attempt to solve the planning problem within one second of
// planning time
ob::PlannerStatus solved = optimizingPlanner->solve(1.0);
if (solved)
{
// get the goal representation from the problem definition (not the same as the goal state)
// and inquire about the found path
og::PathGeometric* path = pdef->getSolutionPath()->as<og::PathGeometric>();
vector<Vector3d> path_points;
for (size_t path_idx = 0; path_idx < path->getStateCount (); path_idx++)
{
const ob::RealVectorStateSpace::StateType *state = path->getState(path_idx)->as<ob::RealVectorStateSpace::StateType>();
/**
*
*
STEP 7: Trandform the found path from path to path_points for rviz display
*
*
*/
auto x = (*state)[0];
auto y = (*state)[1];
auto z = (*state)[2];
Vector3d temp_mat(x,y,z);
path_points.push_back(temp_mat);
}
visRRTstarPath(path_points);
}
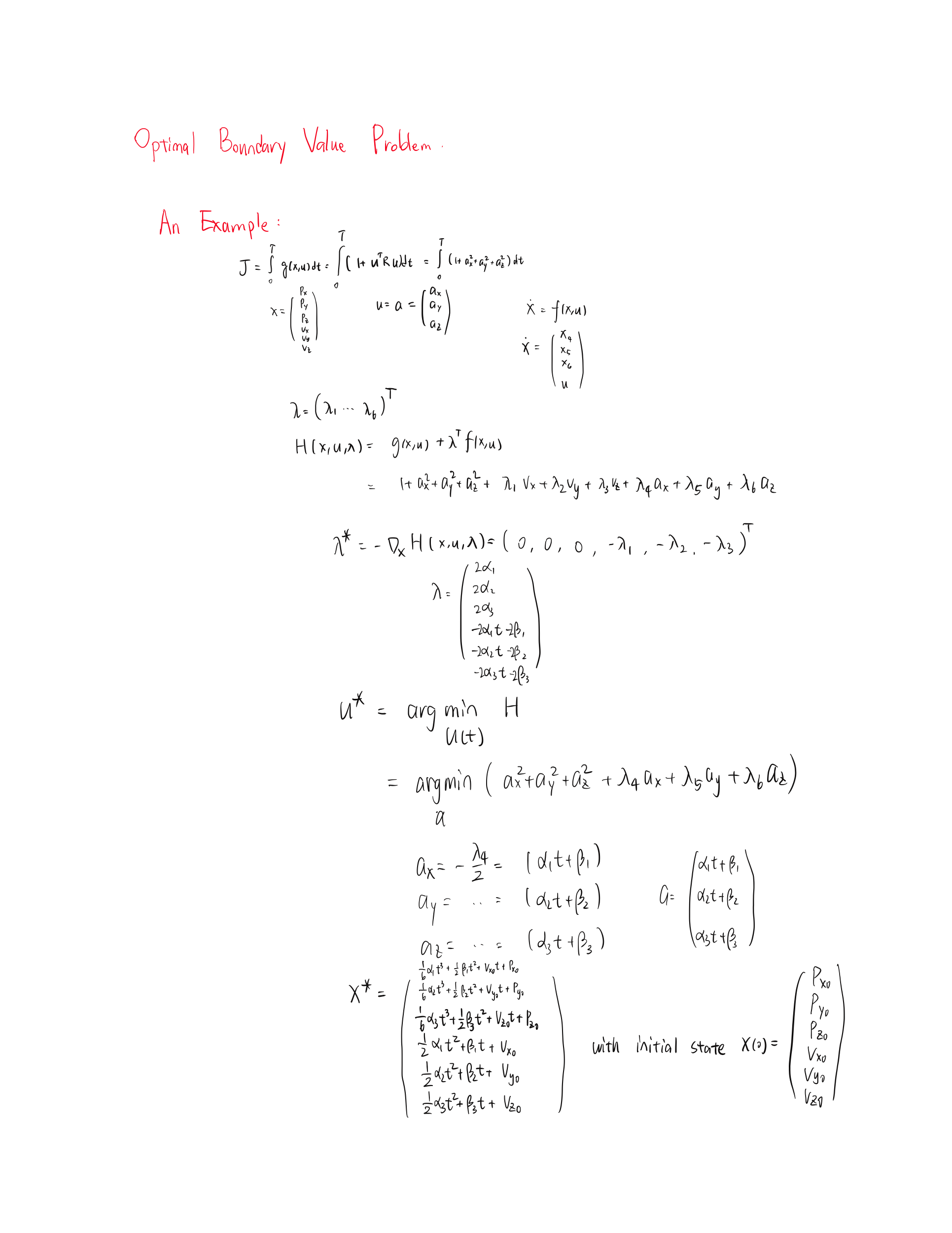
}最后化简到cost function仅与参数T相关,仅需对T作优化即可。
source devel/setup.bash
roslaunch grid_path_searcher demo.launch表达式的化简工作由syspy完成,见脚本test_syspy.ipynb
roslaunch lec5_hw click_gen.launchOBVP求解过程可见论文minco,s=3的情形,实现代码见:
void minimumJerkTrajGen()
MPC 模型预测控制
曲线跟踪
./install_tools.sh
catkin_make -j1
source devel/setup.zsh
roslaunch mpc_car simulation.launch
./src/mpc_car/config/mpc_car.yaml -> mpc parameters
./src/car_simulator/config/car_simulator.yaml -> initial states (in simulation)
Implement MPC of tracking the reference trajectory in C++;
using osqp
Implement MPC with delays in C++;
using runge kutta-4 : 参考四阶龙格库塔法:
inline void step(VectorX& state, const VectorU& input, const double dt) const {
// Runge–Kutta
// fourth-order Runge-Kutta
VectorX k1 = diff(state, input);
VectorX k2 = diff(state + k1 * dt / 2, input);
VectorX k3 = diff(state + k2 * dt / 2, input);
VectorX k4 = diff(state + k3 * dt, input);
state = state + (k1 + k2 * 2 + k3 * 2 + k4) * dt / 6;
}Implement MPCC in C++;
TODO
[ATTENTION] Only <TODO: > of codes in src/mpc_car/include/mpc_car/mpc_car.hpp is required.
该项目为深蓝学院"移动机器人运动规划"课程大作业。大作业涉及如下方面:
- 路径搜索
- 轨迹生成
- 轨迹重优化
- 由传感器范围有限所导致的重规划
安装系统依赖
sudo apt-get install cmake libopenblas-dev liblapack-dev libarpack-dev libarpack2-dev libsuperlu-dev
安装Armadillo
xz -d armadillo-9.870.2.tar.xz
tar -xvf armadillo-9.870.2.tar
cd armadillo-9.870.2
mkdir build
cd build
cmake ..
make
sudo make install
- random_complex:随机生成障碍物点云地图;
- waypoint_generator:给定目标点;
- odom_visualization:四旋翼可视化;
- pcl_render_node:简单版的局部传感器模型,返回局部范围内的障碍物点云;
- trajectory_generator_node :大作业核心部分,生成一条可行的多项式轨迹;
- traj_server:将多项式轨迹转换为控制指令;
- so3_control:将控制指令转换为实际控制量;
- quadrotor_simulator_so3:无人机仿真模型。
- 阅读代码:画出trajectory_generator_node运行流程图,重点是厘清
- 几个状态之间的切换过程;
string state_str[5] = {"INIT", "WAIT_TARGET", "GEN_NEW_TRAJ", "EXEC_TRAJ", "REPLAN_TRAJ"}; //状态切换见:trajectory_generator_node.cpp void execCallback(const ros::TimerEvent &e);
- 各个主要功能之间的调用关系,不需要深入到各个功能的内部例如A*的流程。
- path planning:推荐实现方案为A*,也可采用其他方案;
- simplify the path:将整条path简化为少数几个关键waypoints,推荐方案为RDP算法;
- trajectory optimization:推荐实现方案为minimum snap trajectory generation,也可采用其他方案;
- safe checking: 验证生成的轨迹是否安全;
- trajectory reoptimization:此环节只针对使用minimum snap trajectory generation的时候。由于该方法只对连续性进行优化,并不能保证优化后的轨迹不会撞上障碍物,所以需要对撞上障碍物的部分重优化。推荐方法详见文献:"Polynomial Trajectory Planning for Aggressive Quadrotor Flight in Dense Indoor Environments" part 3.5。
伪代码(来源:维基百科):
function DouglasPeucker(PointList[], epsilon)
// Find the point with the maximum distance
dmax = 0
index = 0
end = length(PointList)
for i = 2 to (end - 1) {
d = perpendicularDistance(PointList[i], Line(PointList[1], PointList[end]))
if (d > dmax) {
index = i
dmax = d
}
}
ResultList[] = empty;
// If max distance is greater than epsilon, recursively simplify
if (dmax > epsilon) {
// Recursive call
recResults1[] = DouglasPeucker(PointList[1...index], epsilon)
recResults2[] = DouglasPeucker(PointList[index...end], epsilon)
// Build the result list
ResultList[] = {recResults1[1...length(recResults1) - 1], recResults2[1...length(recResults2)]}
} else {
ResultList[] = {PointList[1], PointList[end]}
}
// Return the result
return ResultList[]
end
source devel/setup.bash
roslaunch trajectory_generator demo.launch
核心节点:trajectory_generator_node
_exec_timer = nh.createTimer(ros::Duration(0.01), execCallback);//FSM,路径搜索程序接口在这里
_odom_sub = nh.subscribe("odom", 10, rcvOdomCallback);//set odom msg
_map_sub = nh.subscribe("local_pointcloud", 1, rcvPointCloudCallBack);//set Obstacle
_pts_sub = nh.subscribe("waypoints", 1, rcvWaypointsCallBack);//set goal
_traj_pub =
nh.advertise<quadrotor_msgs::PolynomialTrajectory>("trajectory", 50);
_traj_vis_pub = nh.advertise<visualization_msgs::Marker>("vis_trajectory", 1);
_path_vis_pub = nh.advertise<visualization_msgs::Marker>("vis_path", 1);系统的状态机
深蓝学院课程作业: 机器人学中的数值优化
use Armijo condition to solve the Rosenbrock function:
Implement smooth trajectory generation by C++ , using l-bfgs
source devel/setup.bash
roslaunch gcopter curve_gen.launch