Image interpolation refers to the resizing of a digital image. Interpolation is the problem of approximating the value of a function for a non-given point in some space when given the value of that function in points around (neighboring) that point.
Image interpolation have three main techniques:
Nearest-neighbor interpolation (also known as proximal interpolation or, in some contexts, point sampling) is a simple method of multivariate interpolation in one or more dimensions. The nearest neighbor algorithm selects the value of the nearest point and does not consider the values of neighboring points at all, yielding a piecewise-constant interpolant. The algorithm is very simple to implement and is commonly used (usually along with mipmapping) in real-time 3D rendering to select color values for a textured surface (Wikipedia).
Bilinear interpolation is performed using linear interpolation first in one direction, and then again in the other direction. Bilinear interpolation uses values of only the 4 nearest pixels, located in diagonal directions from a given pixel, in order to find the appropriate color intensity values of that pixel (Wikipedia).
In image processing, bicubic interpolation is often chosen over bilinear or nearest-neighbor interpolation in image resampling, when speed is not an issue. In contrast to bilinear interpolation, which only takes 4 pixels (2×2) into account, bicubic interpolation considers 16 pixels (4×4)(Wikipedia)

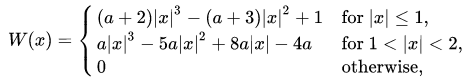
$ git clone https://github.com/yasinEnigma/Image_Interpolation/
$ pip3 install -r requirements.txt
$ python3 main.py





