A blazingly fast JSON serializing & deserializing library, accelerated by JIT (just-in-time compiling) and SIMD (single-instruction-multiple-data).
- Go 1.15/1.16
- Linux/darwin OS
- Amd64 CPU with AVX instruction set
- Runtime object binding without code generation
- Complete APIs for JSON value manipulation
- Fast, fast, fast!
For all sizes of json and all cases of usage, Sonic performs best.
- Small (400B, 11 keys, 3 layers)

- Large (635KB, 10000+ key, 6 layers)
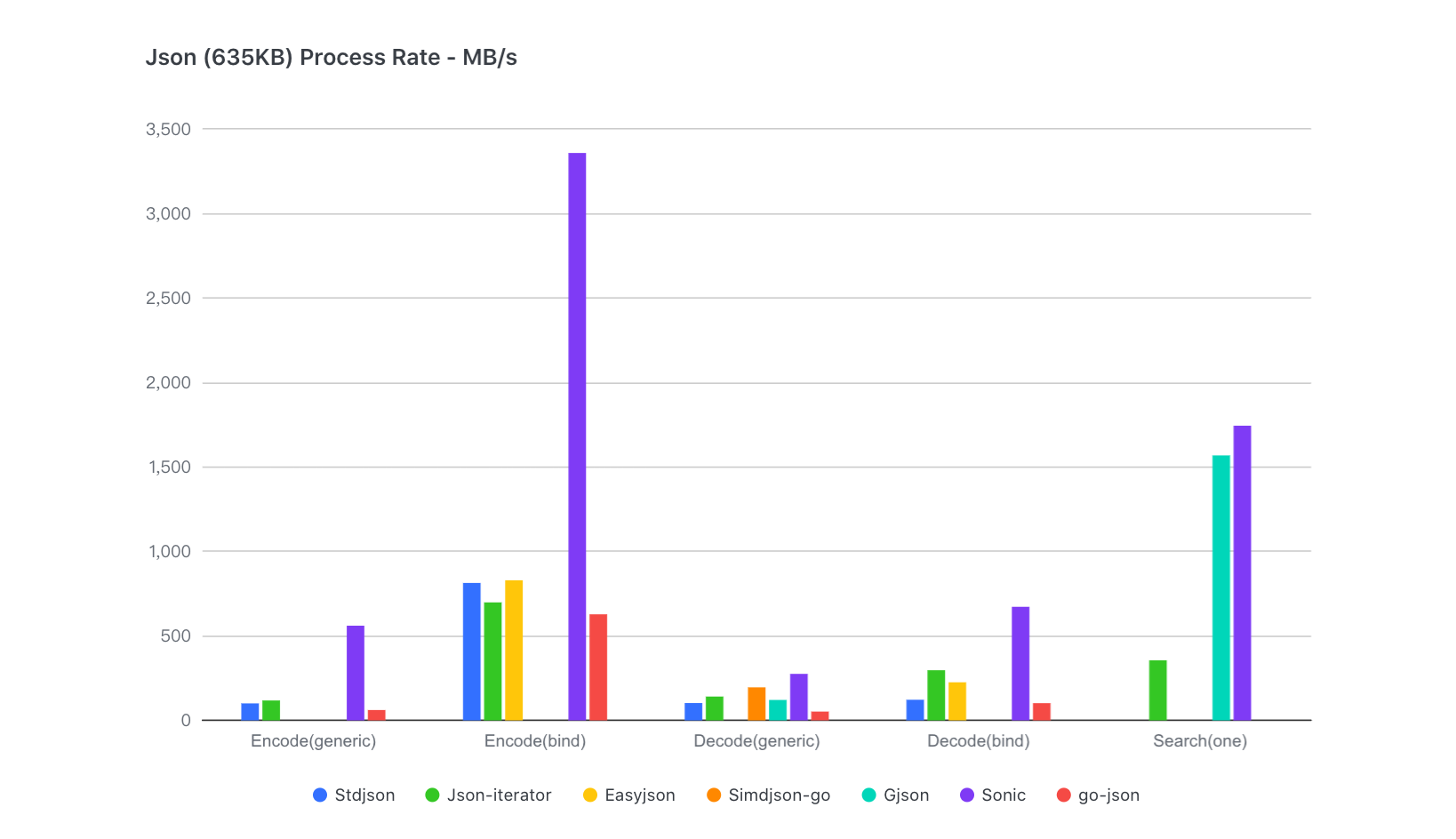
- Medium (13KB, 300+ key, 6 layers)
For medium data, Sonic's speed is 2.6x times of json-iterator's in decoding, 2.5x times in encoding,and 8.3x times in searching.
goos: darwin
goarch: amd64
cpu: Intel(R) Core(TM) i9-9880H CPU @ 2.30GHz
BenchmarkEncoder_Generic_Sonic-16 100000 25911 ns/op 503.06 MB/s 13542 B/op 4 allocs/op
BenchmarkEncoder_Generic_JsonIter-16 100000 46693 ns/op 279.16 MB/s 13434 B/op 77 allocs/op
BenchmarkEncoder_Generic_StdLib-16 100000 143080 ns/op 91.10 MB/s 48177 B/op 827 allocs/op
BenchmarkEncoder_Binding_Sonic-16 100000 6851 ns/op 1902.68 MB/s 14229 B/op 4 allocs/op
BenchmarkEncoder_Binding_JsonIter-16 100000 22264 ns/op 585.49 MB/s 9488 B/op 2 allocs/op
BenchmarkEncoder_Binding_StdLib-16 100000 18685 ns/op 697.61 MB/s 9479 B/op 1 allocs/op
BenchmarkEncoder_Parallel_Generic_Sonic-16 100000 4981 ns/op 2617.14 MB/s 10747 B/op 4 allocs/op
BenchmarkEncoder_Parallel_Generic_JsonIter-16 100000 11225 ns/op 1161.24 MB/s 13447 B/op 77 allocs/op
BenchmarkEncoder_Parallel_Generic_StdLib-16 100000 55846 ns/op 233.41 MB/s 48215 B/op 827 allocs/op
BenchmarkEncoder_Parallel_Binding_Sonic-16 100000 1767 ns/op 7375.09 MB/s 11514 B/op 4 allocs/op
BenchmarkEncoder_Parallel_Binding_JsonIter-16 100000 4904 ns/op 2657.84 MB/s 9487 B/op 2 allocs/op
BenchmarkEncoder_Parallel_Binding_StdLib-16 100000 3958 ns/op 3293.18 MB/s 9477 B/op 1 allocs/op
BenchmarkDecoder_Generic_Sonic-16 100000 55680 ns/op 234.11 MB/s 49755 B/op 313 allocs/op
BenchmarkDecoder_Generic_StdLib-16 100000 144991 ns/op 89.90 MB/s 50897 B/op 772 allocs/op
BenchmarkDecoder_Generic_JsonIter-16 100000 103197 ns/op 126.31 MB/s 55786 B/op 1068 allocs/op
BenchmarkDecoder_Binding_Sonic-16 100000 28399 ns/op 458.99 MB/s 24984 B/op 34 allocs/op
BenchmarkDecoder_Binding_StdLib-16 100000 132178 ns/op 98.62 MB/s 10560 B/op 207 allocs/op
BenchmarkDecoder_Binding_JsonIter-16 100000 39963 ns/op 326.18 MB/s 14674 B/op 385 allocs/op
BenchmarkDecoder_Parallel_Generic_Sonic-16 100000 10999 ns/op 1185.11 MB/s 49658 B/op 313 allocs/op
BenchmarkDecoder_Parallel_Generic_StdLib-16 100000 67083 ns/op 194.31 MB/s 50907 B/op 772 allocs/op
BenchmarkDecoder_Parallel_Generic_JsonIter-16 100000 54292 ns/op 240.09 MB/s 55809 B/op 1068 allocs/op
BenchmarkDecoder_Parallel_Binding_Sonic-16 100000 5699 ns/op 2287.37 MB/s 24968 B/op 34 allocs/op
BenchmarkDecoder_Parallel_Binding_StdLib-16 100000 35801 ns/op 364.09 MB/s 10559 B/op 207 allocs/op
BenchmarkDecoder_Parallel_Binding_JsonIter-16 100000 13783 ns/op 945.74 MB/s 14678 B/op 385 allocs/op
BenchmarkSearchOne_Gjson-16 100000 8992 ns/op 1448.28 MB/s 0 B/op 0 allocs/op
BenchmarkSearchOne_Jsoniter-16 100000 58313 ns/op 223.33 MB/s 27936 B/op 647 allocs/op
BenchmarkSearchOne_Sonic-16 100000 10497 ns/op 1240.61 MB/s 29 B/op 1 allocs/op
BenchmarkSearchOne_Parallel_Gjson-16 100000 1046 ns/op 12449.59 MB/s 0 B/op 0 allocs/op
BenchmarkSearchOne_Parallel_Jsoniter-16 100000 16080 ns/op 809.88 MB/s 27942 B/op 647 allocs/op
BenchmarkSearchOne_Parallel_Sonic-16 100000 1435 ns/op 9074.18 MB/s 285 B/op 1 allocs/opMore detail see decoder/decoder_test.go, encoder/encoder_test.go, ast/search_test.go, ast/parser_test.go, ast/node_test.go
See INTRODUCTION.md
sonic-fuzz is the repository for fuzzing tests. If you find any bug, please report the issue to sonic.
The behaviors are mostly consistent with encoding/json, except some uncommon escaping (see issue4)
import "github.com/bytedance/sonic"
var data YourSchema
// Marshal
output, err := sonic.Marshal(&data)
// Unmarshal
err := sonic.Unmarshal(output, &data) import "github.com/bytedance/sonic/decoder"
var input = `1`
var data interface{}
// default float64
dc := decoder.NewDecoder(input)
dc.Decode(&data) // data == float64(1)
// use json.Number
dc = decoder.NewDecoder(input)
dc.UseNumber()
dc.Decode(&data) // data == json.Number("1")
// use int64
dc = decoder.NewDecoder(input)
dc.UseInt64()
dc.Decode(&data) // data == int64(1)
root, err := sonic.GetFromString(input)
// Get json.Number
jn := root.Number()
jm := root.InterfaceUseNumber().(json.Number) // jn == jm
// Get float64
fn := root.Float64()
fm := root.Interface().(float64) // jn == jmOn account of the performance loss from sorting (roughly 10%), sonic doesn't enable this feature by default. If your component depends on it to work (like zstd), Use it like this:
import "github.com/bytedance/sonic/encoder"
m := map[string]interface{}{}
v, err := encoder.Encode(m, encoder.SortMapKeys)Caution: sonic encode struct in order of its original field declaration, so if you want to sort a struct's keys like the map's, just rewrite your struct.
import "github.com/bytedance/sonic/decoder"
var data interface{}
dc := decoder.NewDecoder("[[[}]]")
if err := dc.Decode(&data); err != nil {
if e, ok := err.(decoder.SyntaxError); ok {
/*Syntax error at index 3: invalid char
[[[}]]
...^..
*/
print(e.Description())
/*"Syntax error at index 3: invalid char\n\n\t[[[}]]\n\t...^..\n"*/
println(fmt.Sprintf("%q", e.Description()))
}
/*Decode: Syntax error at index 3: invalid char*/
t.Fatalf("Decode: %v", err)
}Sonic/ast.Node is a completely self-contained AST for JSON. It implements serialization and deserialization both, and provides robust APIs for obtaining and modification of generic data.
Search partial JSON by given paths, which must be non-negative integer or string or nil
import "github.com/bytedance/sonic"
input := []byte(`{"key1":[{},{"key2":{"key3":[1,2,3]}}]}`)
// no path, returns entire json
root, err := sonic.Get(input)
raw := root.Raw() // == string(input)
// multiple pathes
root, err := sonic.Get(input, "key1", 1, "key2")
sub := root.Get("key3").Index(2).Int64() // == 3Tip: since Index() uses offset to locate data, which is faster much than scanning like Get(), we suggest you use it as much as possible. And sonic also provides another API IndexOrGet() to underlying use offset as well as ensuring the key is matched.
Modify the json content by Set()/Unset()
import "github.com/bytedance/sonic"
// Set
exist, err := root.Set("key4", NewBool(true)) // exist == false
alias1 := root.Get("key4")
println(alias1.Valid()) // true
alias2 := root.Index(1)
println(alias1 == alias2) // true
// Unset
exist, err := root.UnsetByIndex(1) // exist == true
println(root.Get("key4").Check()) // "value not exist"To encode ast.Node as json, use MarshalJson() or json.Marshal() (MUST pass the node's pointer)
import (
"encoding/json"
"github.com/bytedance/sonic"
)
buf, err := root.MarshalJson()
println(string(buf)) // {"key1":[{},{"key2":{"key3":[1,2,3]}}]}
exp, err := json.Marshal(&root) // WARN: use pointer
println(string(buf) == string(exp)) // true- validation:
Check(),Error(),Valid(),Exist() - searching:
Index(),Get(),IndexPair(),IndexOrGet(),GetByPath() - go-type casting:
Int64(),Float64(),String(),Number(),Bool(),Map[UseNumber|UseNode](),Array[UseNumber|UseNode](),Interface[UseNumber|UseNode]() - go-type packing:
NewRaw(),NewNumber(),NewNull(),NewBool(),NewString(),NewObject(),NewArray() - iteration:
Values(),Properties() - modification:
Set(),SetByIndex(),Add(),Cap(),Len()
Since Sonic uses golang-asm as a JIT assembler, which is NOT very suitable for runtime compiling, first-hit running of a huge schema may cause request-timeout or even process-OOM. For better stability, we advise to use Pretouch() for huge-schema or compact-memory application before Marshal()/Unmarshal().
import (
"reflect"
"github.com/bytedance/sonic"
)
func init() {
var v HugeStruct
err := sonic.Pretouch(reflect.TypeOf(v))
}CAUTION: use the STRUCT instead of its POINTER to Pretouch(), otherwise it won't work when you pass the pointer to Marshal()/Unmarshal()!
For alignment to encoding/json, we provide API to pass []byte as argument, but the string-to-bytes copy is conducted at the same time considering safety, which may lose performance when origin JSON is huge. Therefore, you can use UnmarshalString, GetFromString to pass a string, as long as your origin data is a string or nocopy-cast is safe for your []byte.
In most cases, Unmarshal() with schemalized data performs better than ast.Loads()/node.Interface() with generic data. But if you only have a schema for partial json, you can combine Get() and Unmarshal() together:
import "github.com/bytedance/sonic"
node, err := sonic.GetFromString(_TwitterJson, "statuses", 3, "user")
var user User // your partial schema...
err = sonic.UnmarshalString(node.Raw(), &user)Even if you don't have any schema, Use InterfaceUseNode() as the container of generic values instead of Map() or Interface():
import "github.com/bytedance/sonic"
node, err := sonic.GetFromString(_TwitterJson, "statuses", 3, "user")
user := node.InterfaceUseNode() // use node.Interface() as little as possibleWhy?
- using
Interface()means Sonic must parse all the underlying values, while in most cases you only need several of them; map[x]is not efficient enough compared toarray[x], butast.Nodecan useIndex(), for either array or object node;map's performance degrades a lot once rehashing triggered, butast.Nodedoesn't has this concern;