 "gilot" is a tool to analyze and visualize git logs.
"gilot" is a tool to analyze and visualize git logs.
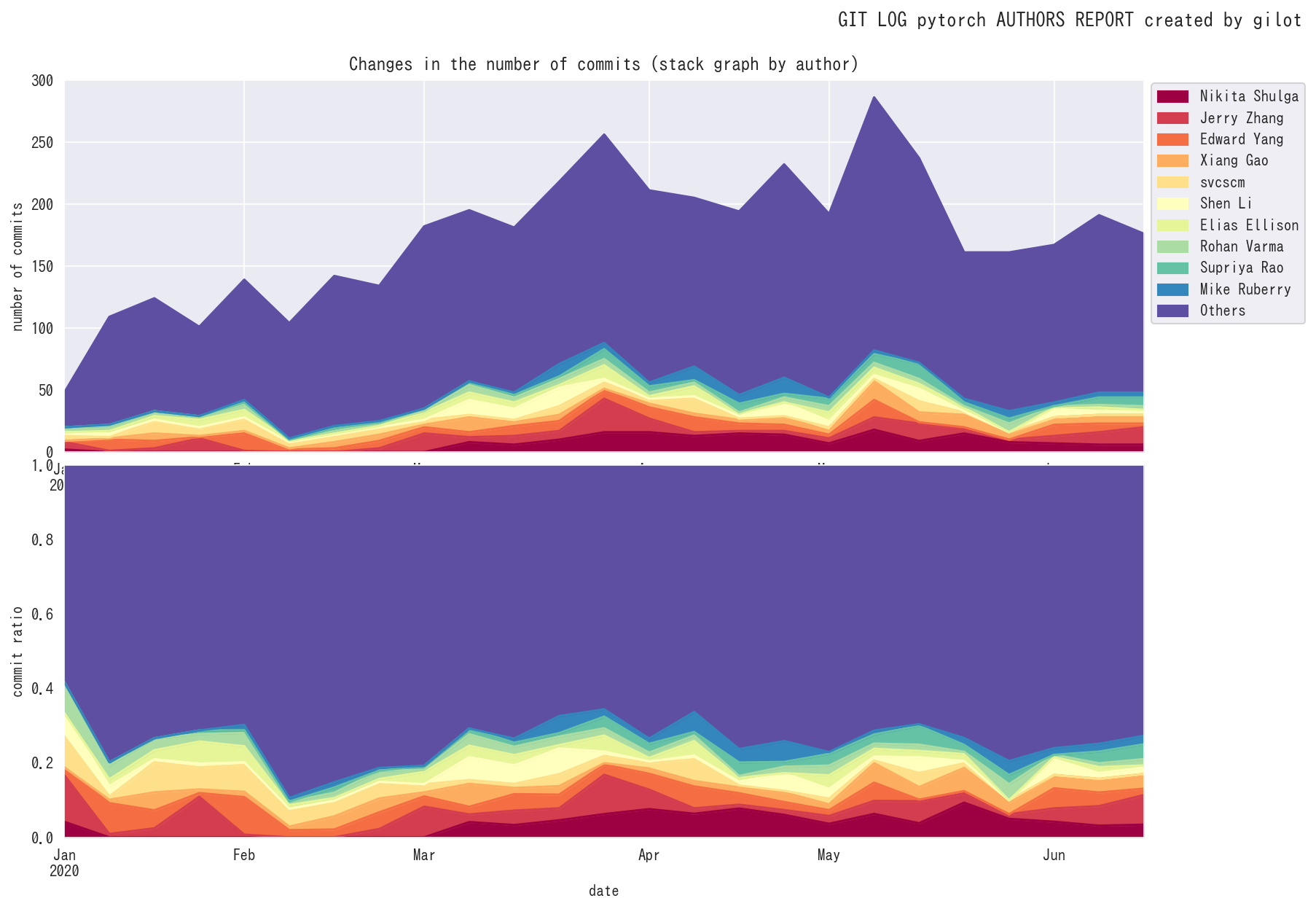
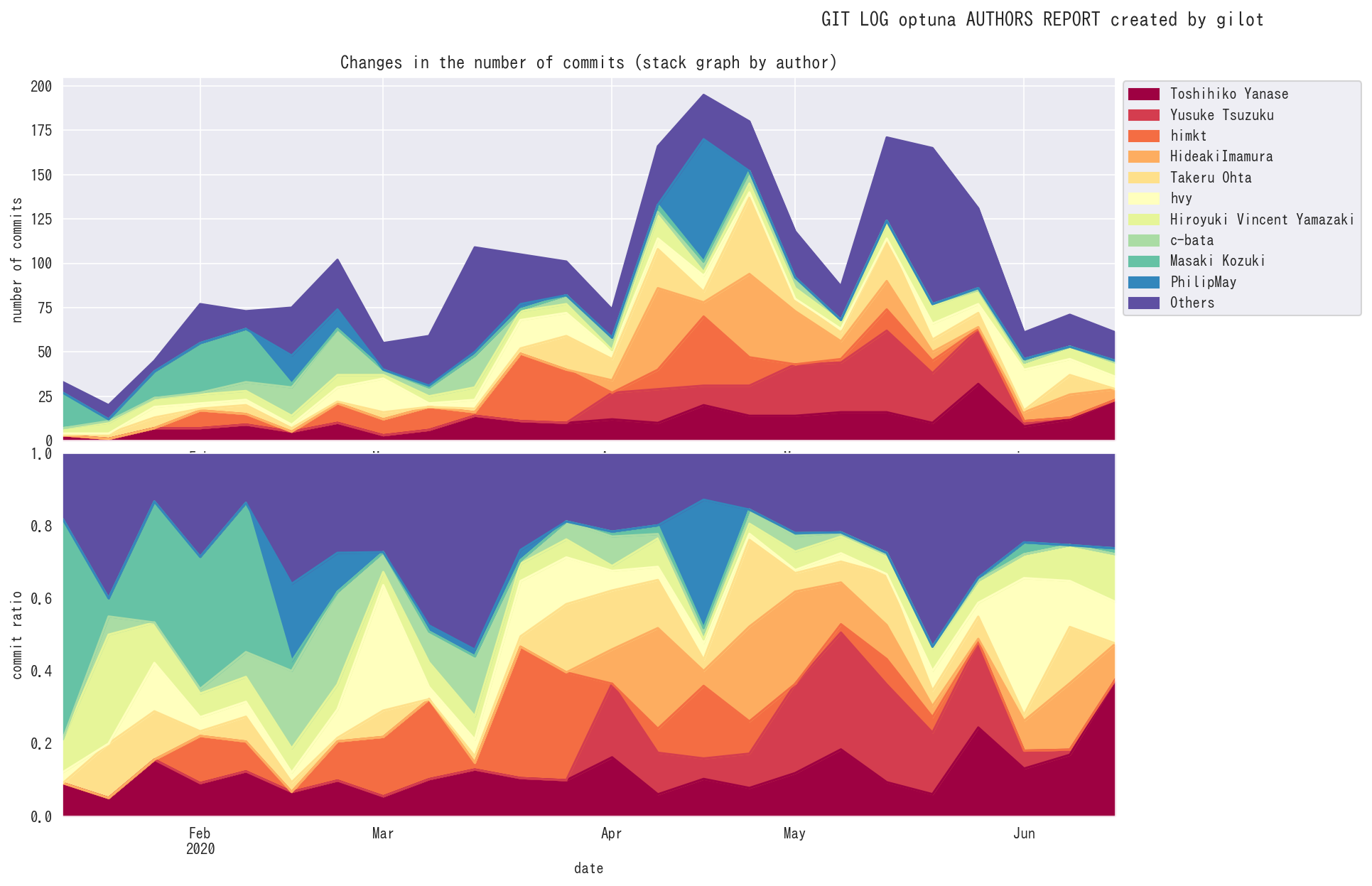
One of the most reliable records of a software project's activity is the history of the version control system. This information is then used to create graphs to visualize the state of the software development team in a mechanical way.
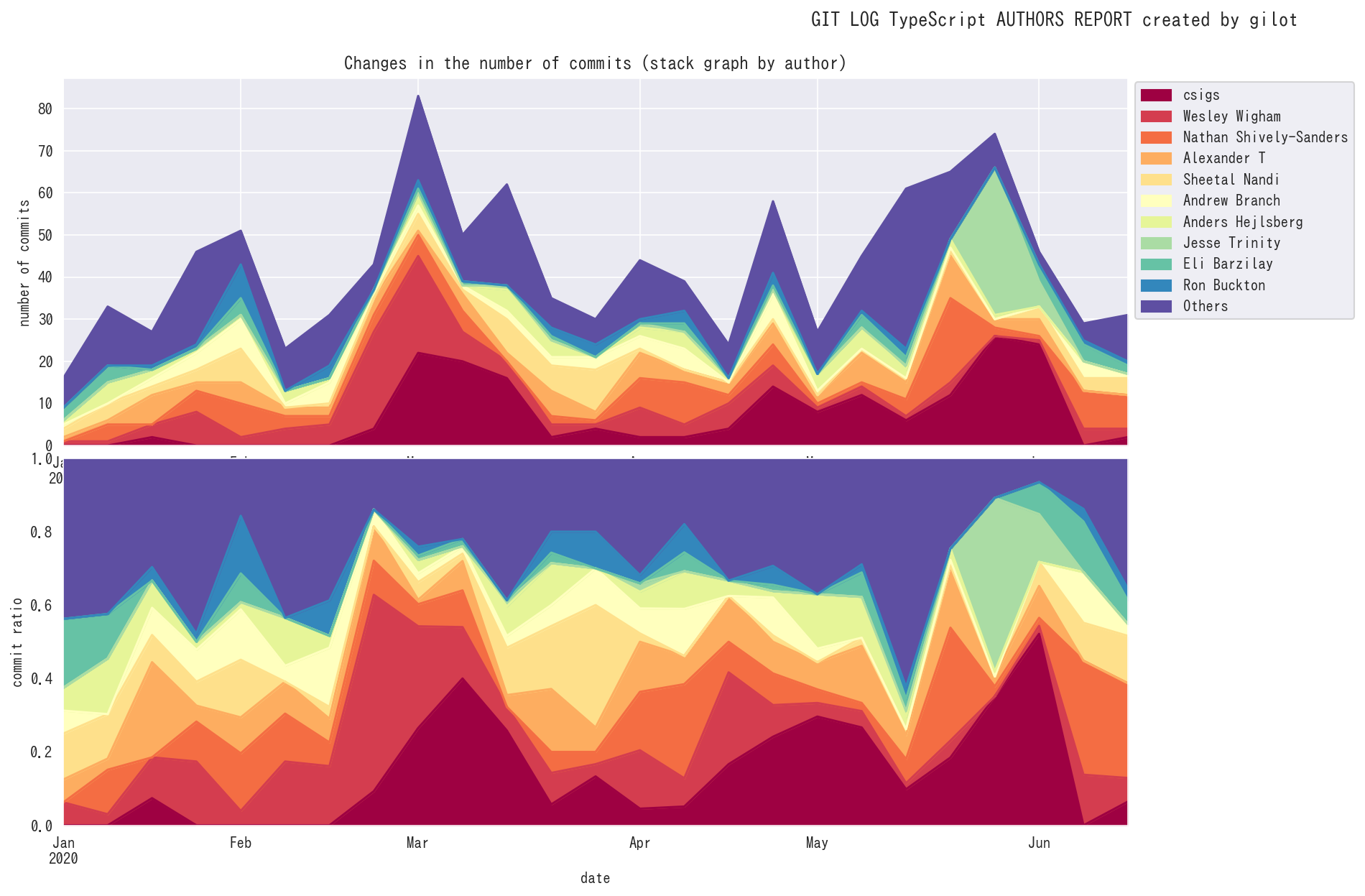
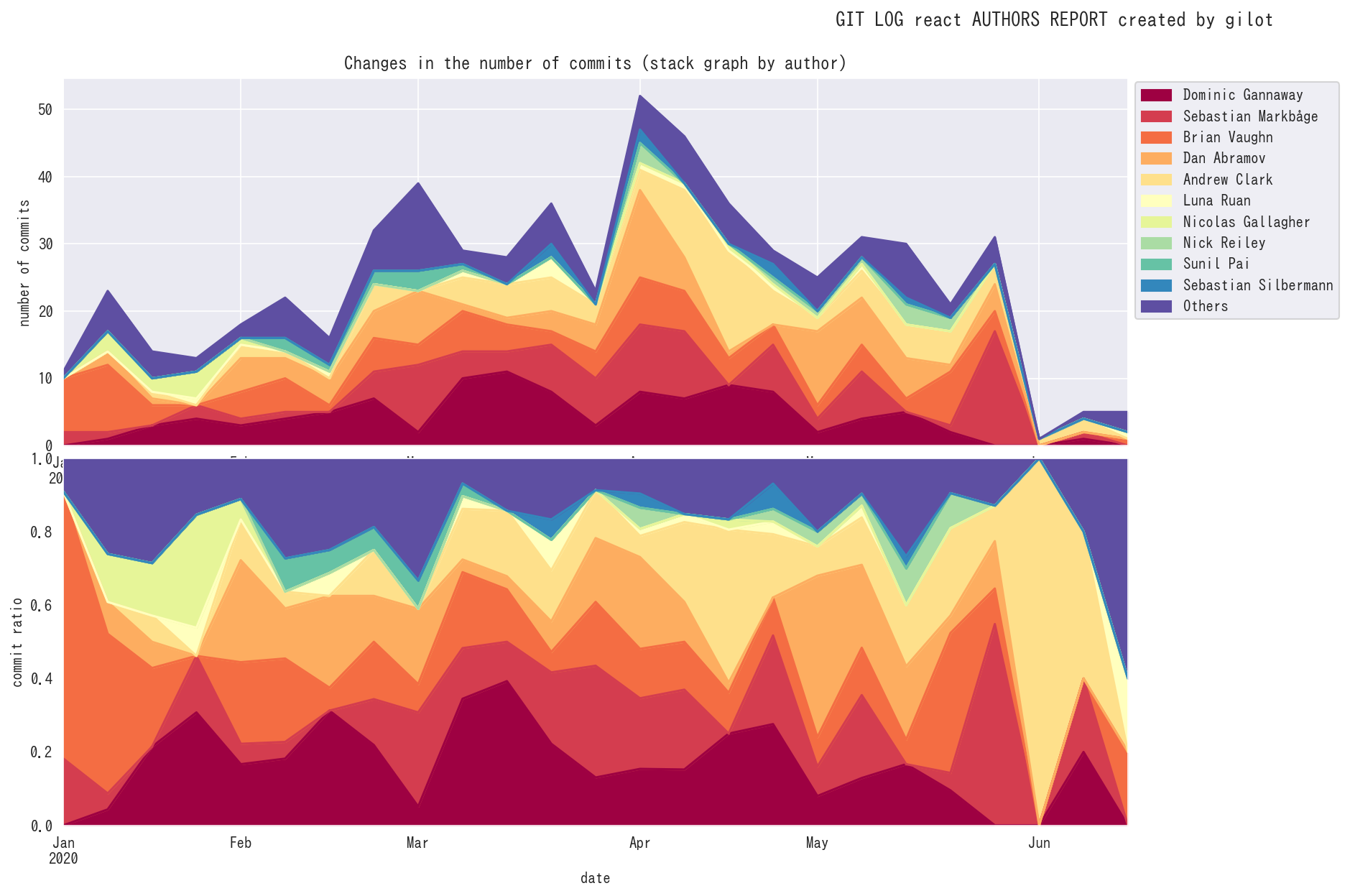
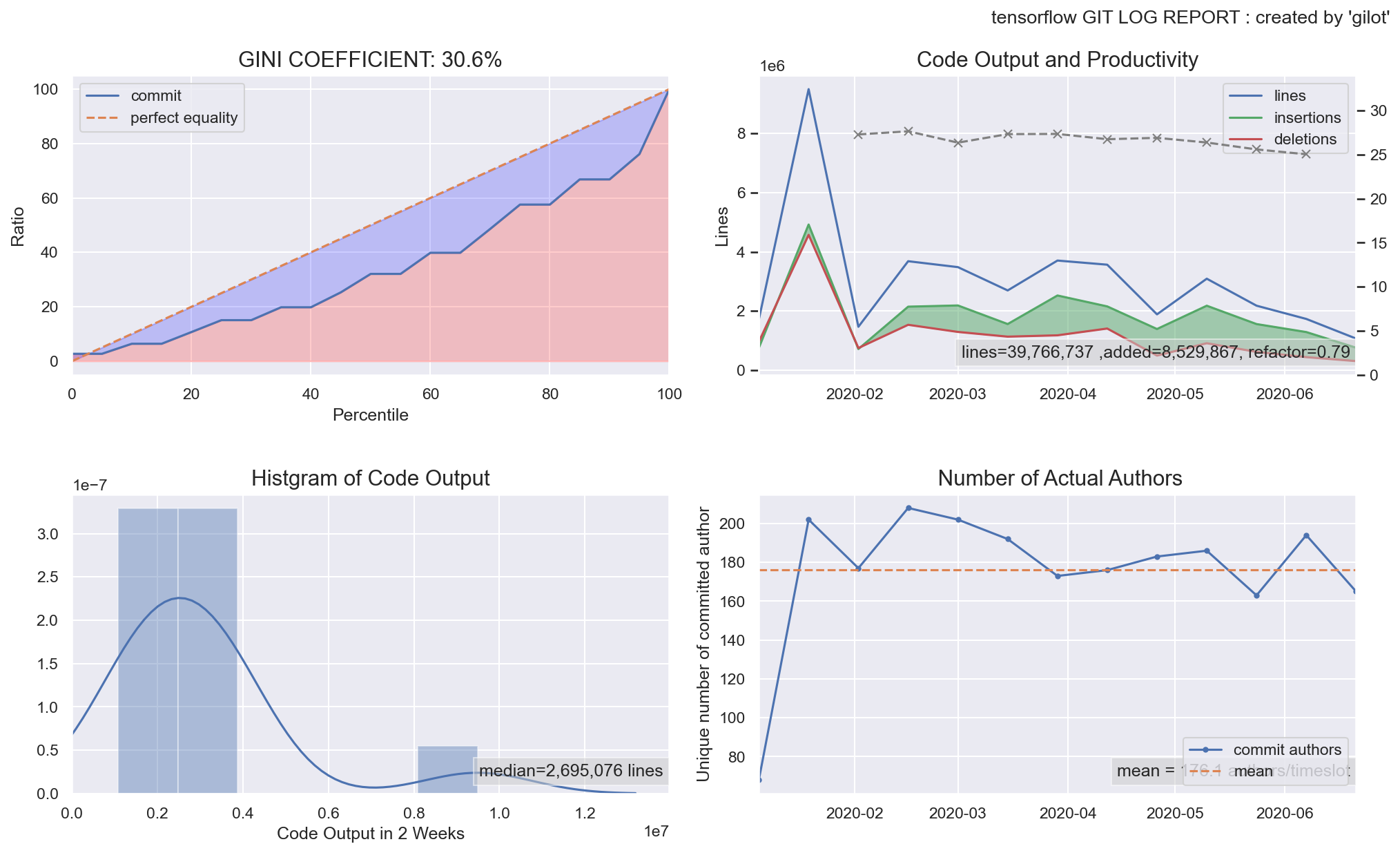
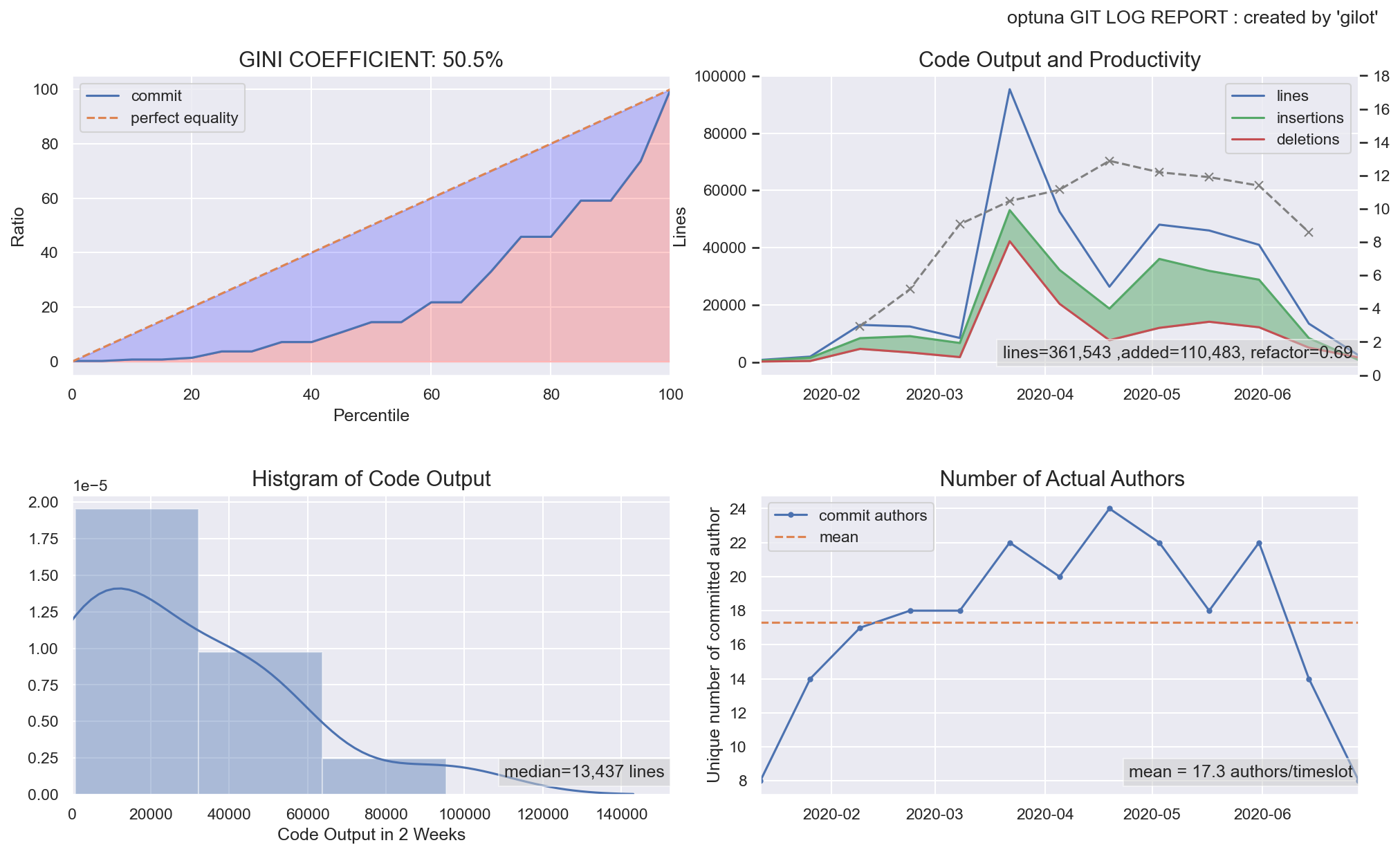
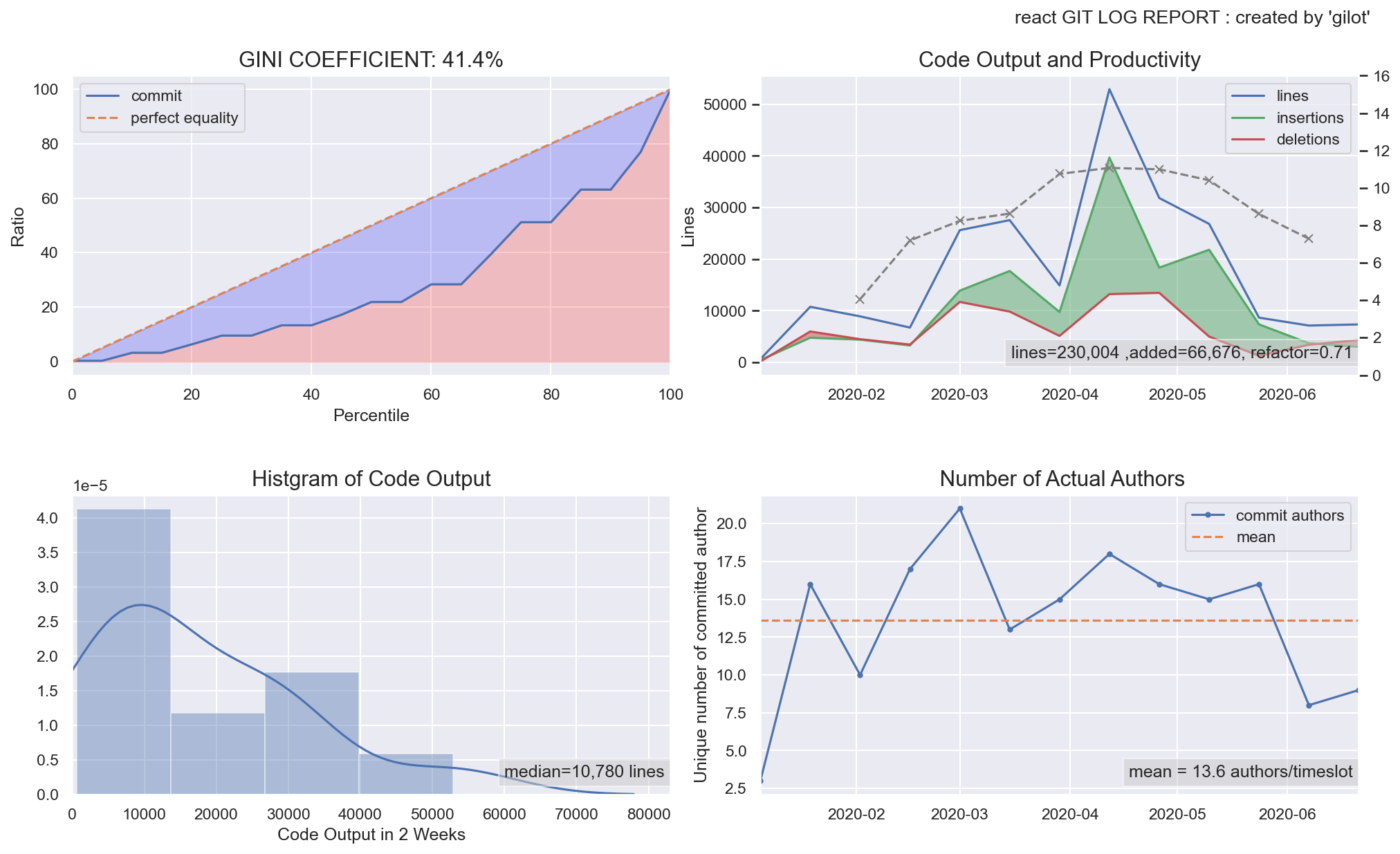
gilot plot creates four graphs.
-
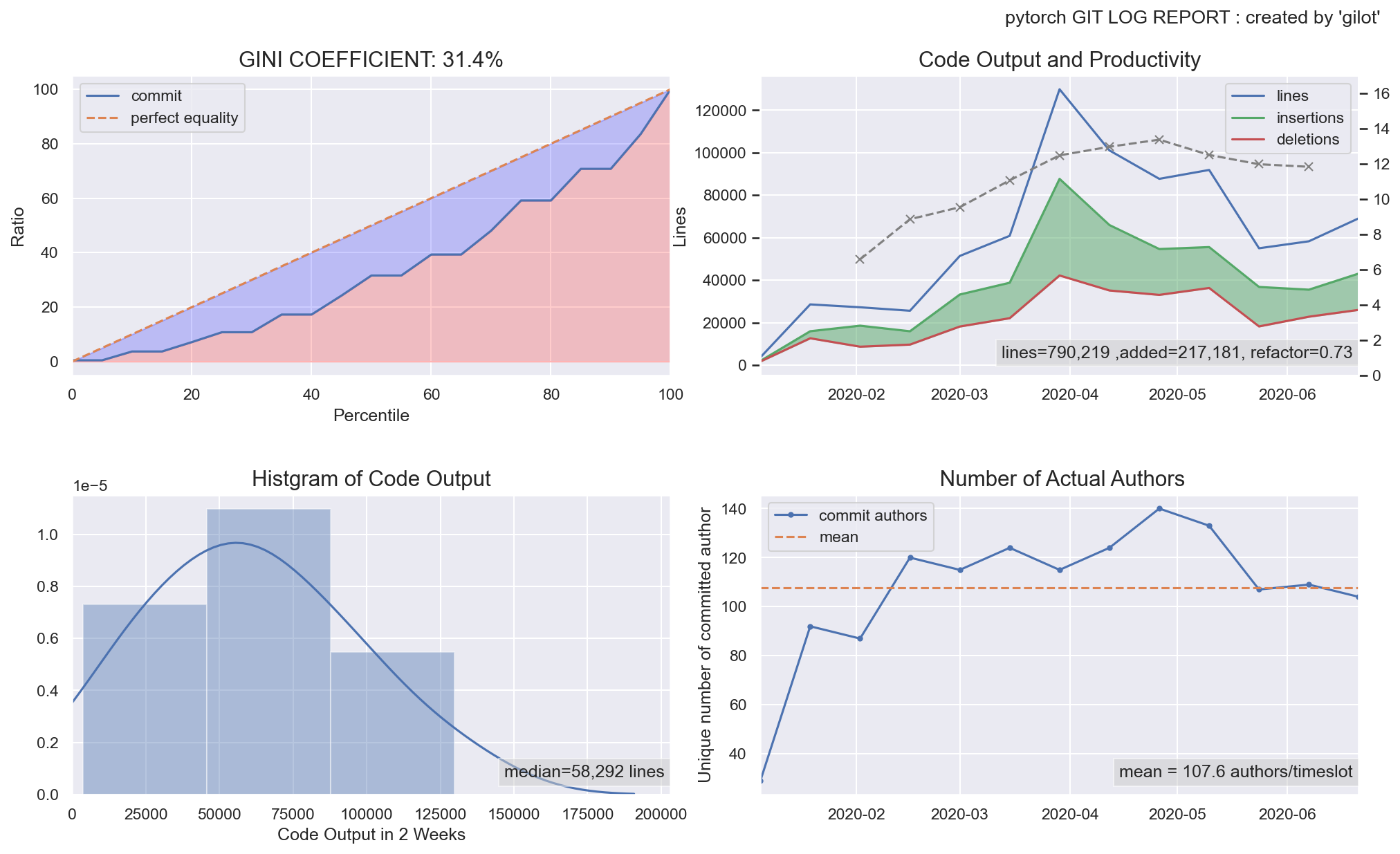
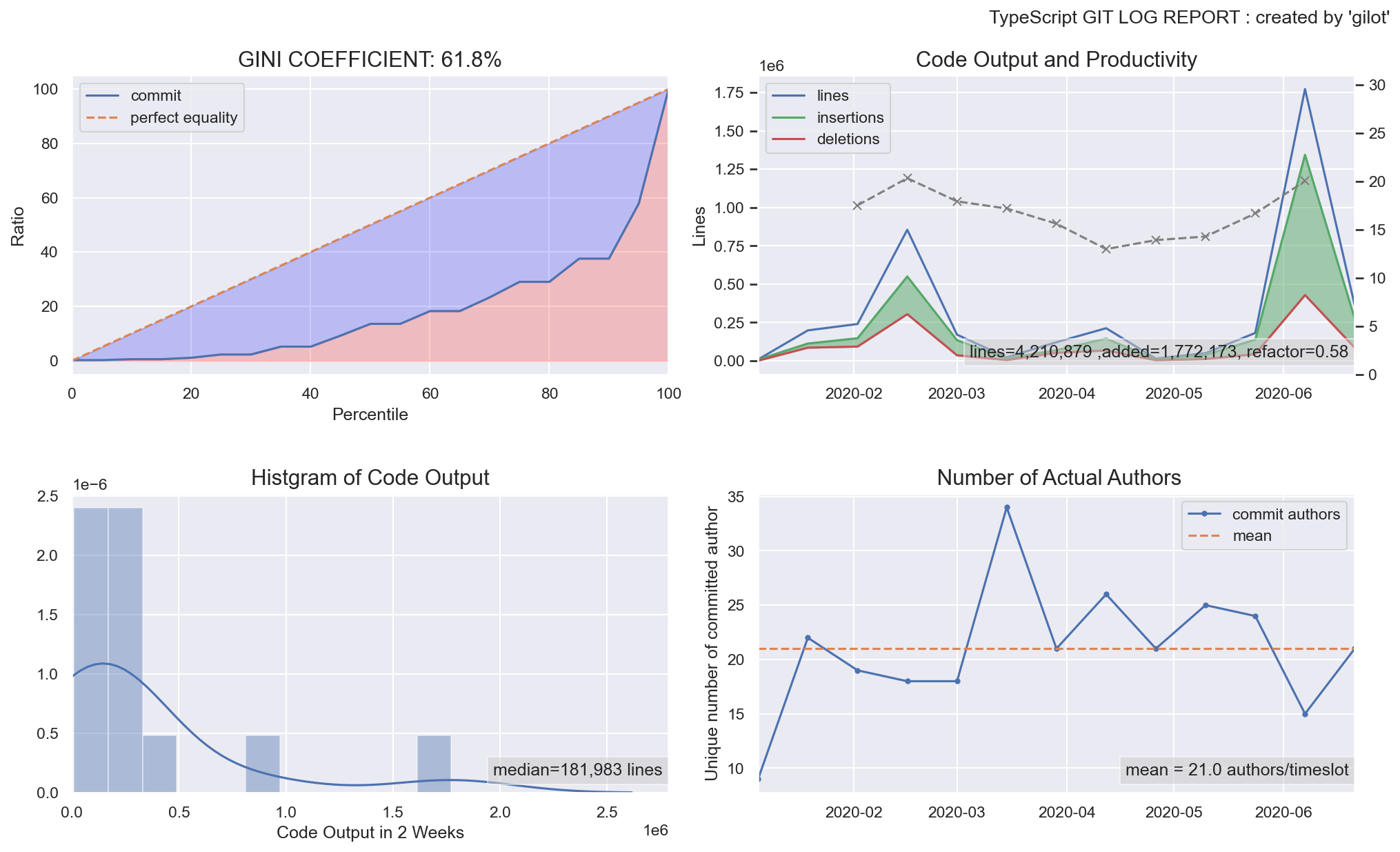
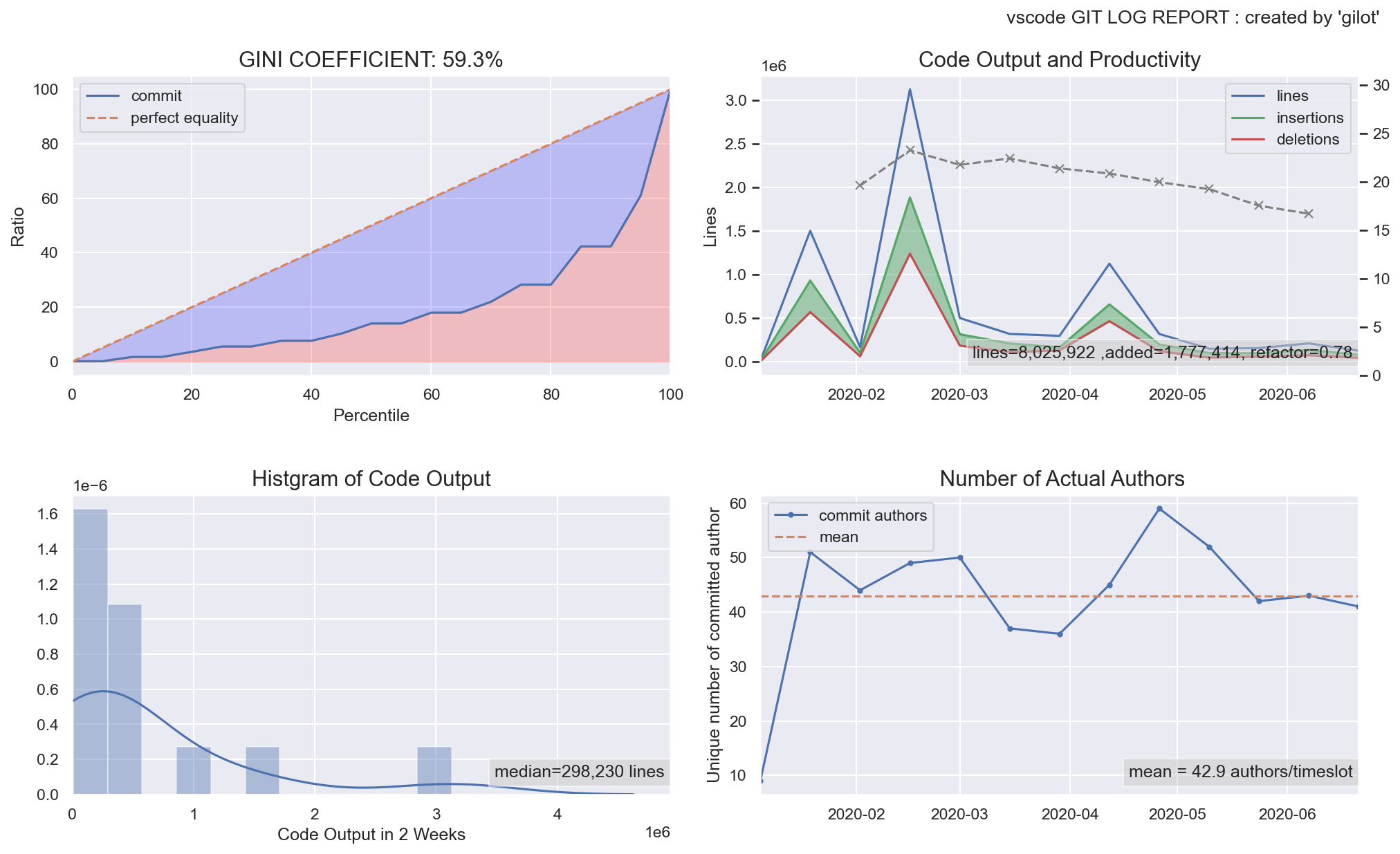
The first graph shows the bias in the amount of code changes for a given time slot as a Gini coefficient and a Lorentz curve. The closer the Gini coefficient is to 1, the more unequal it is, and the closer it is to 0, the more perfect equality it is an indicator of economics. It tends to go down when a project has stable agility, and the more volatile and planaristic the project, the closer it is to 1.
-
The second graph shows a histogram of the bias in the amount of code changes in a given time slot.
-
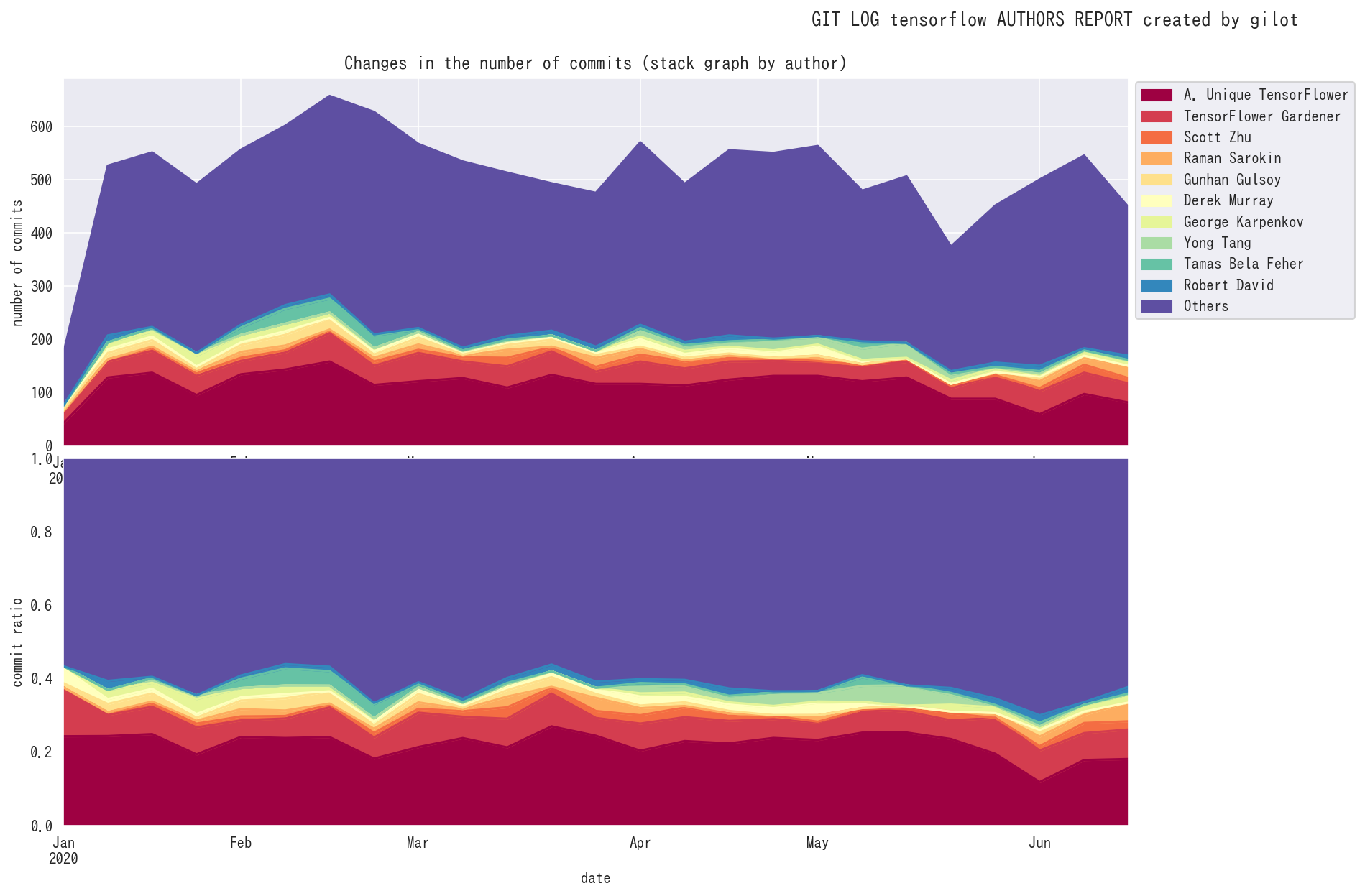
The third graph shows the change in the amount of code changes per time slot. It is displayed in green when the total amount of codes is increasing and in red when the total amount of codes is decreasing.
-
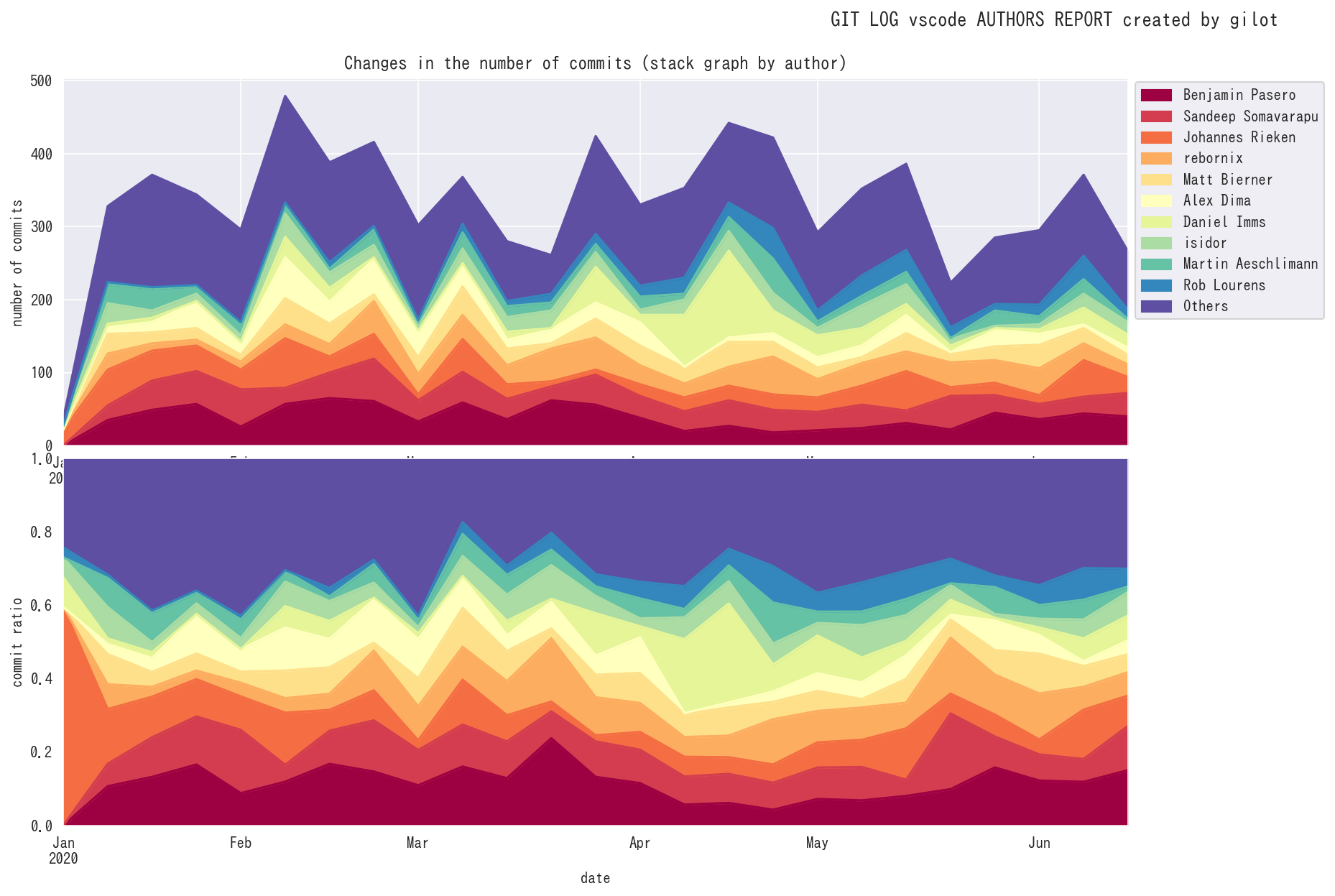
The fourth graph shows the number of authors who committed per given time slot. The effective team size is estimated.
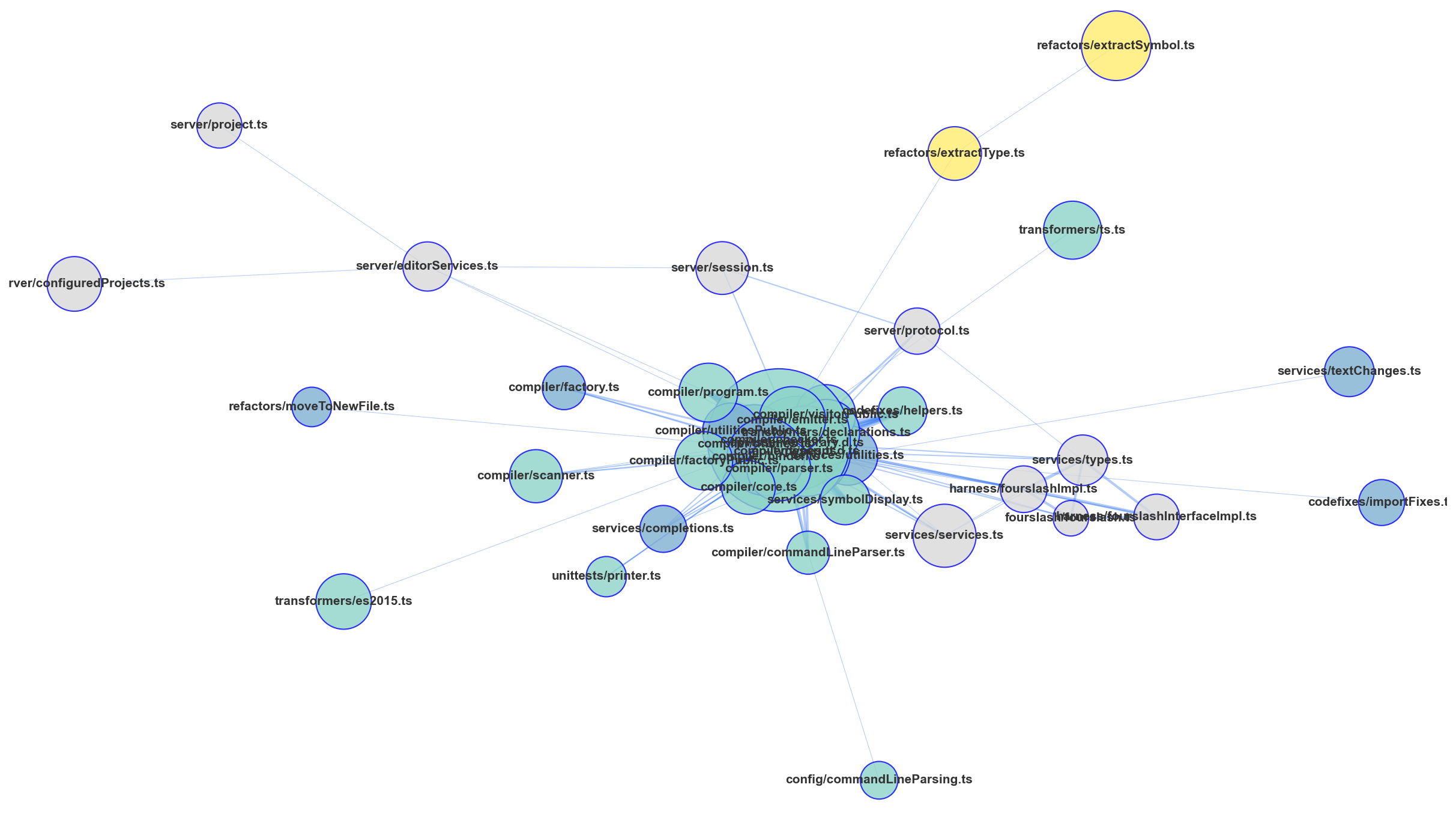
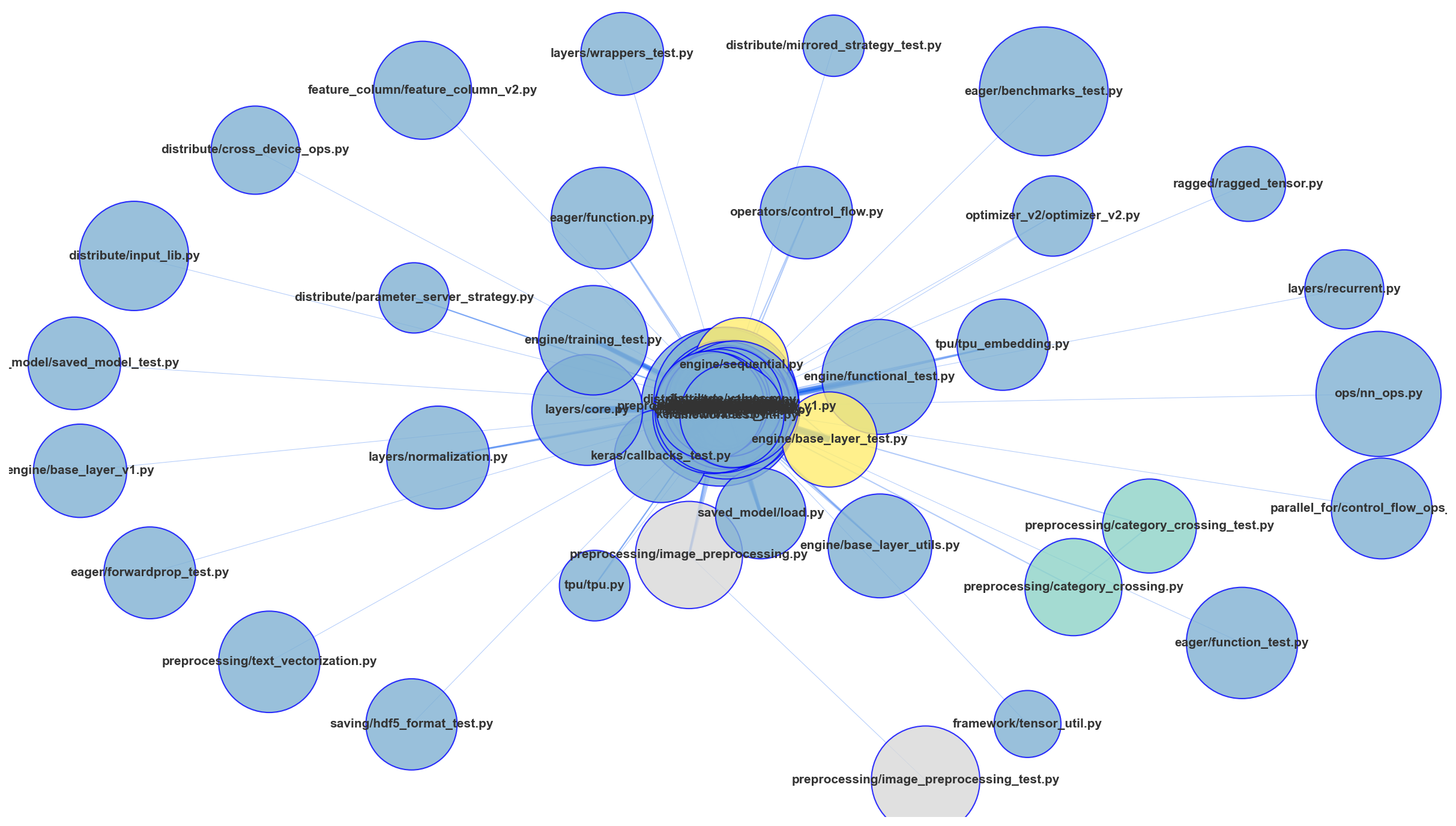
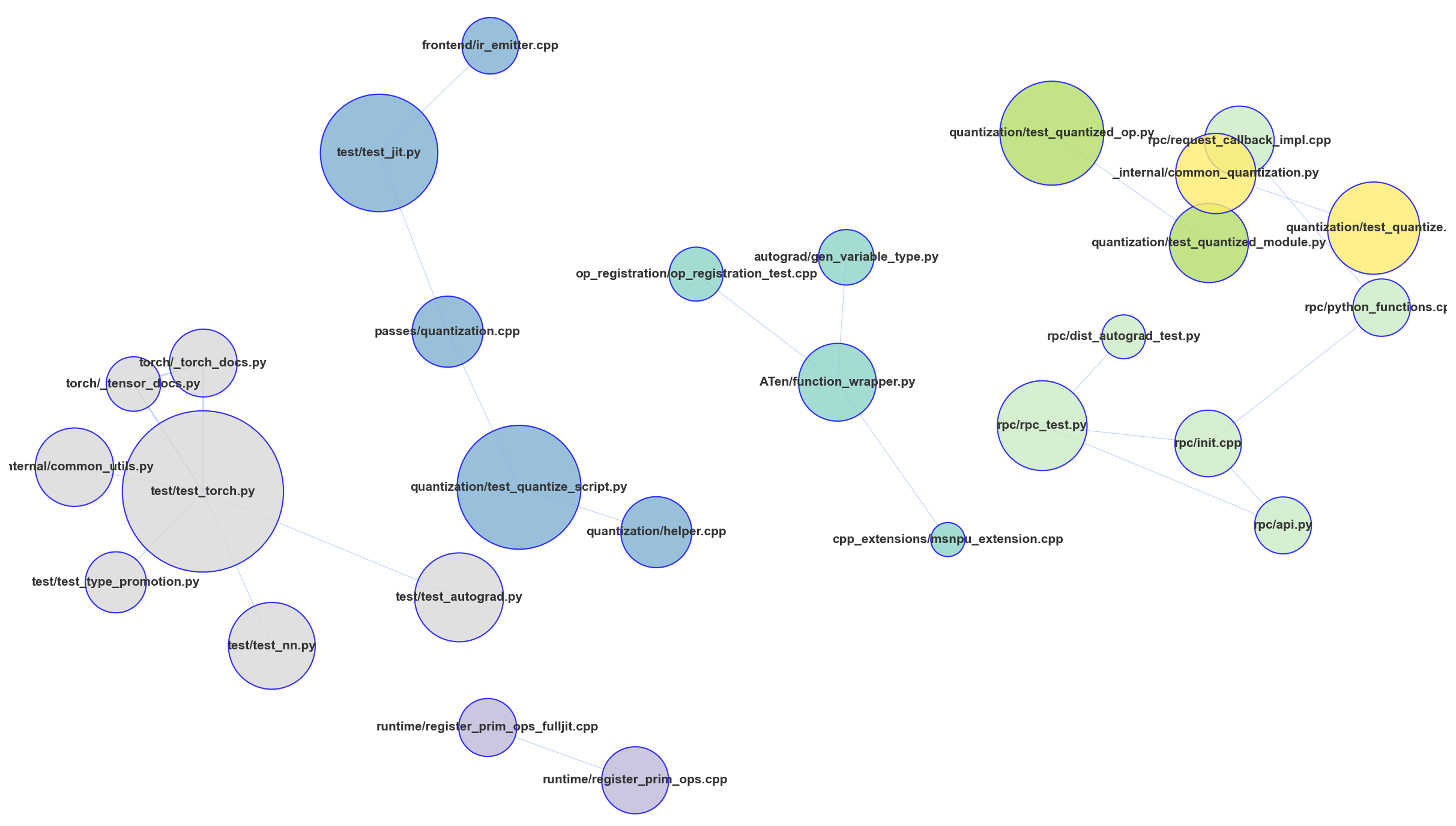
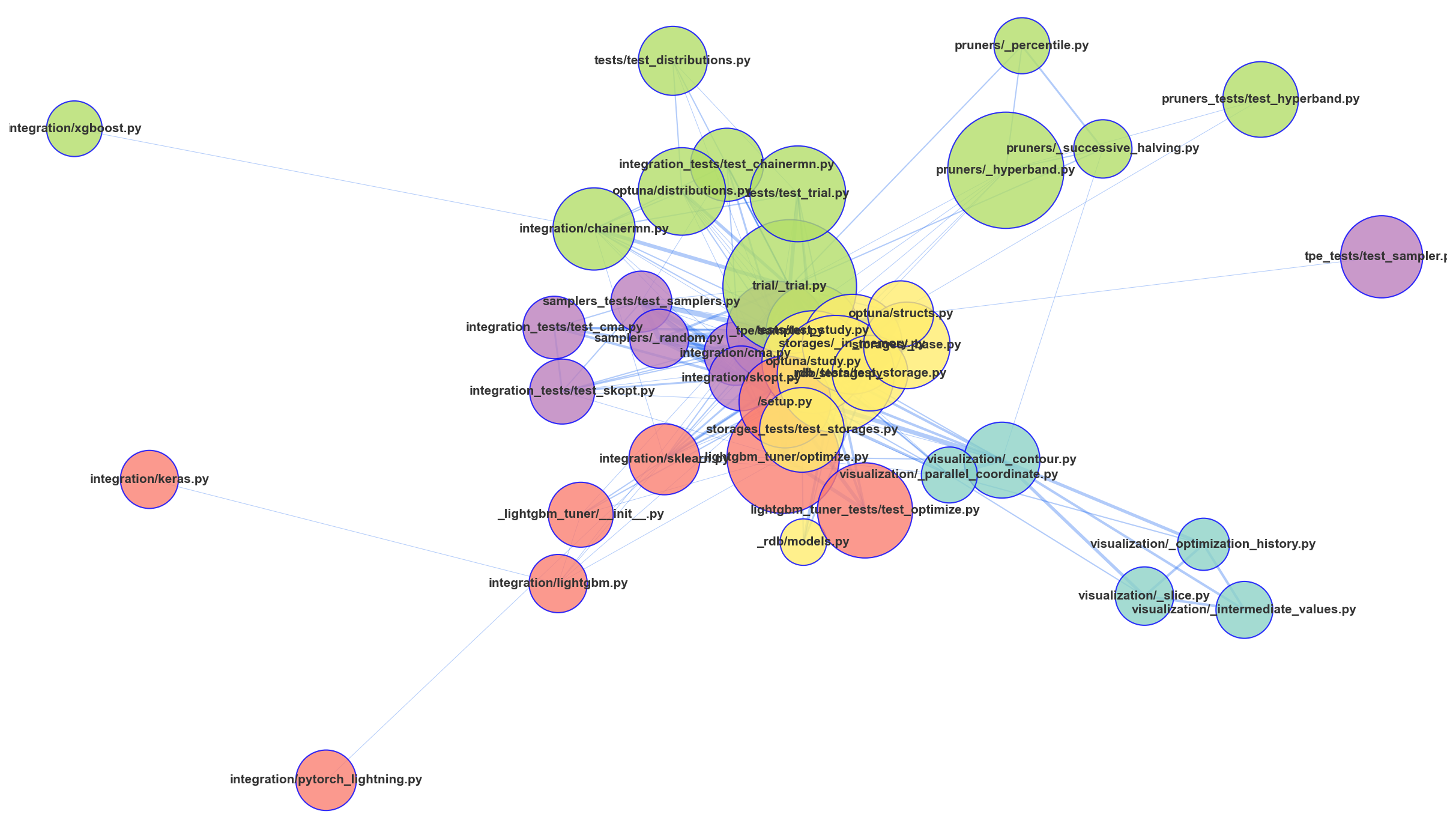
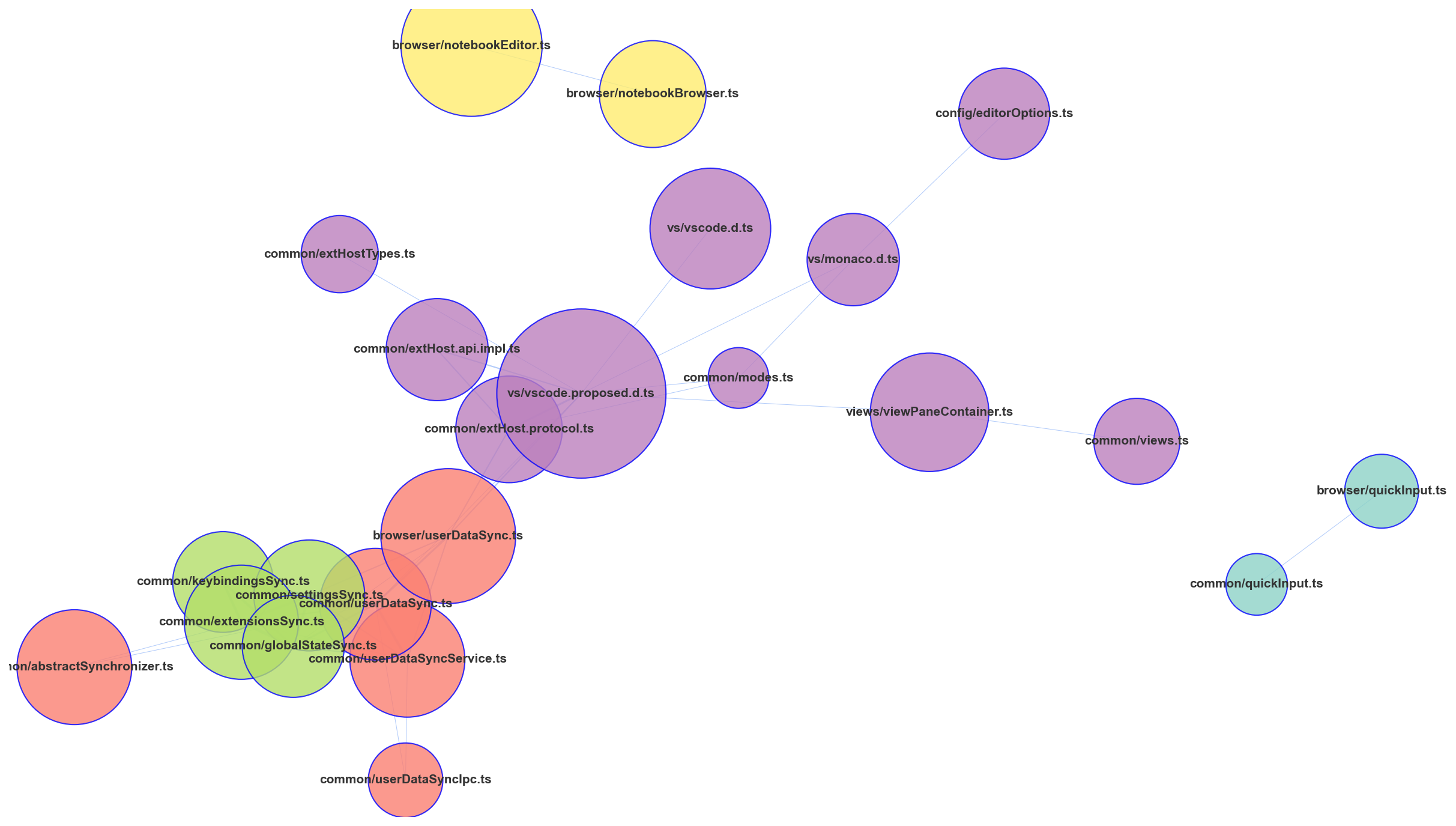
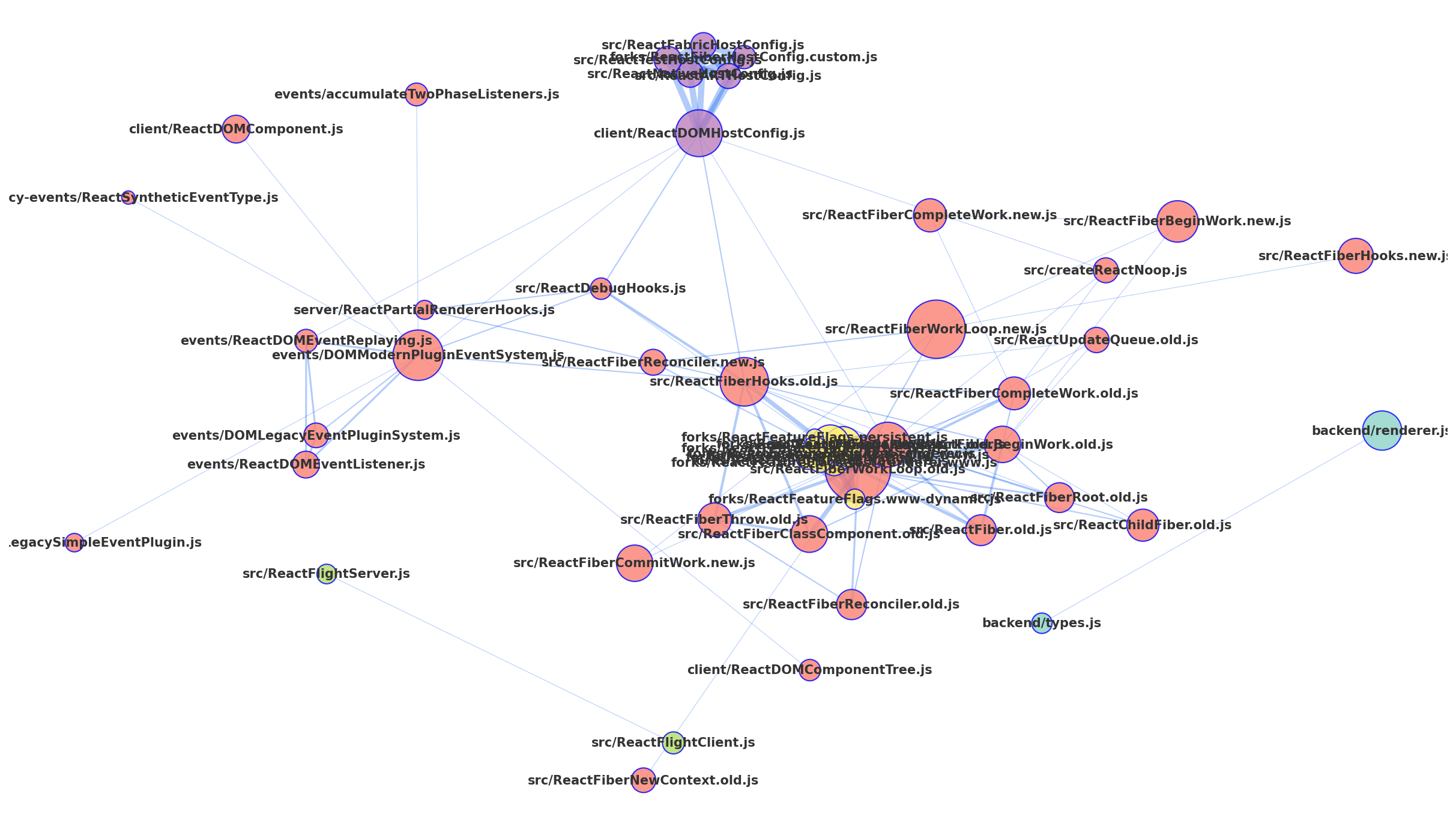
gilot hotgraph visualizes the hidden connections between files in a repository and allows you to see the hidden connections in the and refactoring. Assuming that there is a structural connection between the files committed at the same time, the Analyze the network structure. The "shopping cart" and "products" are often used as examples of association analysis, but in this case, we will use The "shopping cart" is "1 commit" and "products" is "modified files".
just:
pip install gilot
or
pip install git+https://github.com/hirokidaichi/gilot
gilot log REPO_DIR | gilot plot
gilot log REPO_DIR > repo.csv
gilot plot -i repo.csv -o graph.png
gilot has 5 commands, log , plot , info , hotgraph and hotspot
-
logcommand generates a csv from the repository information -
plotcommand generates a graph image (or matplotlib window) from that csv. -
infocommand, like the plot command, takes a csv file as input and outputs only JSON format statistical information. -
hotspotcommand displays the files that are likely to contain bugs in ranking. We judge that the most recently modified files are likely to contain bugs.( likebugspots) -
hotspotcommand displays the files that are likely to contain bugs in ranking. We judge that the most recently modified files are likely to contain bugs.( likebugspots) -
hotgraphcommand is able to visualize hidden file connections from a given CSV.
The simplest way to use the gilot log command is to specify the repository directory as follows. This means saving the output as a CSV file.
gilot log REPO > REPO.csv
gilot log REPO -o REPO.csv
The default period is six months, but you can specify the time.
gilot log REPO --since 2020-01-20 -o REPO.csv
gilot log REPO --month 18 -o REPO.csv
By specifying a period of time, such as when you want to see the stability of the service after the launch, you can eliminate the impact of commits during the initial release.
gilot log REPO --branch develop -o REPO.csv
You can use the branch option to see what the development branch looks like, or to see the results for each branch. By default, origin/HEAD is specified. This is because we want to see how well we can develop in a trunk-based way.
Also, with the --full option, detailed information such as the committed file name and the number of lines will be output. It is used for verification including file names such as hotspot command and ignore-files/allow-files.
gilot log REPO --full | gilot plot --ignore-files "*.lock" "package.json"
If you want to count so that a specific file is not included, use the --full option and --ignore-files together as follows.
gilot log REPO --full | gilot hotspot
All options are here
usage: gilot log [-h] [-b BRANCH] [-o OUTPUT] [--since SINCE] [--until UNTIL] [--month MONTH] [--full] repo
positional arguments:
repo REPO must be a root dir of git repository
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-b BRANCH, --branch BRANCH
target branch name. default 'origin/HEAD'
-o OUTPUT, --output OUTPUT
--since SINCE SINCE must be ISO format like 2020-01-01.
--until UNTIL UNTIL must be ISO format like 2020-06-01.
--month MONTH MONTH is how many months of log data to output. default is 6
--full If this flag is enabled, detailed data including the commuted file name will be output.
The simplest way to use the gilot plot command is to take the CSV file output from the gilot log command as input and specify the name of the file you want to save as output, as shown below.
gilot plot -i TARGET.csv -o TARGET_REPORT.png
gilot plot --input TARGET.csv -o TARGET_REPORT.png
Also, since the input from the standard input is also interpreted as a CSV, it can be connected to a pipe as shown below.
cat target.csv | gilot plot
gilot repo . | gilot plot
For example, if one team is working in a multi-repository services, you may want to know the activity of multiple repositories as a whole, instead of focusing on one repository. In this case, you can combine multiple inputs into a graph as follows.
gilot log repo-a > repo-a.csv
gilot log repo-b > repo-b.csv
gilot plot -i repo*.csv
All options are here:
usage: gilot plot [-h] [-i [INPUT [INPUT ...]]] [-t TIMESLOT] [-o OUTPUT] [-n NAME] [--allow-files [ALLOW_FILES [ALLOW_FILES ...]]] [--ignore-files [IGNORE_FILES [IGNORE_FILES ...]]]
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-i [INPUT [INPUT ...]], --input [INPUT [INPUT ...]]
-t TIMESLOT, --timeslot TIMESLOT
resample period like 2W or 7D or 1M
-o OUTPUT, --output OUTPUT
OUTPUT FILE
-n NAME, --name NAME name
--allow-files [ALLOW_FILES [ALLOW_FILES ...]]
Specify the files to allow. You can specify more than one like 'src/*' '*.rb'. Only data with the --full flag is valid.
--ignore-files [IGNORE_FILES [IGNORE_FILES ...]]
Specifies files to ignore. You can specify more than one like 'dist/*' '*.gen.java'. Only data with the --full flag is valid.
info command, like the plot command, takes a csv file as input and outputs only JSON format statistical information.
# gilot info -i sample/react.csv
{
"gini": 0.42222013847205725,
"output": {
"lines": 242999,
"added": 70765,
"refactor": 0.7087848098140321
},
"since": "2019-12-03T10:53:08.000000000",
"until": "2020-05-30T06:34:43.000000000",
"timeslot": "2 Weeks",
"insertions": {
"mean": 11205.857142857143,
"std": 10565.324647217372,
"min": 781.0,
"25%": 3788.75,
"50%": 8544.0,
"75%": 16761.25,
"max": 39681.0
},
"deletions": {
"mean": 6151.214285714285,
"std": 4437.0289466743825,
"min": 327.0,
"25%": 3397.0,
"50%": 5076.0,
"75%": 9333.75,
"max": 13477.0
},
"lines": {
"mean": 17357.071428571428,
"std": 14236.531424279776,
"min": 1108.0,
"25%": 7383.25,
"50%": 12860.0,
"75%": 26531.75,
"max": 52914.0
},
"files": {
"mean": 377.7857142857143,
"std": 271.95196933718574,
"min": 70.0,
"25%": 155.75,
"50%": 402.0,
"75%": 450.0,
"max": 1062.0
},
"authors": {
"mean": 13.357142857142858,
"std": 4.70036238958302,
"min": 4.0,
"25%": 10.0,
"50%": 15.0,
"75%": 16.0,
"max": 21.0
},
"addedlines": {
"mean": 5054.642857142857,
"std": 7742.596112089604,
"min": -1210.0,
"25%": 266.5,
"50%": 2062.5,
"75%": 5770.75,
"max": 26448.0
}
}
Integration with jq command makes it easy to get only the information you need.
# gilot info -i sample/react.csv | jq .gini
> 0.42222013847205725
# gilot info -i sample/react.csv | jq .output.lines
All options are here :
usage: gilot info [-h] [-i [INPUT [INPUT ...]]] [-t TIMESLOT] [--allow-files [ALLOW_FILES [ALLOW_FILES ...]]] [--ignore-files [IGNORE_FILES [IGNORE_FILES ...]]]
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-i [INPUT [INPUT ...]], --input [INPUT [INPUT ...]]
-t TIMESLOT, --timeslot TIMESLOT
resample period like 2W or 7D or 1M
--allow-files [ALLOW_FILES [ALLOW_FILES ...]]
Specify the files to allow. You can specify more than one like 'src/*' '*.rb'. Only data with the --full flag is valid.
--ignore-files [IGNORE_FILES [IGNORE_FILES ...]]
Specifies files to ignore. You can specify more than one like 'dist/*' '*.gen.java'. Only data with the --full flag is valid.
hotspot command displays the files that are likely to contain bugs in ranking. We judge that the most recently modified files are likely to contain bugs.( like bugspots)
gilot hotspot -i react-full.csv --ignore-files "*/__tests__/*" "*.lock" -n 10
output
------------------------------------------------------------
gilot hotspot ( https://github.com/hirokidaichi/gilot )
------------------------------------------------------------
hotspot commits authors file_name
8.81 29 4 packages/react-reconciler/src/ReactFiberWorkLoop.new.js
7.14 25 4 packages/react-reconciler/src/ReactFiberWorkLoop.old.js
7.01 44 3 packages/react-dom/src/events/DOMModernPluginEventSystem.js
5.50 44 8 packages/react-dom/src/client/ReactDOMHostConfig.js
4.85 29 8 scripts/rollup/bundles.js
4.47 17 5 packages/react-reconciler/src/ReactFiberBeginWork.new.js
3.73 17 5 packages/react-reconciler/src/ReactFiberCommitWork.new.js
3.32 13 4 packages/react-reconciler/src/ReactFiberHooks.new.js
3.28 17 5 packages/react-reconciler/src/ReactFiberCompleteWork.new.js
3.18 15 5 packages/react-reconciler/src/ReactFiberCommitWork.old.js
All options are here :
usage: gilot hotspot [-h] [-i [INPUT [INPUT ...]]] [--csv] [-o OUTPUT] [--allow-files [ALLOW_FILES [ALLOW_FILES ...]]] [--ignore-files [IGNORE_FILES [IGNORE_FILES ...]]]
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-i [INPUT [INPUT ...]], --input [INPUT [INPUT ...]]
--csv dump csv
-o OUTPUT, --output OUTPUT
--allow-files [ALLOW_FILES [ALLOW_FILES ...]]
Specify the files to allow. You can specify more than one like 'src/*' '*.rb'. Only data with the --full flag is valid.
--ignore-files [IGNORE_FILES [IGNORE_FILES ...]]
Specifies files to ignore. You can specify more than one like 'dist/*' '*.gen.java'. Only data with the --full flag is valid.
gilot hotgraph visualizes the hidden connections between files in a repository and allows you to see the hidden connections in the and refactoring. Assuming that there is a structural connection between the files committed at the same time, the Analyze the network structure. The "shopping cart" and "products" are often used as examples of association analysis, but in this case, we will use The "shopping cart" is "1 commit" and "products" is "modified files".
gilot hotgraph -i this.csv --allow-files "*.ts"
All options are here :
usage: gilot hotgraph [-h] [-v] [-i [INPUT [INPUT ...]]] [-r RANK] [--stop-retry] [--csv] [-o OUTPUT] [--allow-files [ALLOW_FILES [ALLOW_FILES ...]]]
[--ignore-files [IGNORE_FILES [IGNORE_FILES ...]]]
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-v, --verbose increase log level
-i [INPUT [INPUT ...]], --input [INPUT [INPUT ...]]
-r RANK, --rank RANK
--stop-retry
--csv dump csv
-o OUTPUT, --output OUTPUT
--allow-files [ALLOW_FILES [ALLOW_FILES ...]]
Specify the files to allow. You can specify more than one like 'src/*' '*.rb'. Only data with the --full flag is valid.
--ignore-files [IGNORE_FILES [IGNORE_FILES ...]]
Specifies files to ignore. You can specify more than one like 'dist/*' '*.gen.java'. Only data with the --full flag is valid.
TODO