When a service is running in a WSL instance, like Ubuntu for example, we want the service to be accessible from any device that is connected to the local network.
This script automates the configuration process of a bridged connection between a WSL Instance and the Host. Thus, forwarding the TCP port of a WSL 2 service to the Host.
To run this script, you will need the following:
- Windows 10 (version 1903 or later)
- PowerShell (version 5.1 or later)
- WSL2
-
Download auto_port-forwarding.ps1 to your local machine.
-
Open a PowerShell terminal (Run as administrator).
-
Navigate to the directory where the script is located.
-
Make sure the WSL Instance, on which the service is running, is set as Default
- Run:
wsl -l -vto list all the WSL Instances - If the WSL Instance, on which your service is running, is not set as default then run:
wsl --setdefault <WSL_DISTRO_NAME>
- Run:
-
Run the script using the following command:
powershell.exe -ExecutionPolicy Bypass -File "auto_port-forwarding.ps1" -WslInstanceName <WSL_DISTRO_NAME> -ListenPort <LISTENING_PORT> -ConnectPort <SERVICE_PORT> -RuleName <FIREWALL_INBOUND_RULE_NAME>
-
-WslInstanceName <WSL_DISTRO_NAME>
The name of the WSL Instance on which the service is running -
-ListenPort <LISTENING_PORT>
The port number which your service will be accessible from within your LAN -
-ConnectPort <SERVICE_PORT>
The port number of the service that is running on the WSL Instance -
-RuleName <FIREWALL_INBOUND_RULE_NAME>
The name of the inbound rule that will be created in Firewall.
This can be any name. For example you can name it "WSL8080".
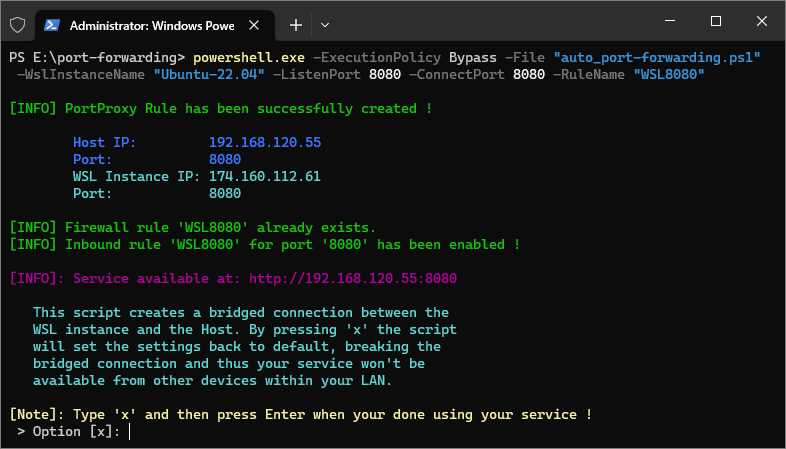
Here's an example of how to use the command to run the script:
powershell.exe -ExecutionPolicy Bypass -File "auto_port-forwarding.ps1" -WslInstanceName "Ubuntu-22.04" -ListenPort 8080 -ConnectPort 8080 -RuleName "WSL8080"
-
-
Follow the on-screen instructions.
This project is licensed under the MIT License.