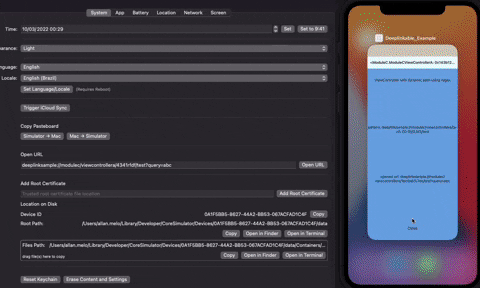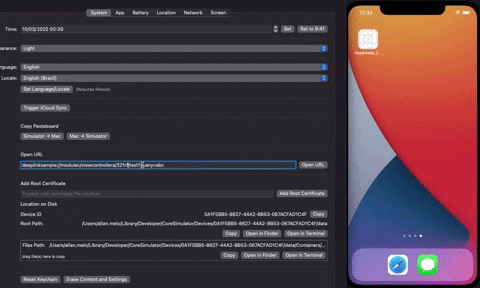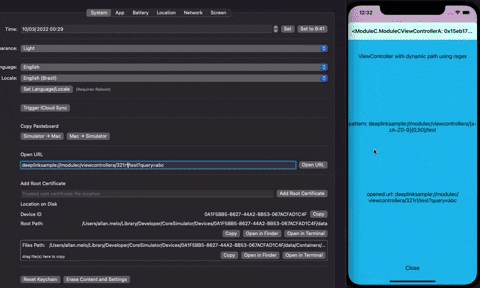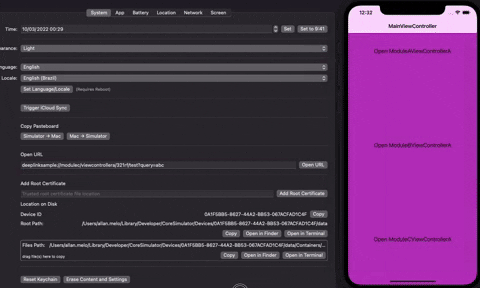
The sdk create a way to map deeplinks easily, you just need to implement the Deeplinkable protocol, nothing more is necessary. You do not need to register and your deeplinks would be indexed, to be reached quickly. Deeplinkable can handle static and dynamic urls using regex expressions.
You should to import Deeplinkable SDK.
If you want to create static deeplinks, you should to return the property isDynamicPath as false. For the deeplinkPath property you need to define the static url without query parameters (but you can receive query parameters in open function normally). On open function you can decide if you really want to open that url conform your restriction, and if is a good time to open it.
import Deeplinkable
extension ModuleAViewControllerA: Deeplinkable {
public static var isDynamicPath: Bool {
false
}
public static var deeplinkPath: String {
// Here you define your deeplink path
"deeplinksample://modulea/viewcontrollera"
}
public static func open(url: URL) -> Bool {
// Here you define if/how you will handle your deeplink
// Open in modal style
guard let navigation = UIApplication.shared.rootNavigation else {
return false
}
let flowNavigation = UINavigationController(rootViewController: ModuleAViewControllerA())
navigation.present(flowNavigation, animated: true)
return true
}
}If you have a dynamic deeplink you can use regex expressions, to conform with some specific urls with dynamic properties in the path.
So, in this case ModuleCViewControllerA can conform with urls like:
- deeplinksample://modulec/viewcontrollera/f14g23h132/test?query=abc
- deeplinksample://modulec/viewcontrollera/b12g3132/test?query=123
import Deeplinkable
extension ModuleCViewControllerA: Deeplinkable {
public static var isDynamicPath: Bool {
true
}
public static var deeplinkPath: String {
// Here you define your deeplink path
"deeplinksample://modulec/viewcontrollera/[a-zA-Z0-9]{0,50}/test"
}
public static func open(url: URL) -> Bool {
// Here you define if/how you will handle your deeplink
// Open with push
guard let navigation = UIApplication.shared.rootNavigation else {
return false
}
navigation.pushViewController(ModuleCViewControllerA(url: url), animated: true)
return true
}
}To run the example project, clone the repo, and run pod install from the Example directory first.
Deeplinkable is available through CocoaPods. To install it, simply add the following line to your Podfile:
pod 'Deeplinkable'You just need to call setup() function of DeeplinkRouter, and if want to see all indexed deeplinks, you can pass the optional parameter shouldLogIndexedDeeplinks with true.
DeeplinkRouter.setup(shouldLogIndexedDeeplinks: true)If you enable log indexed deeplinks, you will see something like this:
Deeplinkable: Indexed static urls
Indexed url: deeplinksample://modulea/viewcontrollera at: ModuleA.ModuleAViewControllerA
Indexed url: deeplinksample://moduleb/viewcontrollera at: ModuleB.ModuleBViewControllerA
Deeplinkable: Indexed dynamic urls
Indexed url: deeplinksample://modulec/viewcontrollera/[a-zA-Z0-9]{0,50}/test at: ModuleC.ModuleCViewControllerA
We recommend initialize the library on didFinishLaunchingWithOptions function.
Allan Melo, [email protected]
Deeplinkable is available under the MIT license. See the LICENSE file for more info.